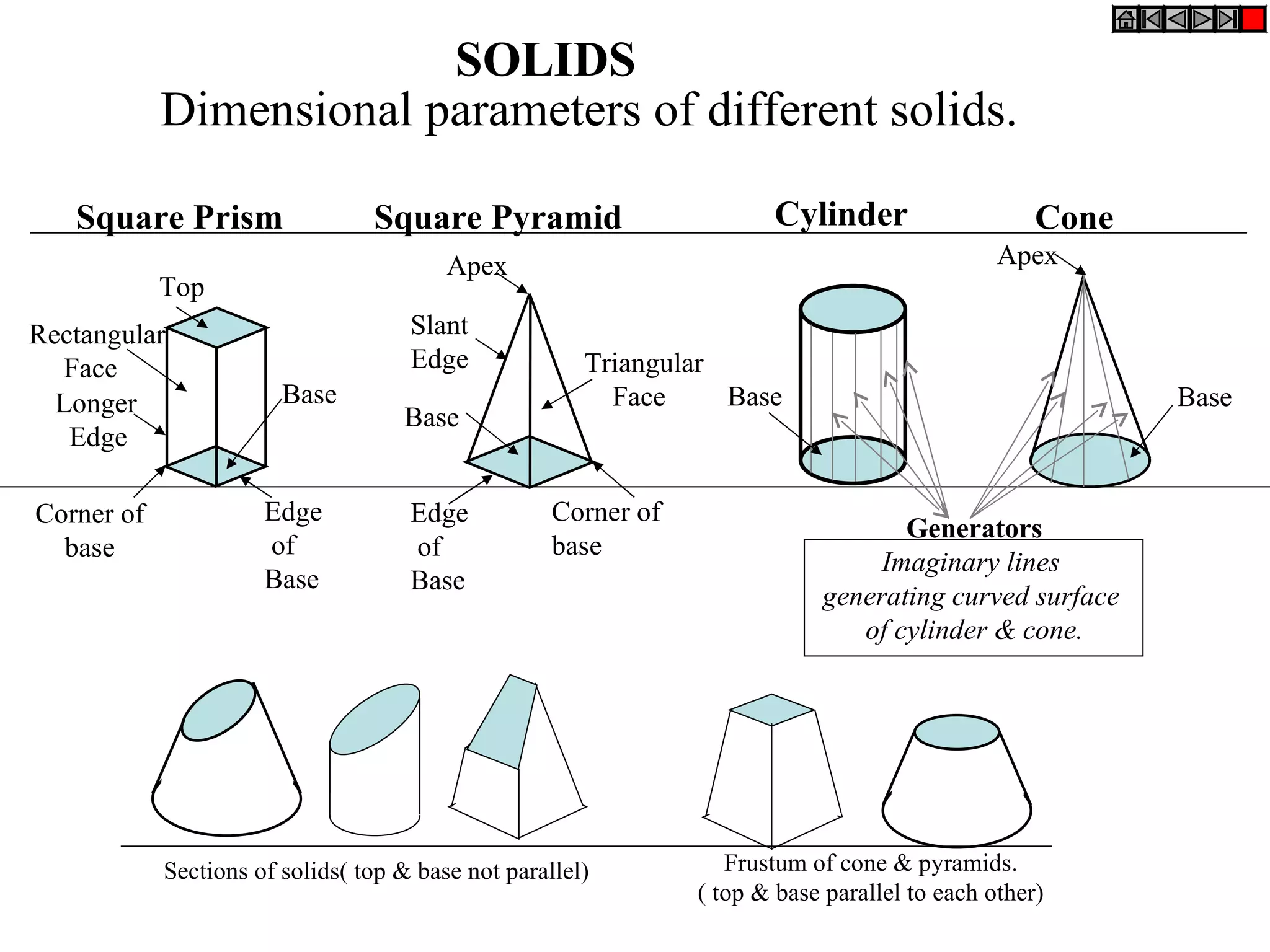
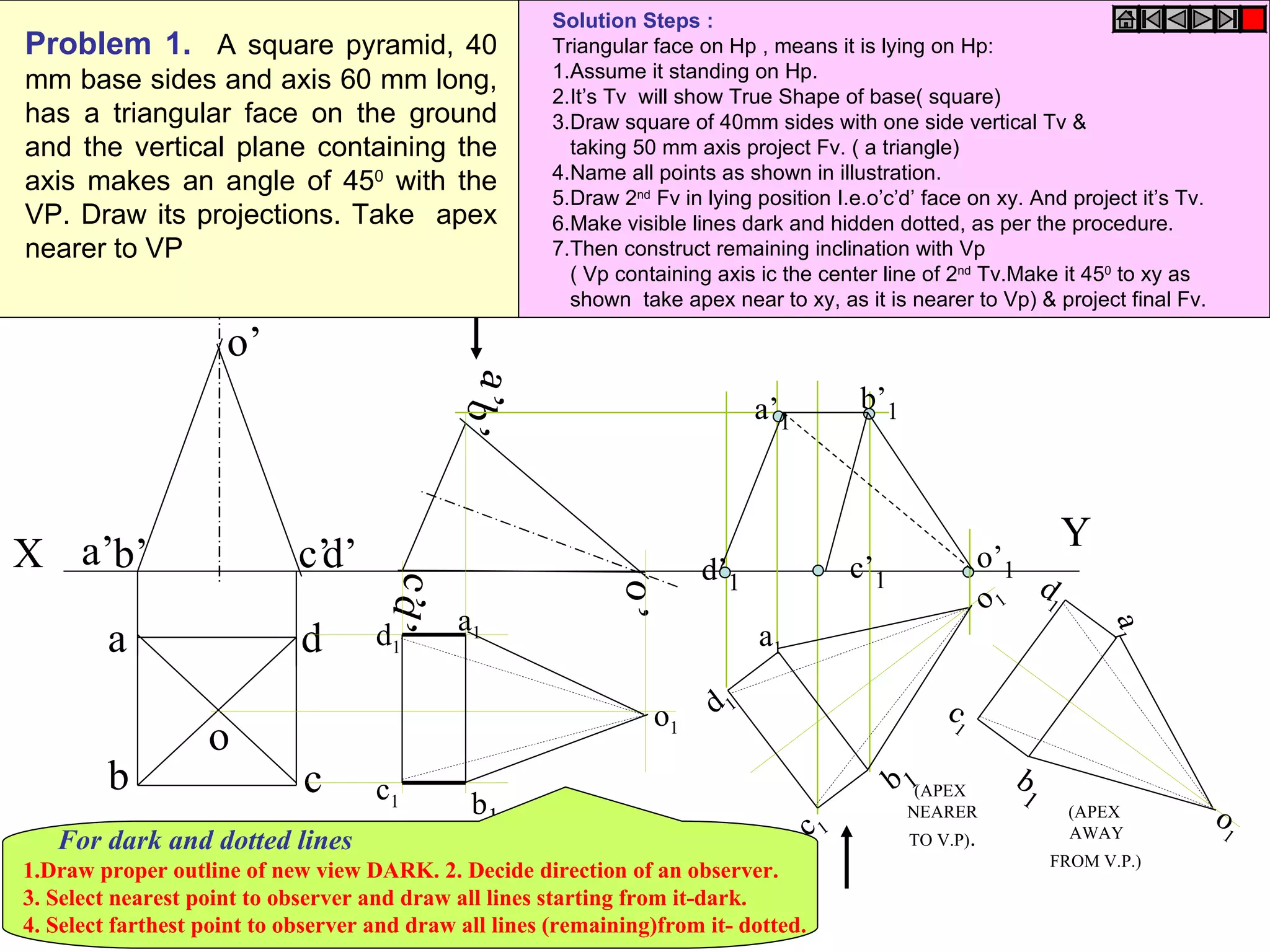
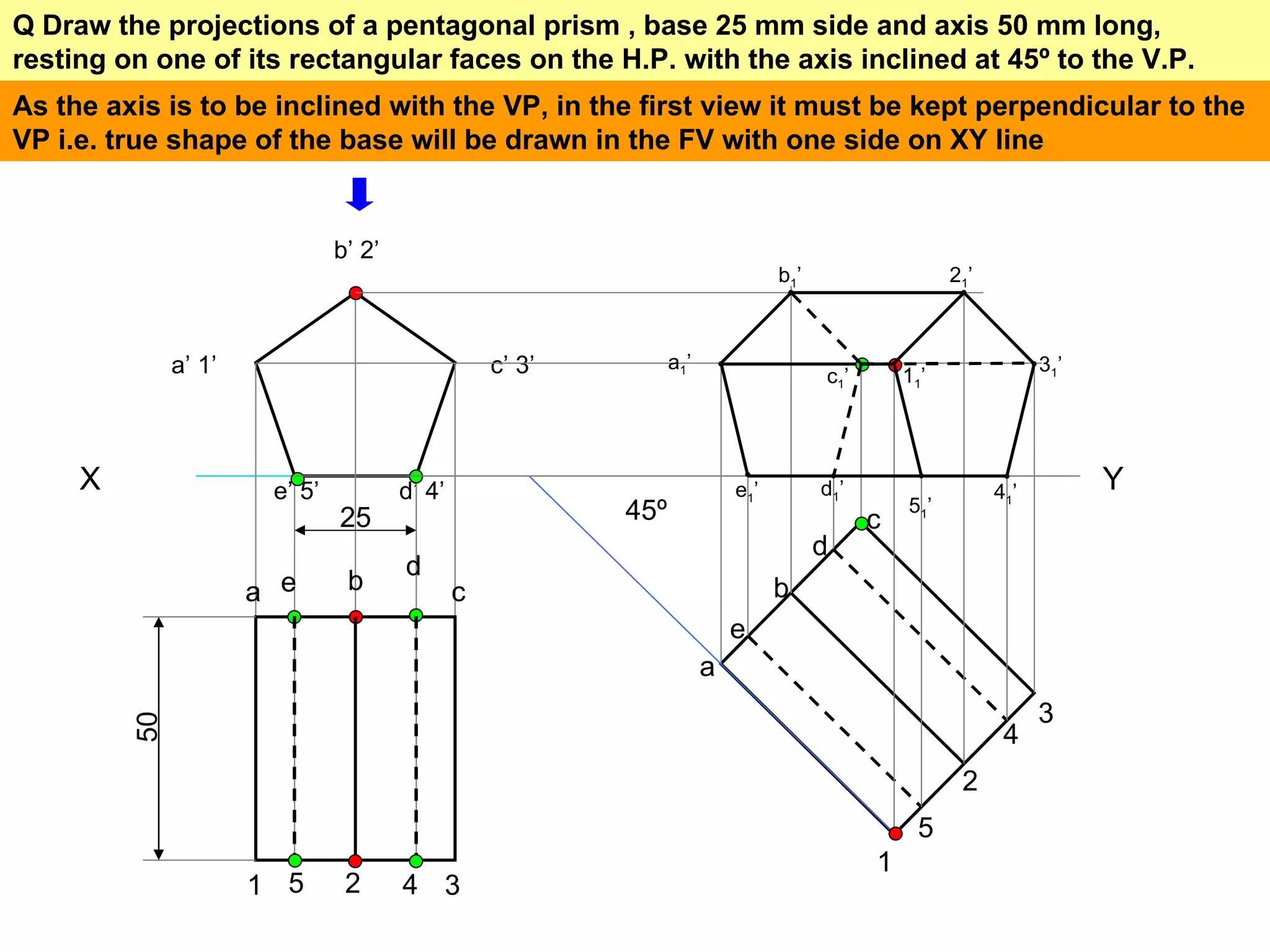
