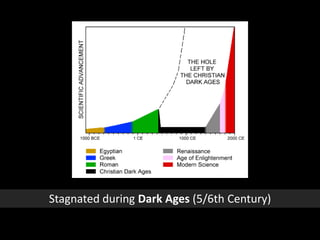
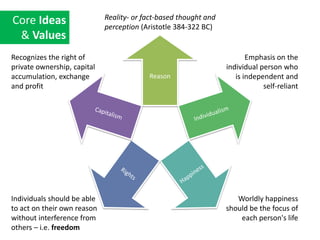
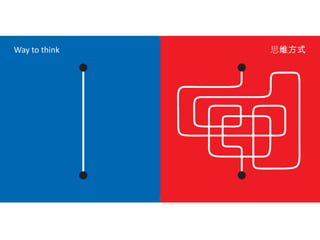
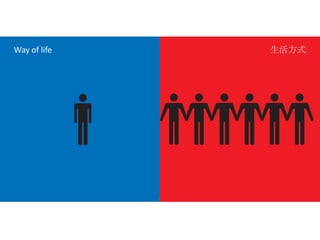
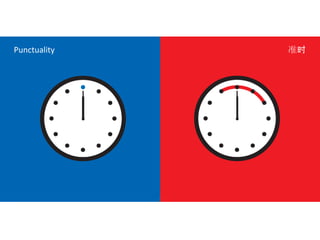
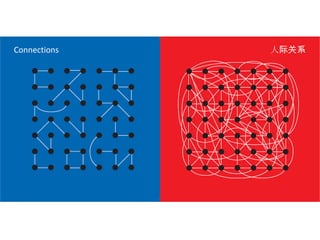
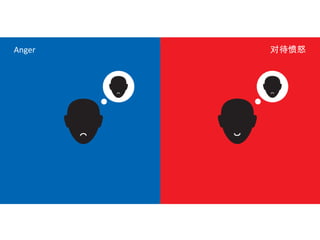
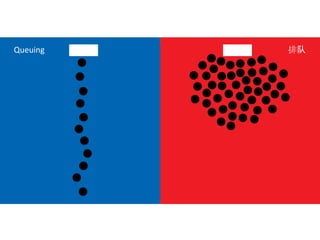
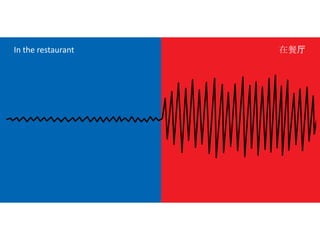
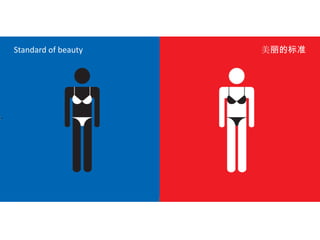
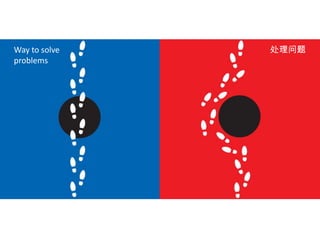
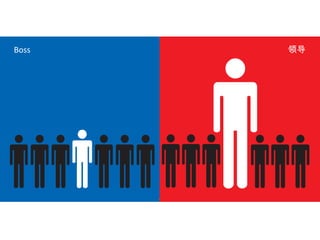
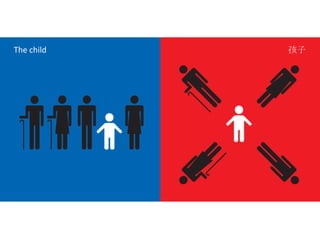
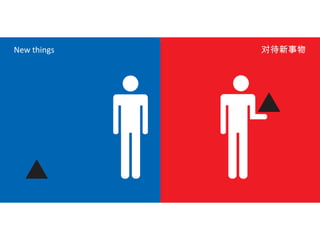
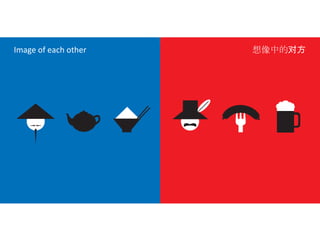
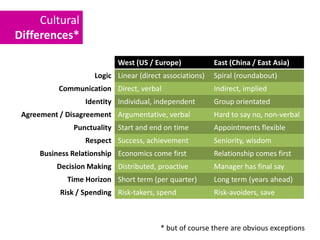
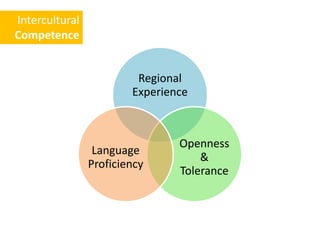
The document discusses Western culture's evolution from ancient Greece to modern civilization, highlighting key influences such as the Renaissance and the Age of Enlightenment. It emphasizes core values of individualism, personal freedom, and a focus on worldly happiness, while also considering cultural differences between East and West. It concludes with tips on effective intercultural communication and the importance of adaptability and openness.