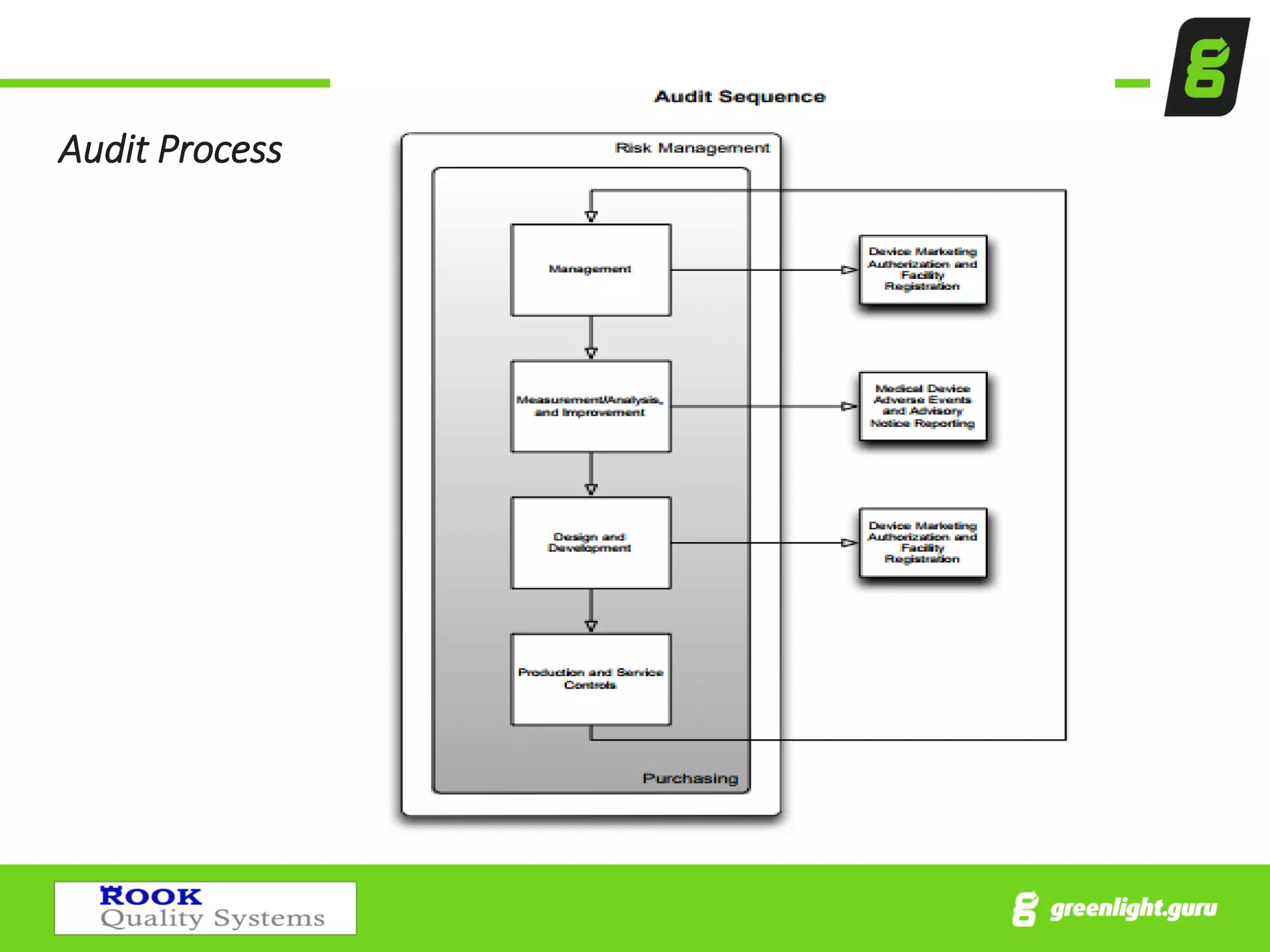
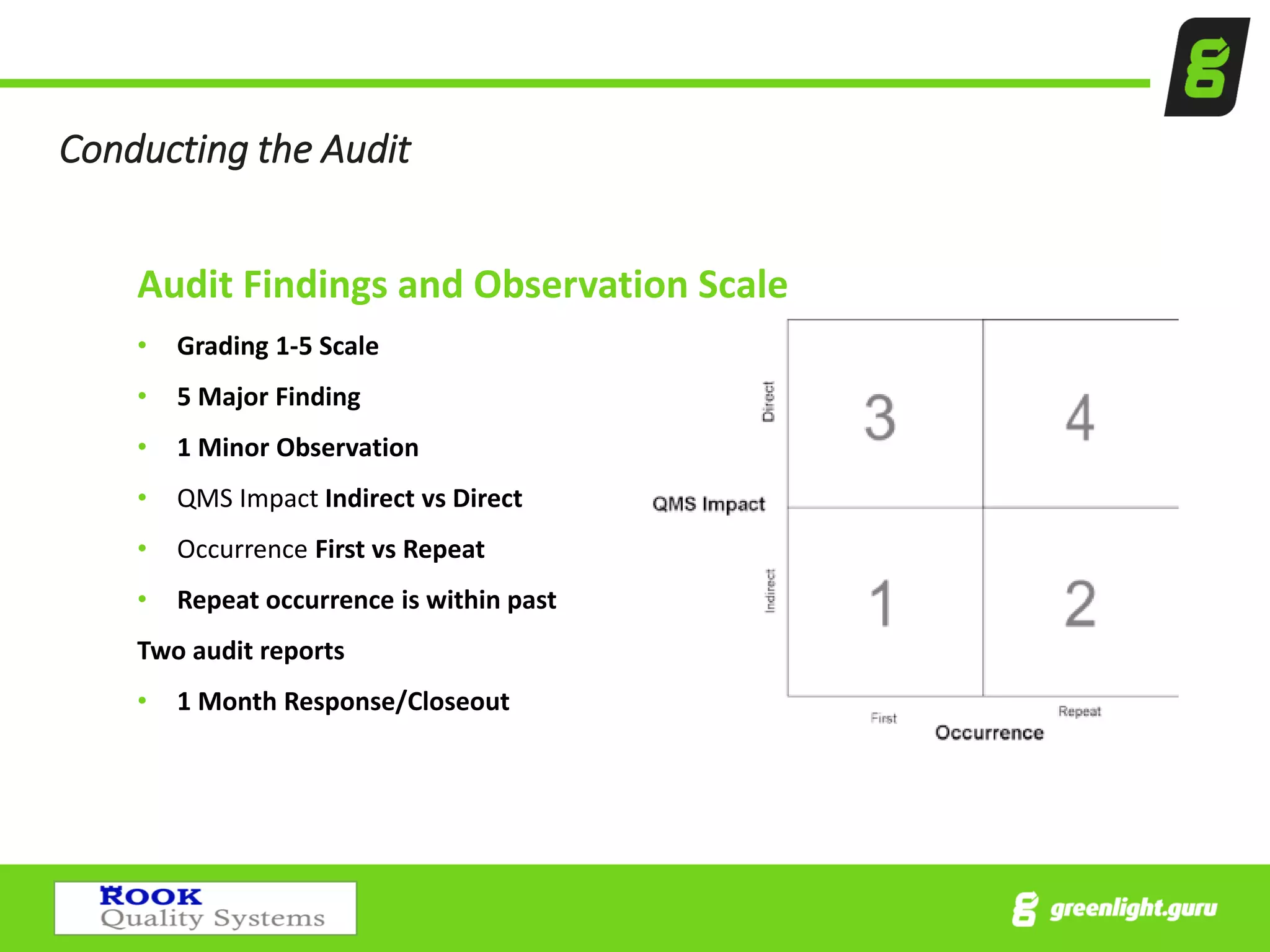
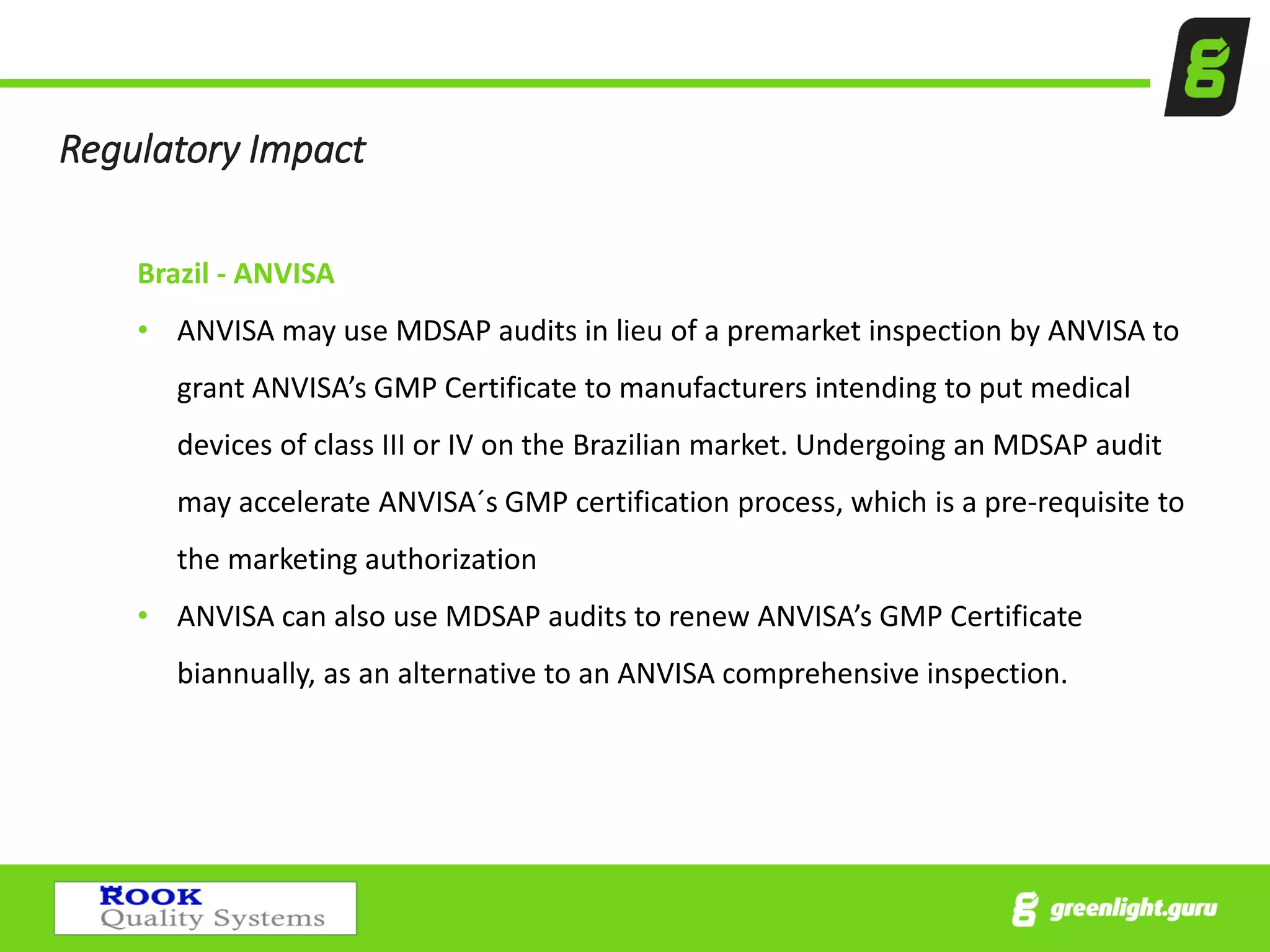
The document provides an overview of the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP), which allows manufacturers to consolidate regulatory audits from multiple countries, including the USA, Canada, and Australia, into a single audit to streamline the approval process and reduce costs. It outlines the audit process, transition year changes related to ISO 13485:2016, and the regulatory impacts in different regions. It also emphasizes the importance of proper quality management systems and offers consulting services to assist companies in preparing for MDSAP audits.