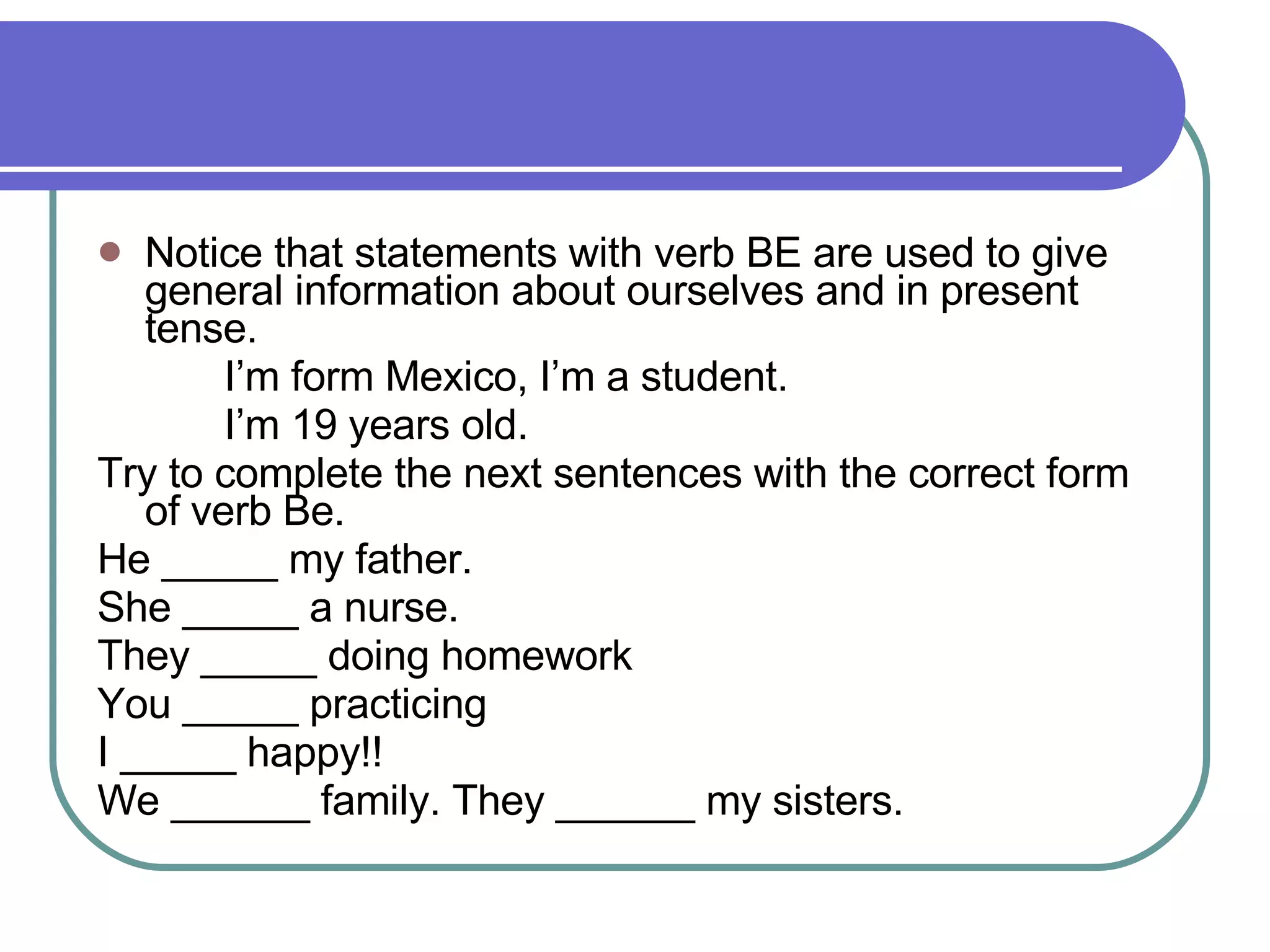
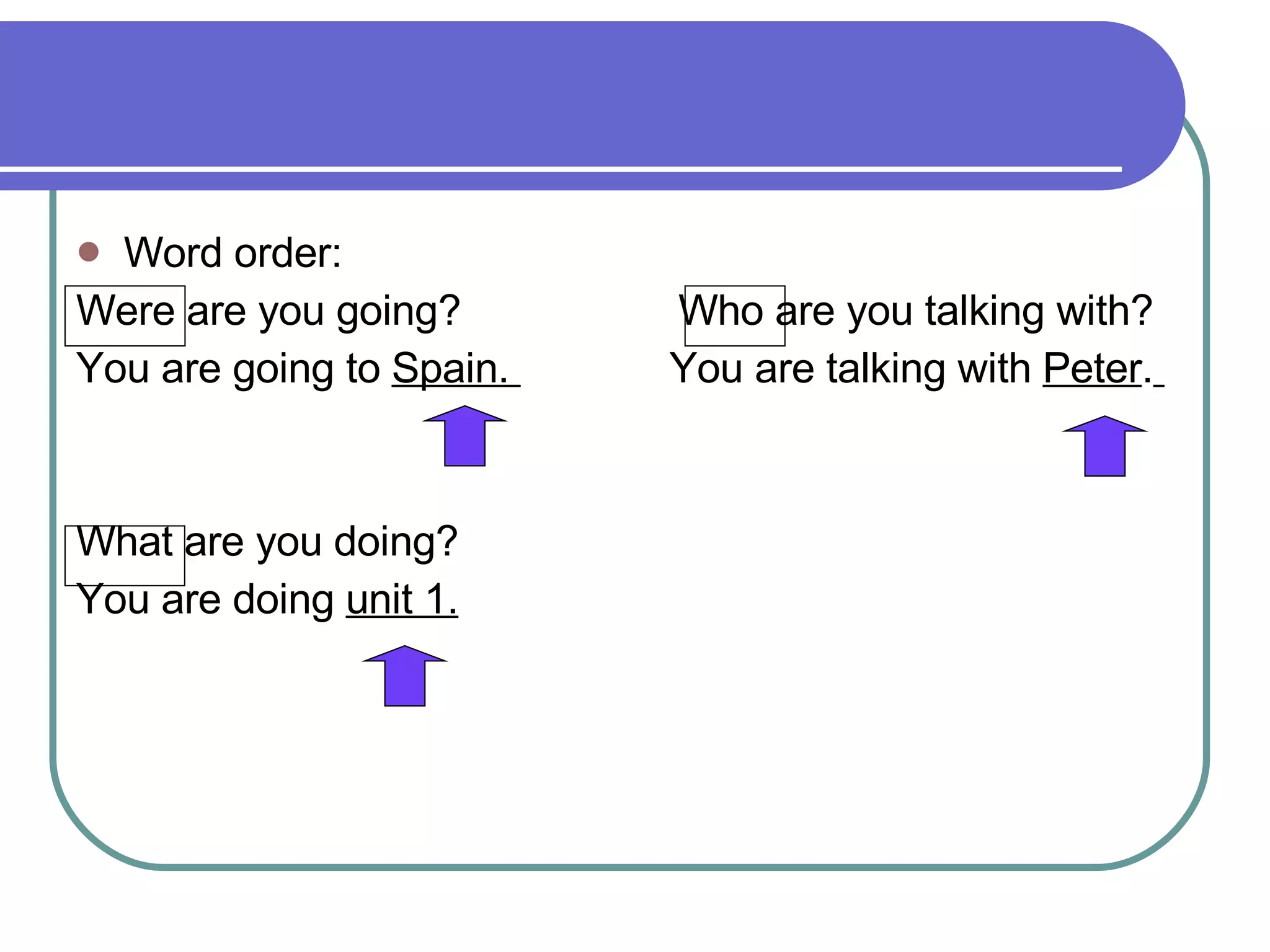
The document provides examples and explanations of using statements with the verb "be", possessive adjectives, and wh-questions with the verb "be" in English. It includes examples such as "I'm from Mexico" and "What's your name?". The document also discusses word order in wh-questions and provides exercises for learners to practice the targeted grammar points.