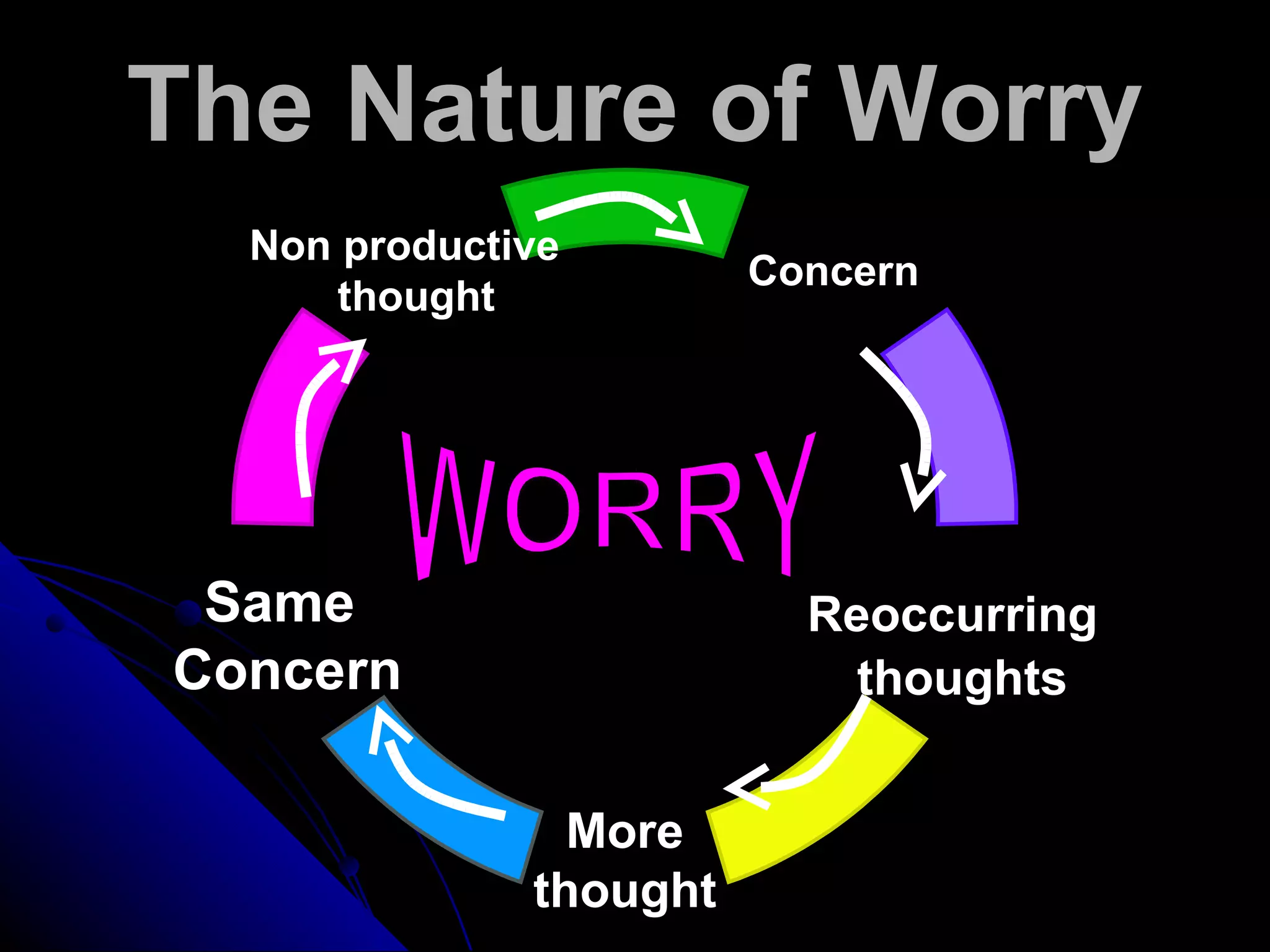
The document discusses cognitive distortions and negative thought patterns that can impact happiness and provides recommendations for developing gratitude, mindfulness, and focusing on positive attributes in order to improve well-being. It also suggests taking action through deep breathing, challenging distortions, expressing gratitude, and maintaining a positive outlook for at least 21 days to potentially change one's perceptions and increase happiness.