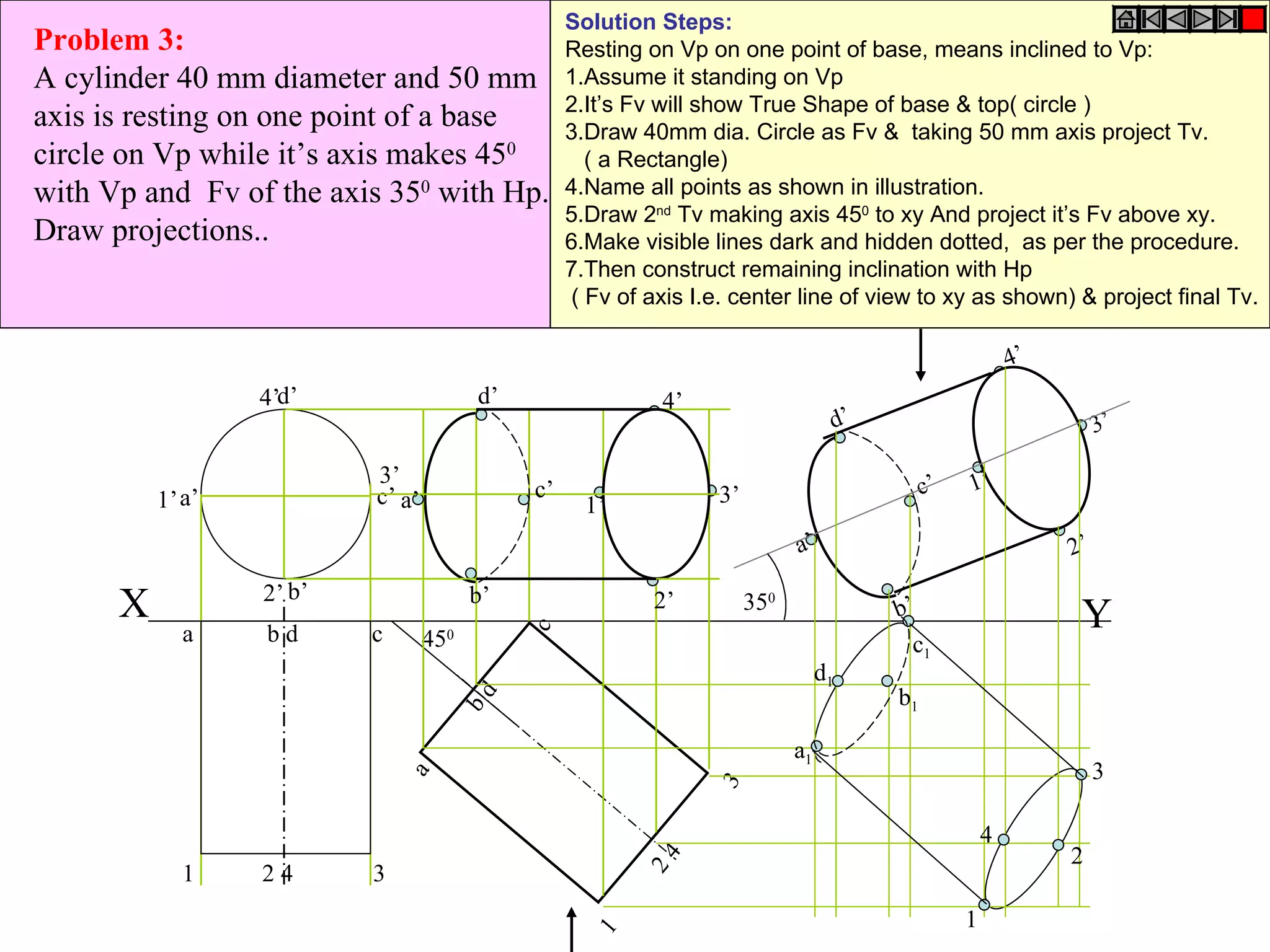
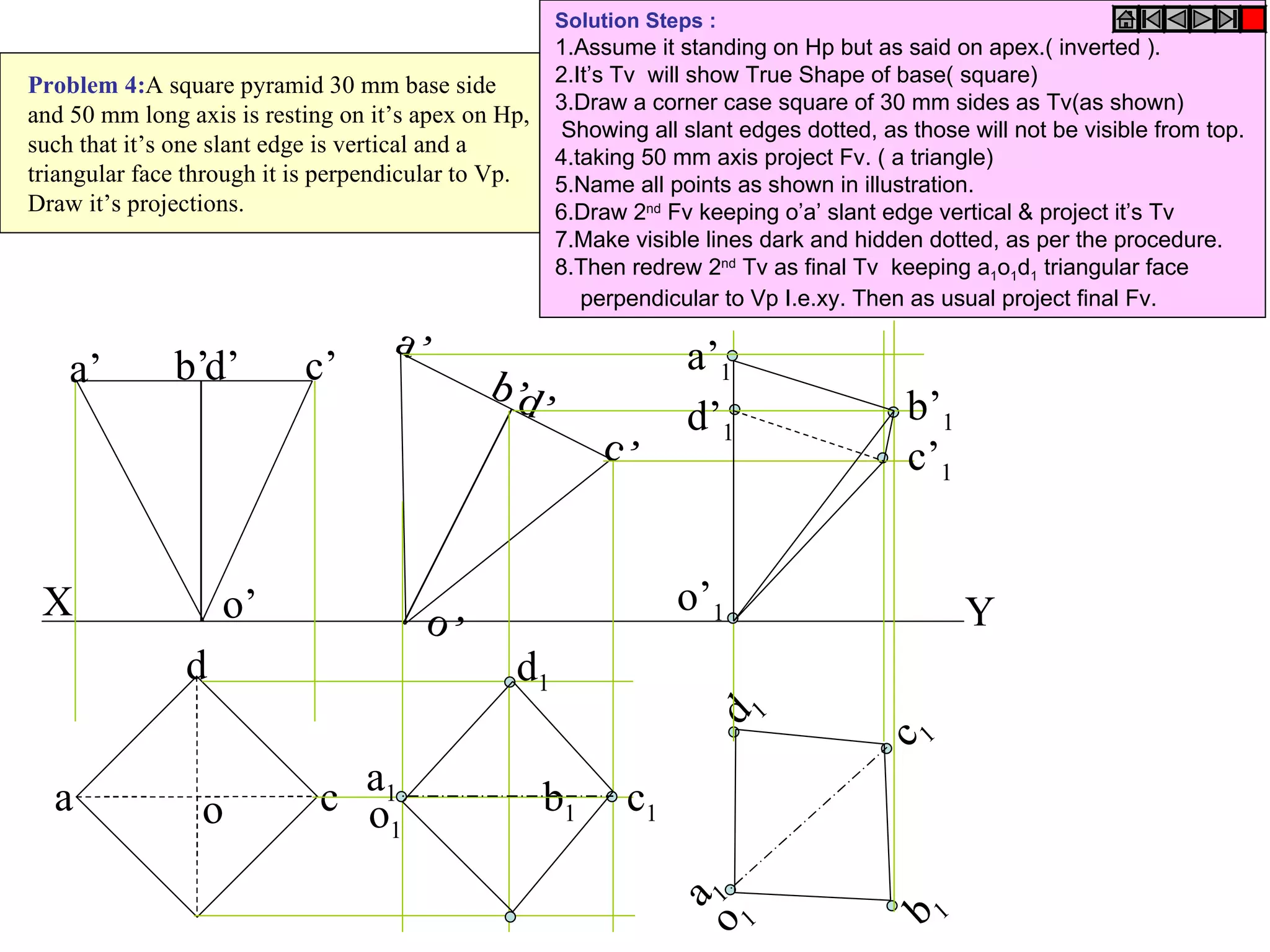
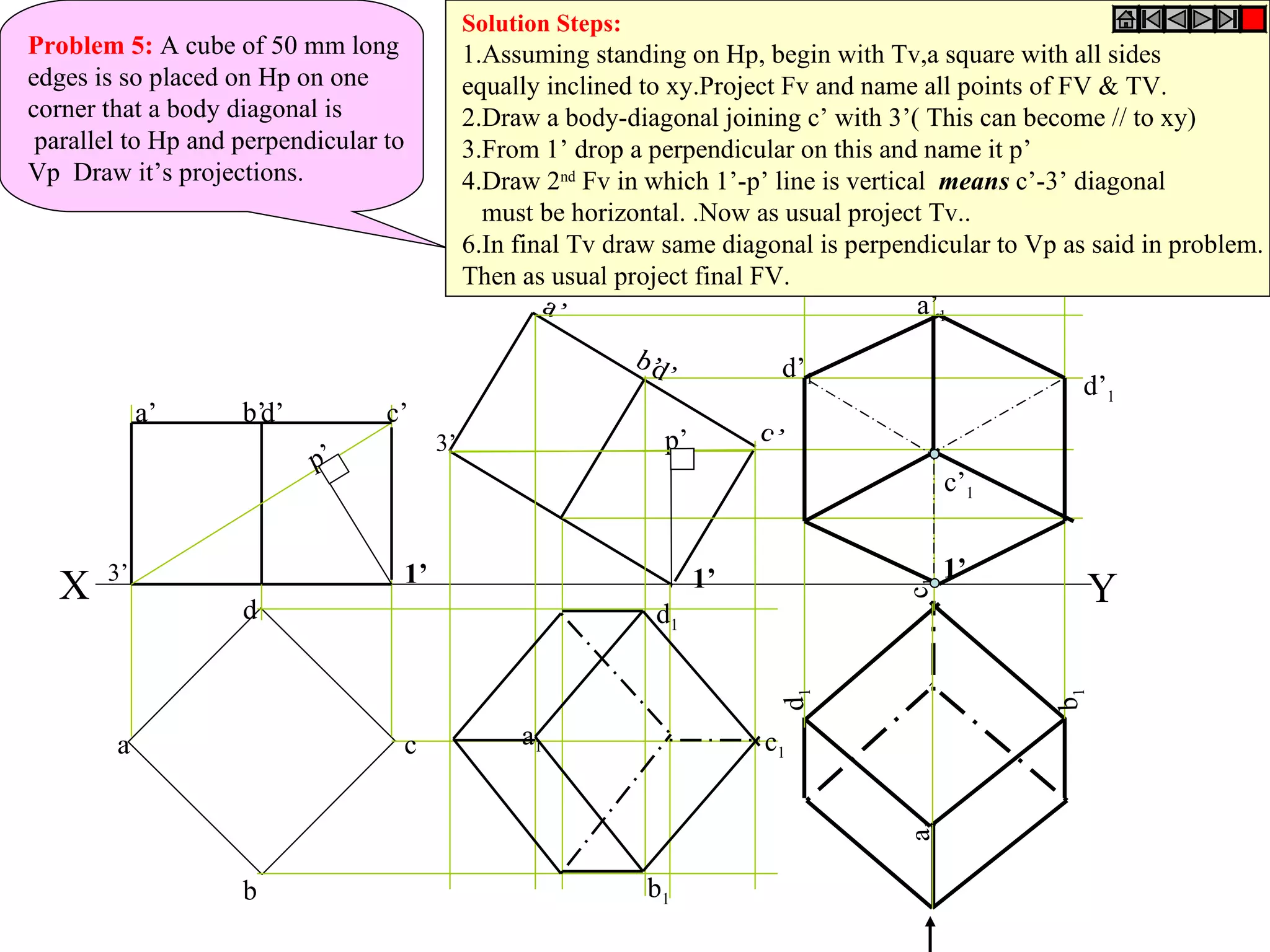
