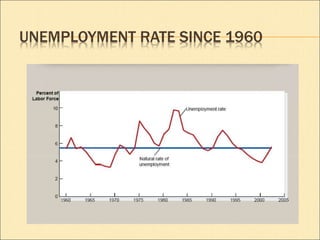
This document discusses unemployment, defining it as a situation where willing and able workers cannot find employment. It outlines the main types of unemployment: frictional, structural, cyclical, and seasonal. Causes of unemployment include high population growth, lack of job opportunities, and slow industry development. Costs of unemployment include financial hardship for individuals and lower economic output for society. Unemployment is measured using the unemployment rate, which is the number of unemployed workers as a percentage of the total labor force. Suggested solutions include changing investment patterns, small business encouragement, and reorienting education policy.