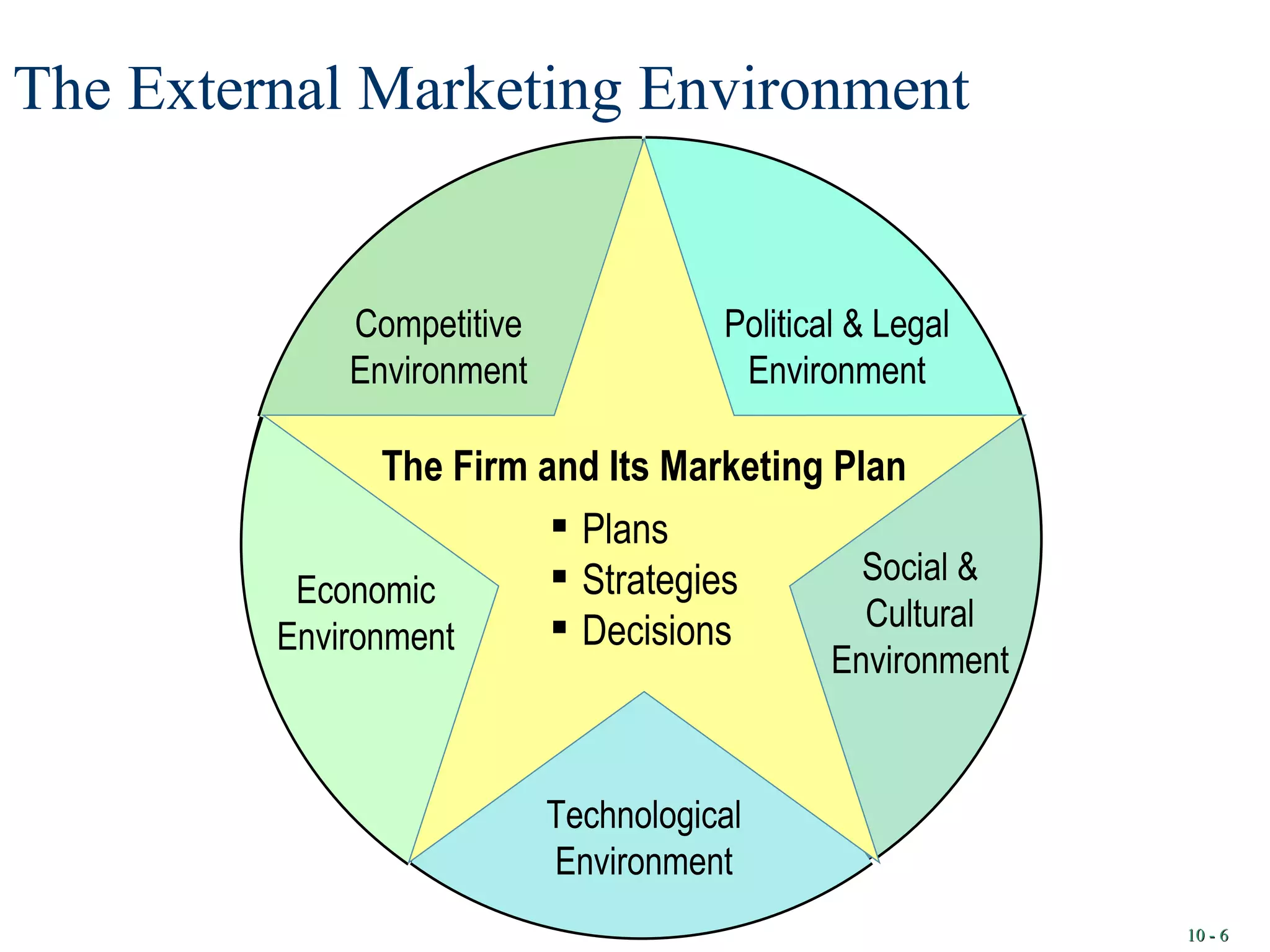
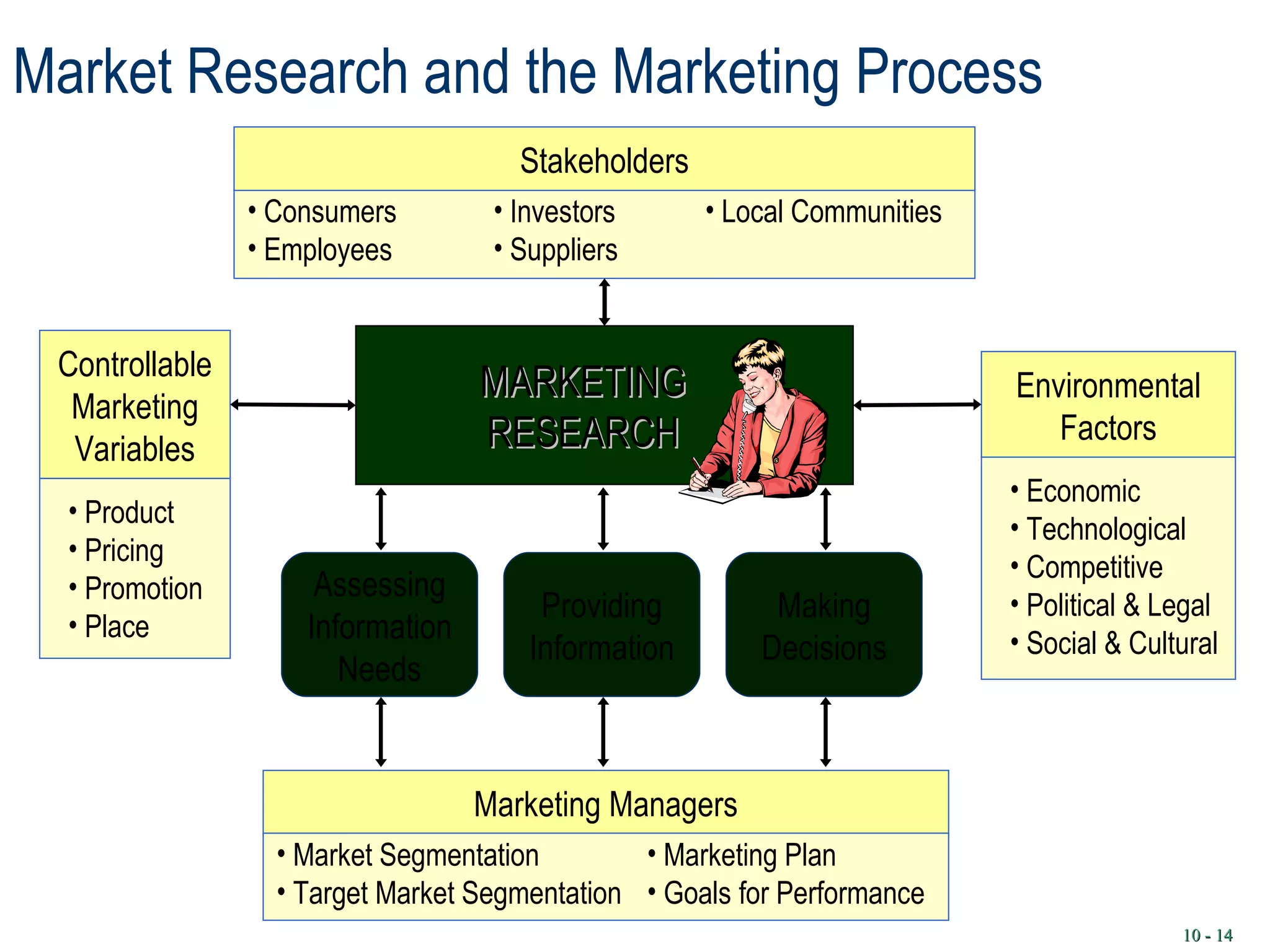
1. Marketing involves planning and executing the conception, pricing, promotion, and distribution of goods, services, and ideas to create exchanges that satisfy objectives. This is known as the "marketing mix."
