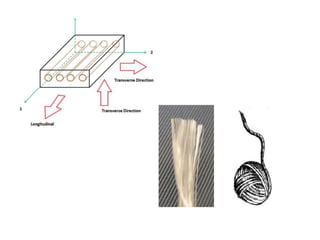
A lamina is the basic building block of composite laminates. It can contain fibers of different materials and orientations. A laminate consists of multiple stacked laminae, each with potentially different thicknesses, fiber orientations, fiber materials, and matrix materials. Due to planes of material symmetry, laminae exhibit orthotropic behavior and have different material properties depending on the direction. Failure prediction for non-isotropic composite laminates, like unidirectional laminates, requires evaluating allowable stresses in the principal material directions rather than just maximum principal stresses due to varying material strengths by direction.