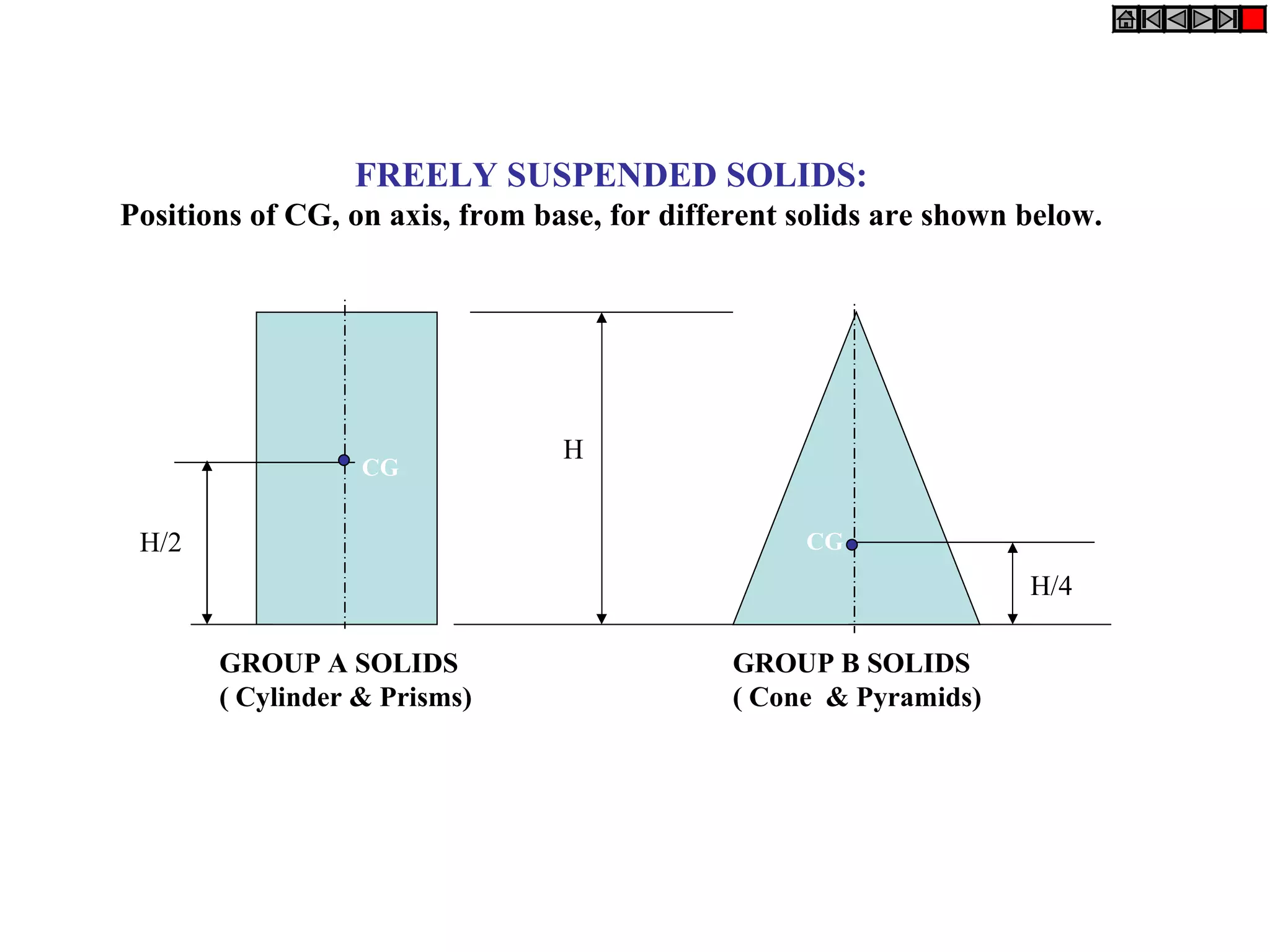
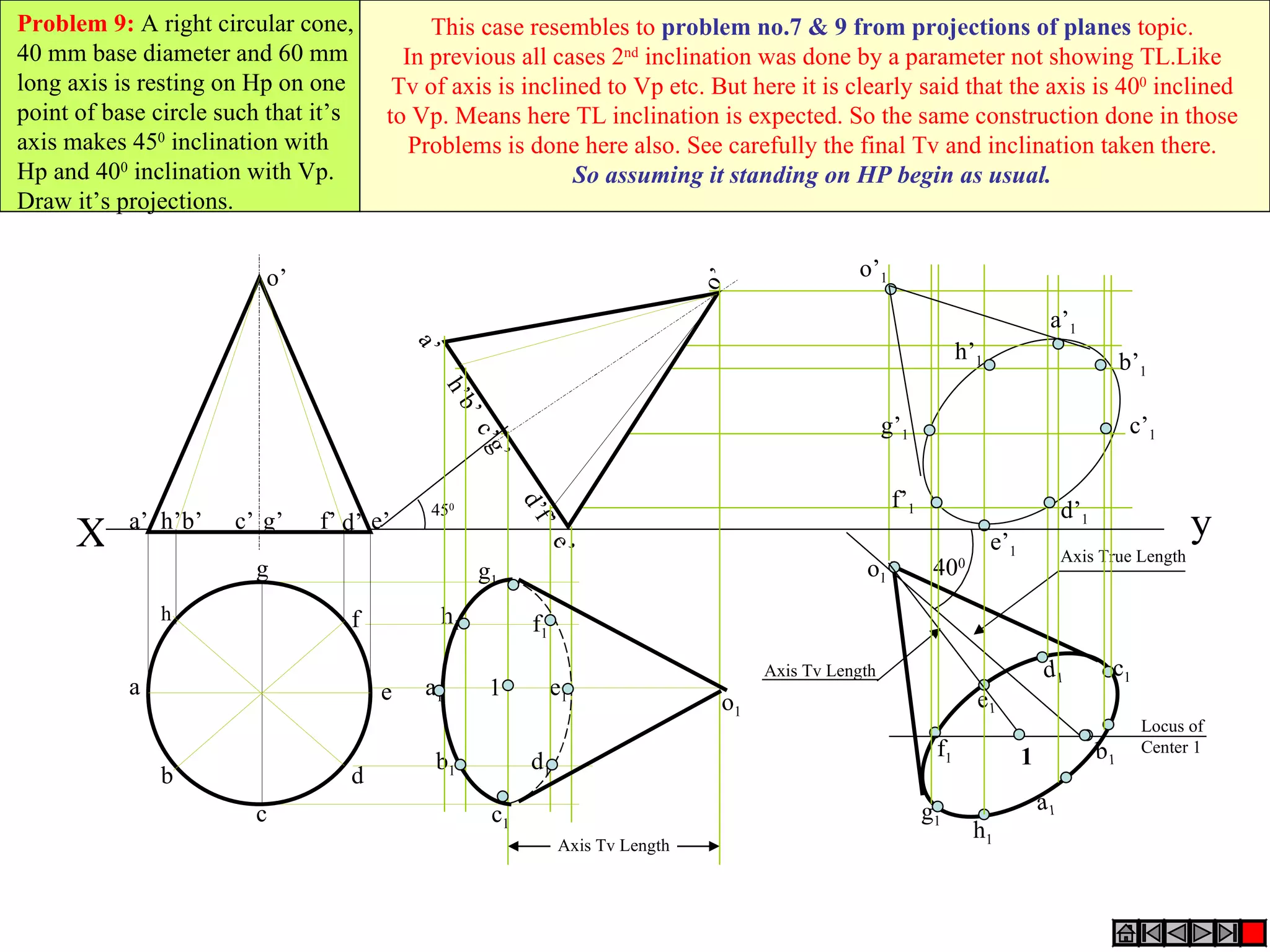
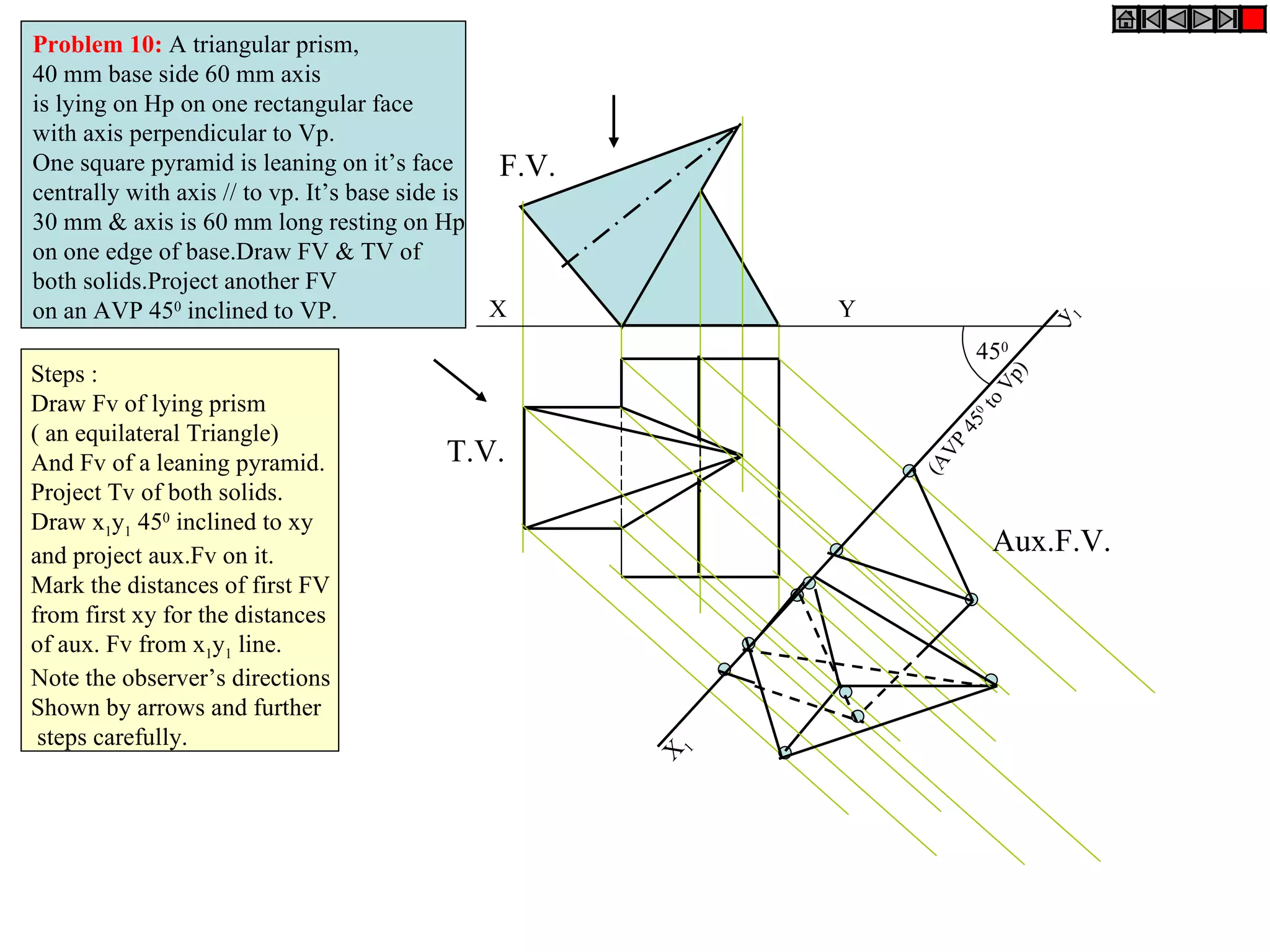