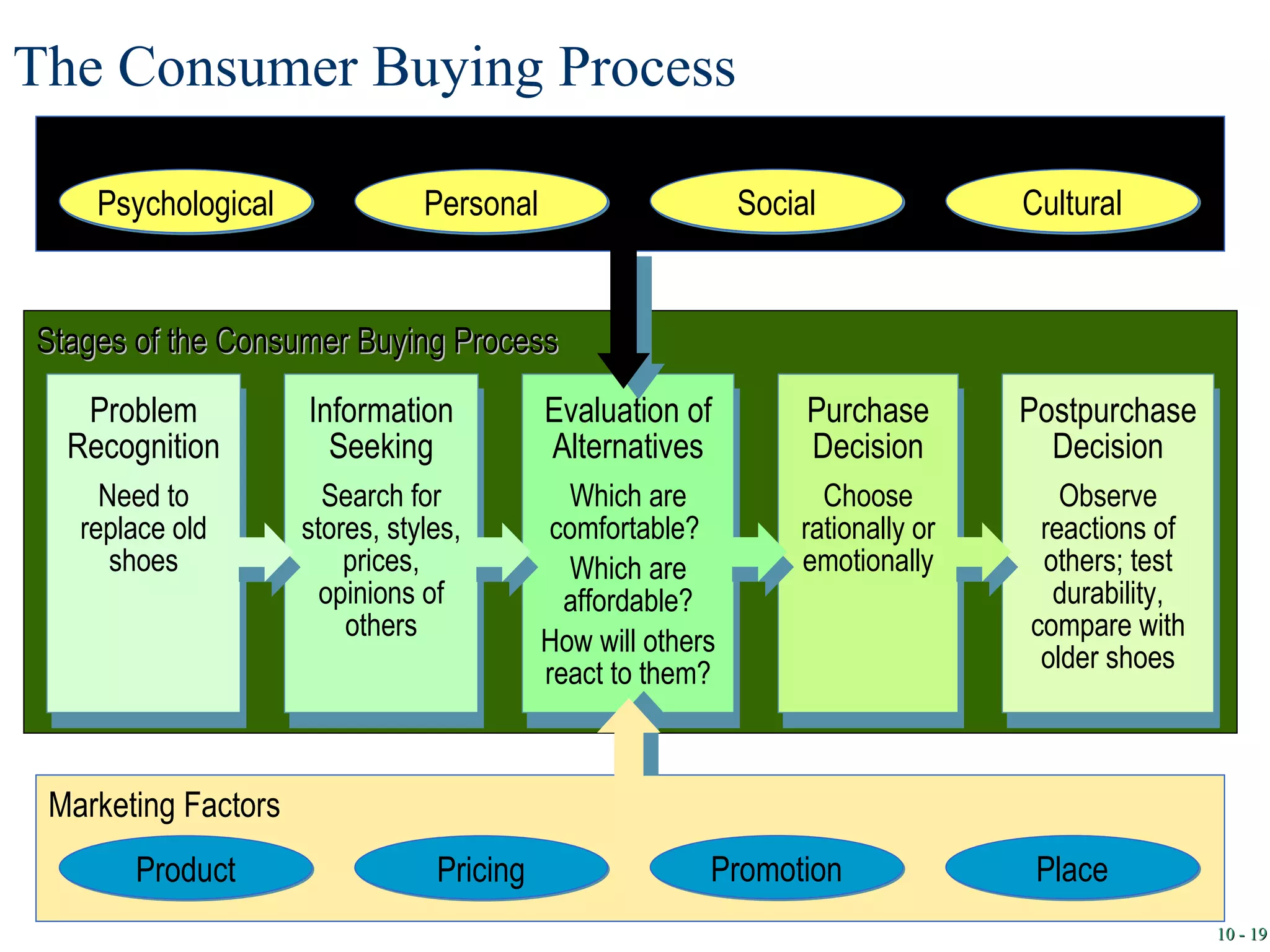
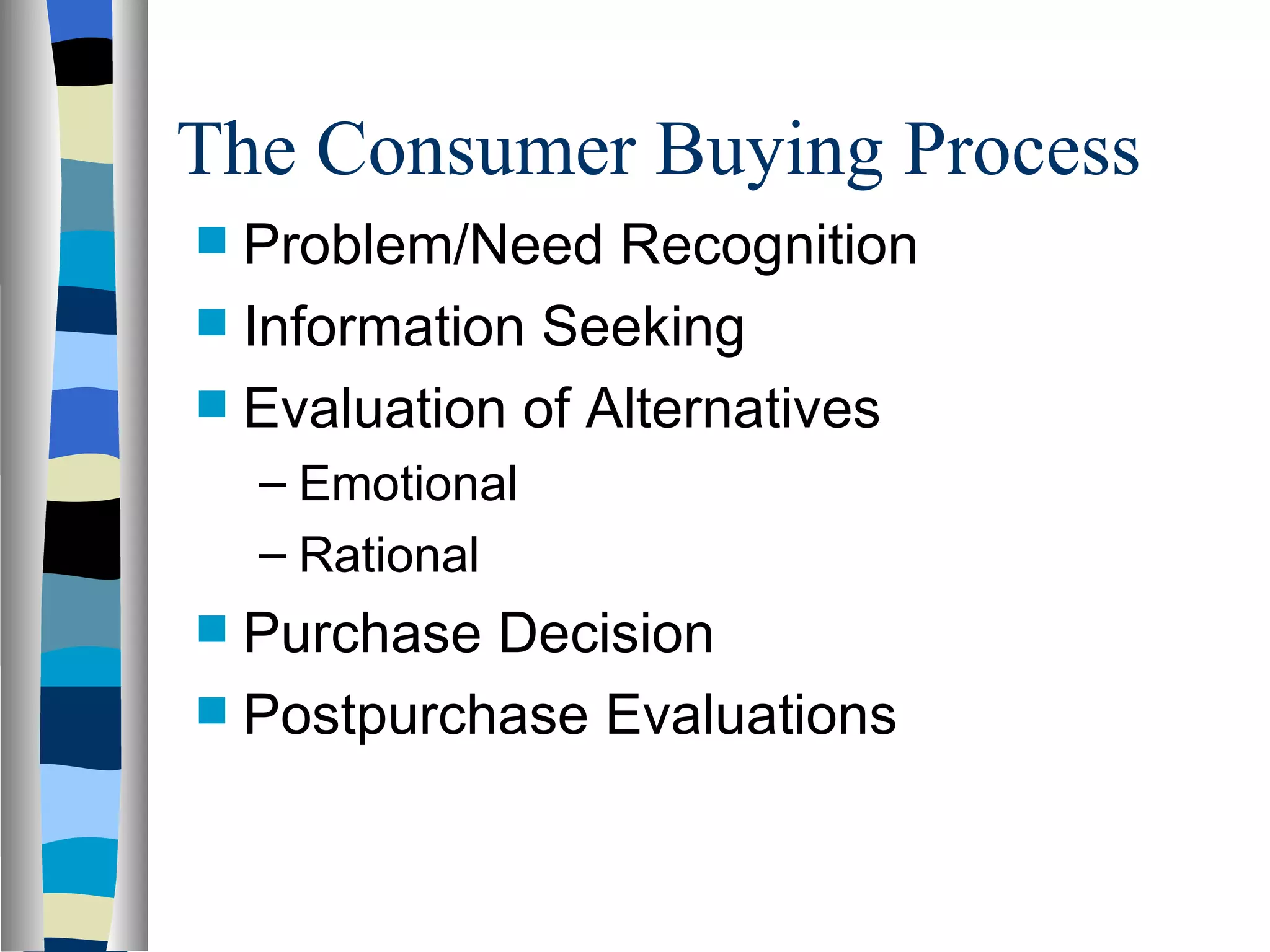
2. Understanding consumer behavior and how external factors influence consumers is important for developing marketing strategies. Research is conducted to study consumer needs, wants, and decision-making processes.
