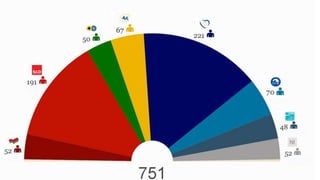
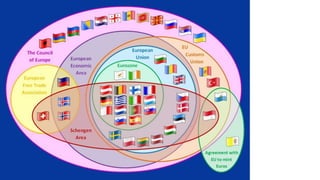
The European External Action Service (EEAS) manages the EU's diplomatic relations and aims to make EU foreign policy more consistent and influential globally. It works closely with national diplomatic services and supports the EU's strategic partnerships. The Council of the European Union adopts legislative acts with the European Parliament and coordinates policies in fields like economics and foreign affairs. The European Council sets the EU's overall political direction and priorities. The European Parliament acts as a co-legislator with the Council and oversees other EU bodies.