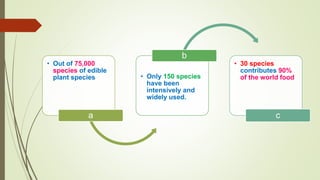
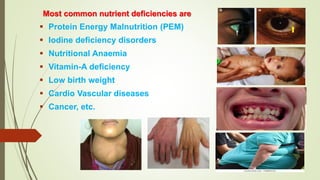
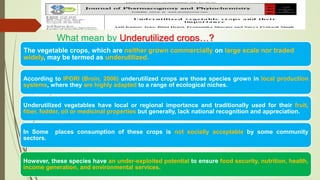
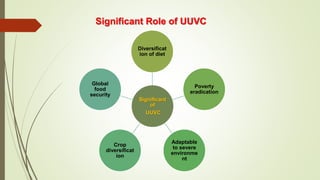
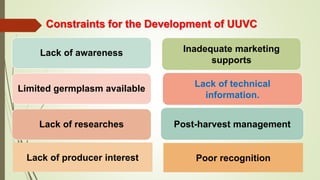
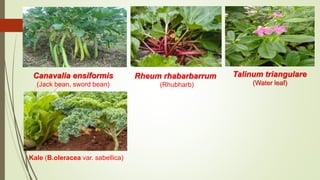
This document discusses underutilized vegetable crops and their potential. It begins by explaining that while over 75,000 edible plant species exist globally, only around 150 are widely cultivated. It then discusses the nutritional value of various vegetables and common nutrient deficiencies. The concept of underutilized vegetable crops (UUVCs) is introduced as crops that are locally important but lack national recognition. UUVCs have potential for food security, income generation, and environmental benefits. Some constraints to their development include lack of awareness, research, and marketing support. The document concludes by listing examples of UUVCs from Central India along with their uses.