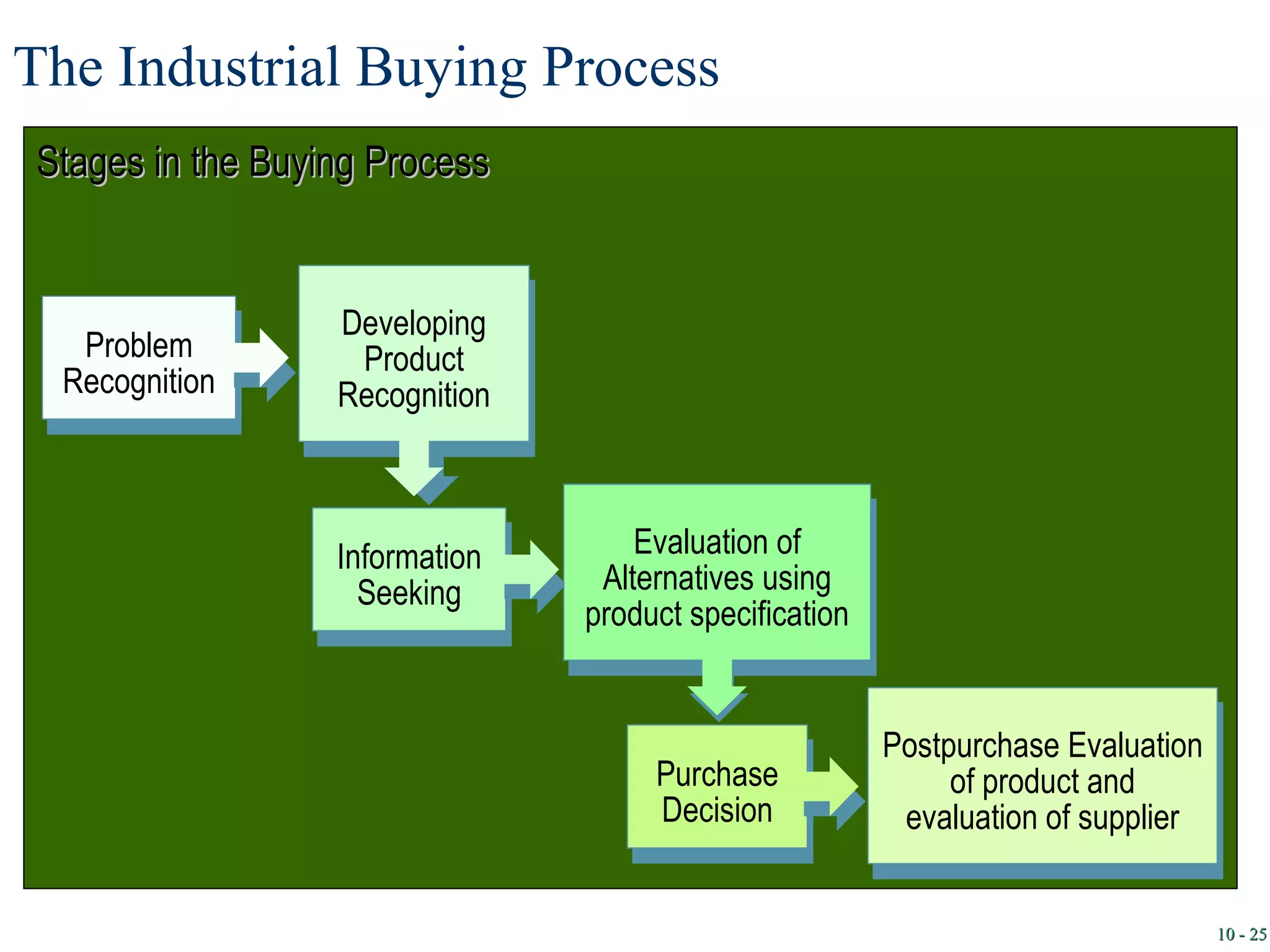
3. Organizational buying differs from consumer buying in that organizational buyers are professionals who follow a process of problem recognition, information search, evaluation, purchase decision, and post-purchase evaluation when buying goods for business use.