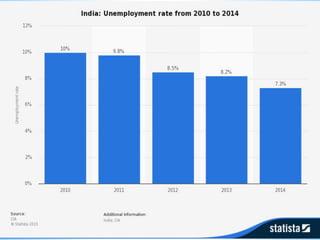
The document discusses different types of unemployment in India including seasonal unemployment, voluntary unemployment, frictional unemployment, cyclical unemployment, disguised unemployment, and reasons for unemployment such as rapid population growth, limited land, seasonal and backward agriculture, fragmentation of land, decline of cottage industries, defective education, and inadequate employment planning. Unemployment in India decreased from 5.2% in 2012 to 4.9% in 2013 but is projected to remain around 4.6% through 2020.