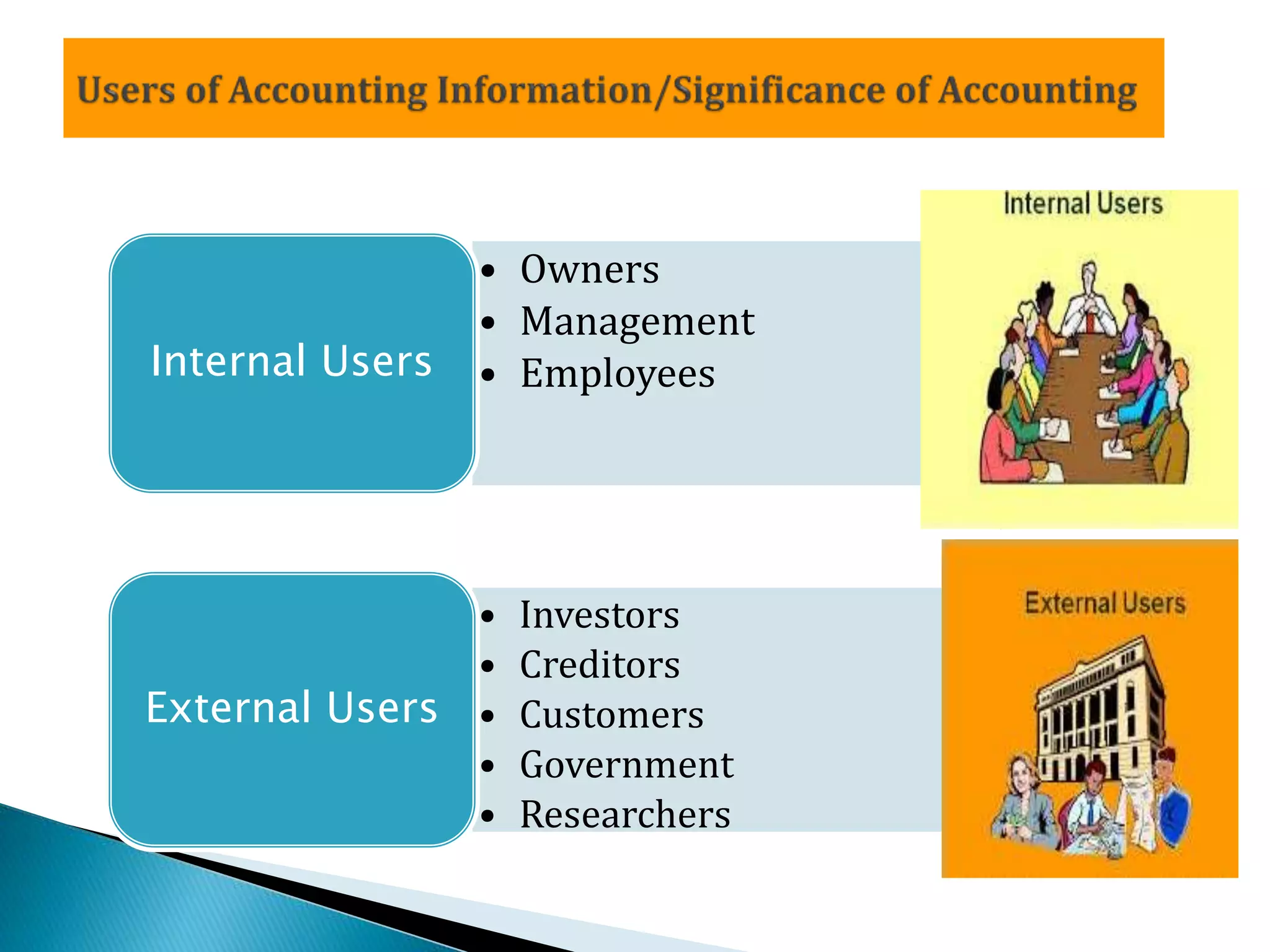
This document discusses the history and purpose of accounting. It notes that accounting originated in India thousands of years ago as described in the book "Arthashastra," and the modern double-entry system was first published by Luca Pacioli in 1494. The document defines accounting as recording, classifying, and summarizing financial information and transactions to facilitate decision making about a business. It outlines the objectives of accounting as maintaining records, meeting legal requirements, protecting assets, facilitating decisions, and communicating results to stakeholders.