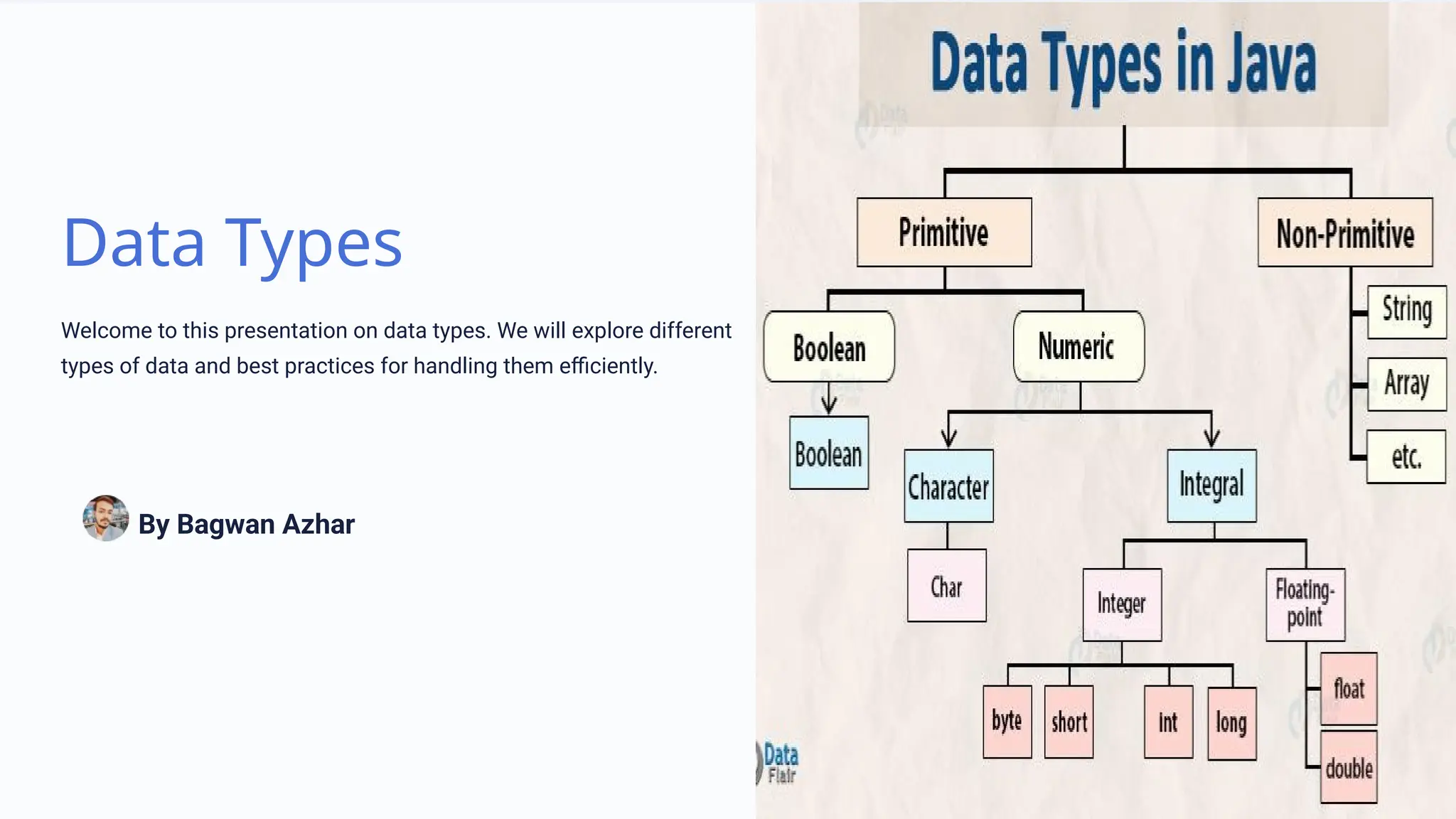
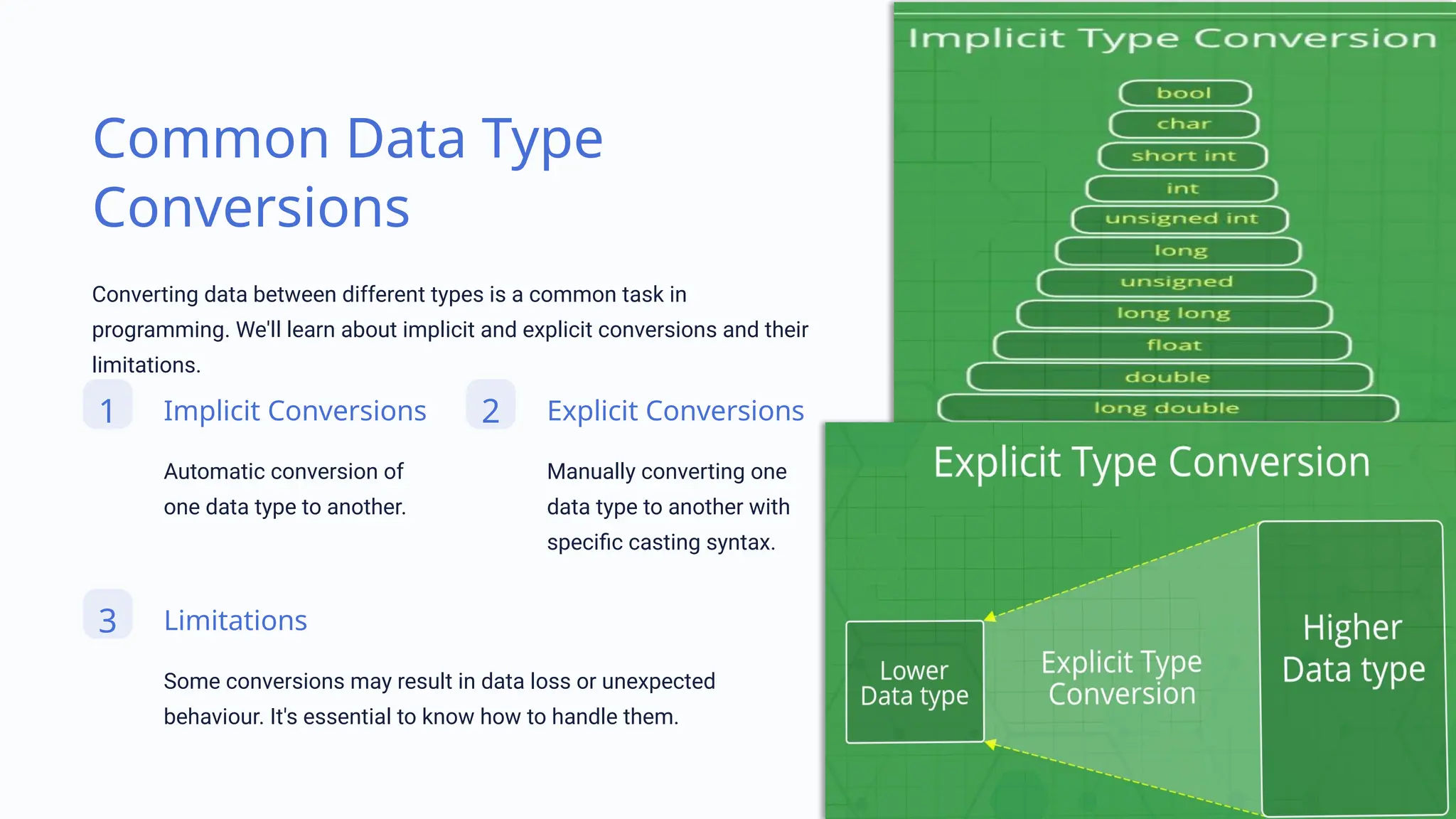
This presentation covers various data types in programming, including numeric, character, string, boolean, and date/time types, emphasizing their definitions and best practices for handling them. It highlights how to declare, manipulate, and convert these types while also addressing the importance of choosing the right data type and avoiding errors through type checking. Overall, understanding data types is essential for robust and efficient programming.