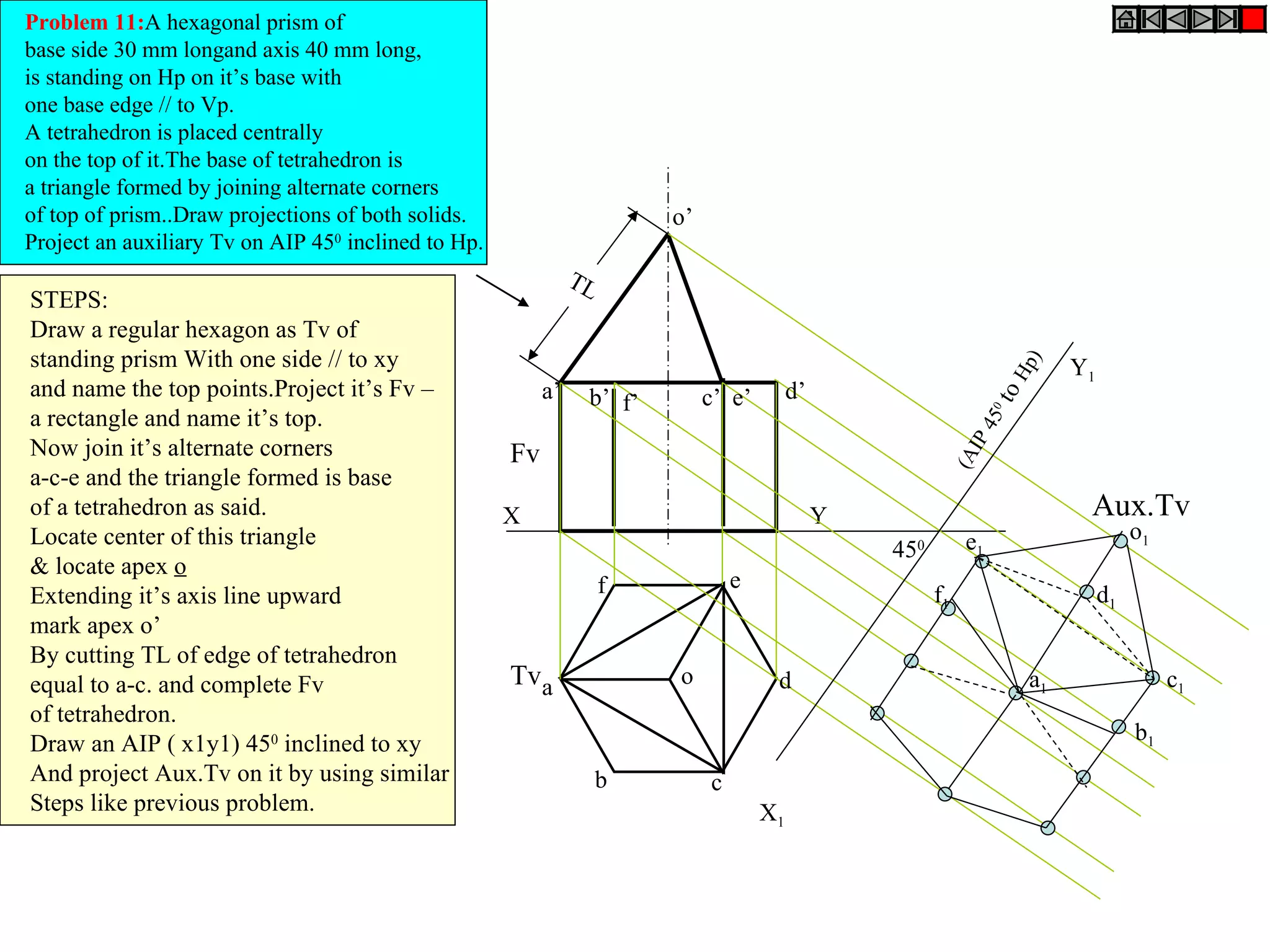
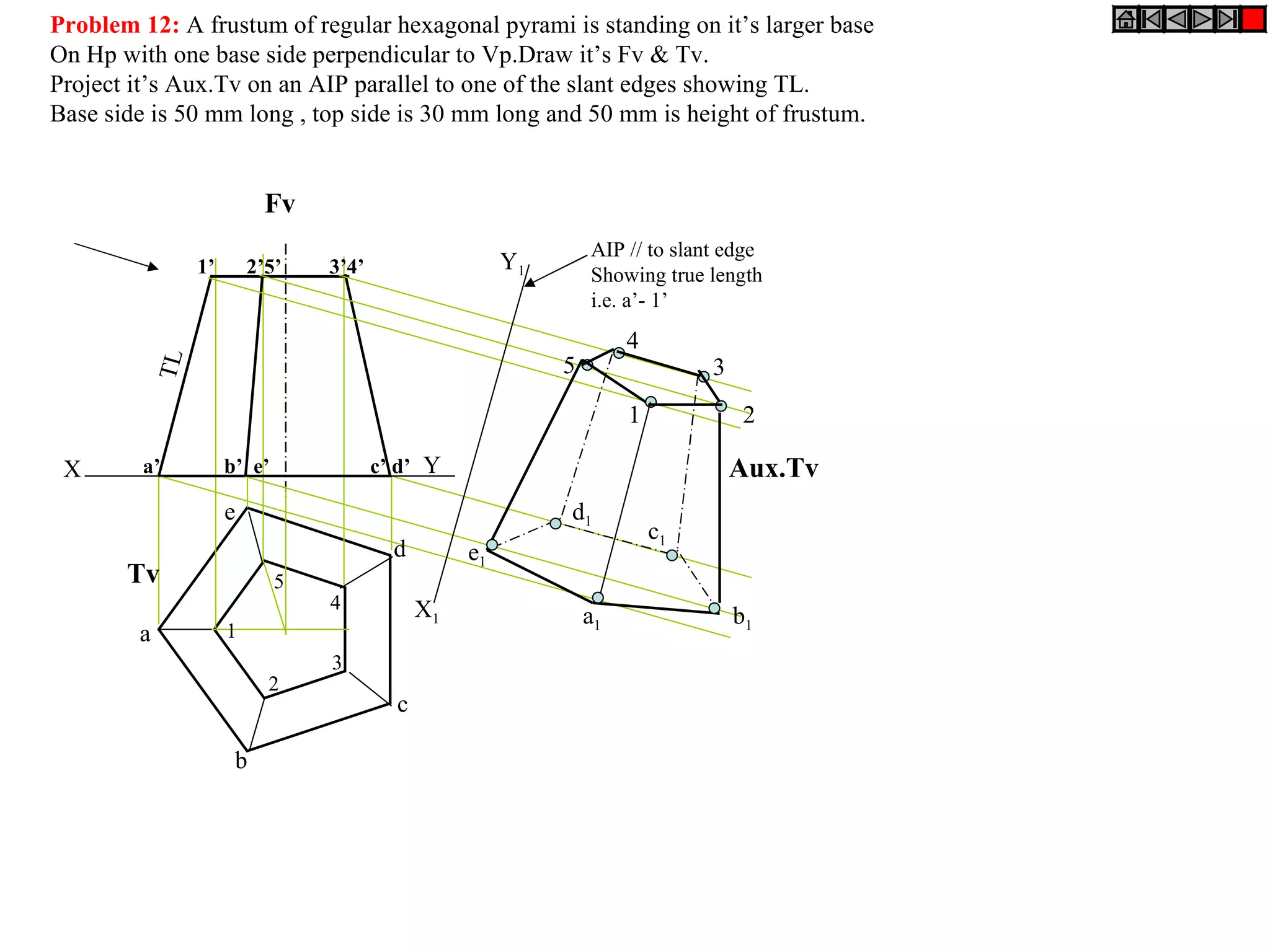
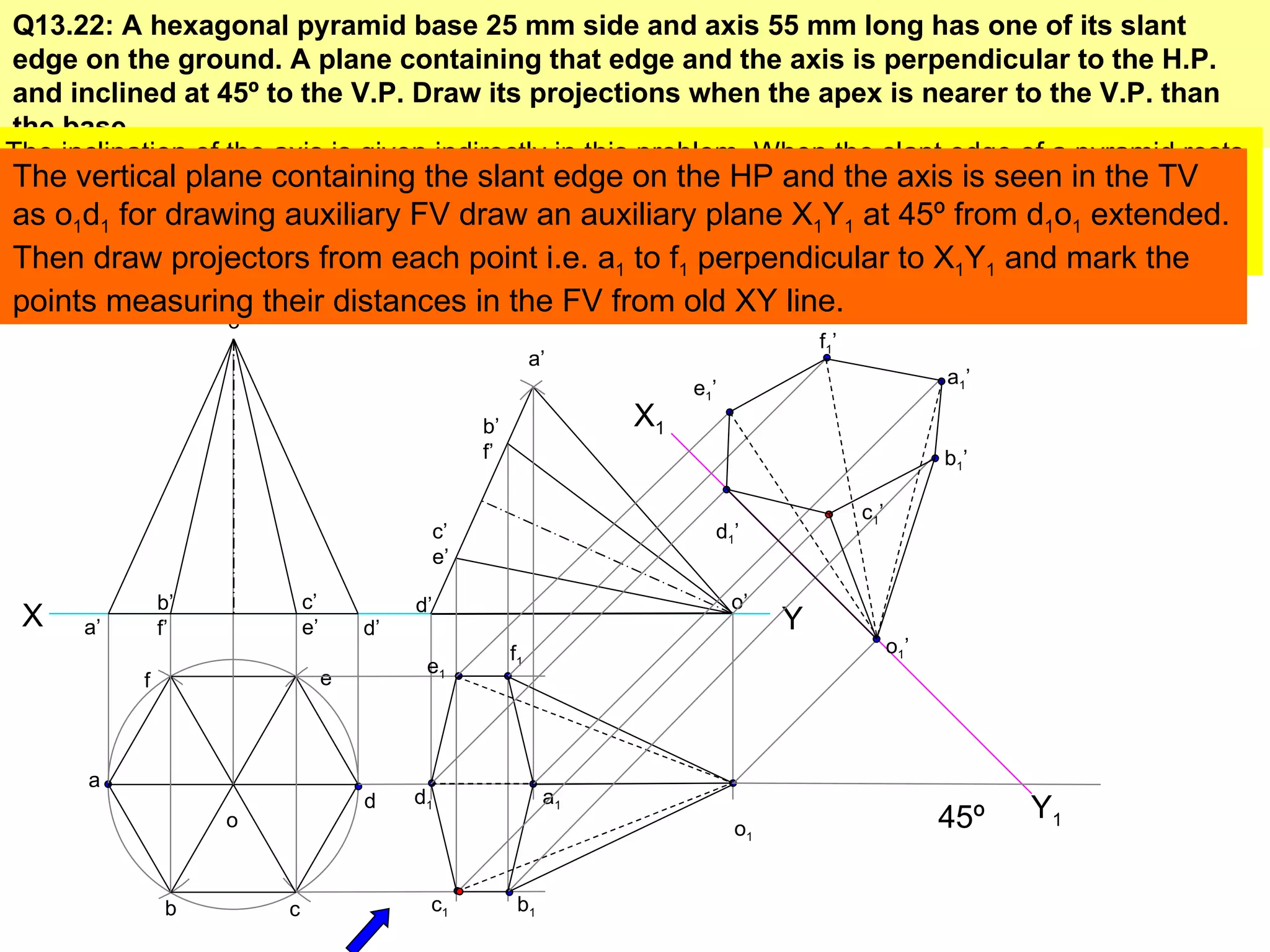
The document provides a comprehensive overview of various solids classified into two groups: solids with the same shape top and base (Group A) and those with an apex (Group B). It outlines the dimensional parameters, aspects of solving 3D solid problems, and the steps for deriving plan views and front views of these solids based on various inclinations. The text also includes examples and problem-solving techniques for different solid shapes, including cones, cylinders, pyramids, and prisms.