1) The document discusses the importance of developing a clear mission statement and asking technical questions to focus product design efforts. It provides examples of a mission statement and technical questions for designing a fingernail clipper.
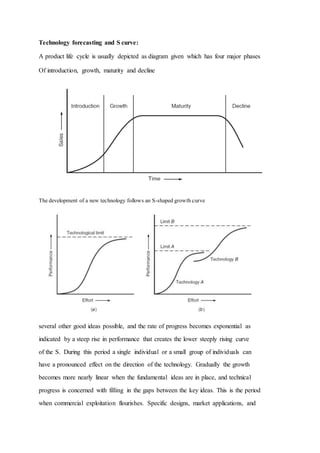
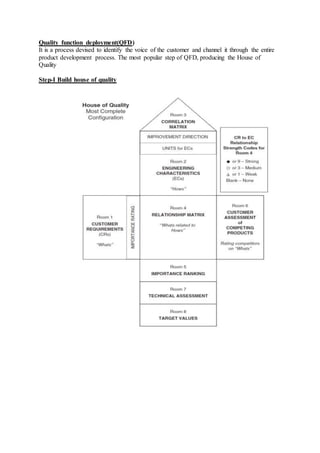
2) It also covers topics like developing a business case analysis, using technology forecasting to understand product life cycles, identifying customer needs, using quality function deployment (QFD) to prioritize engineering characteristics, creating a product design specification (PDS), and understanding market segmentation.
3) The document provides information to guide a new product development process, from initially defining goals and requirements through technical development and understanding markets.