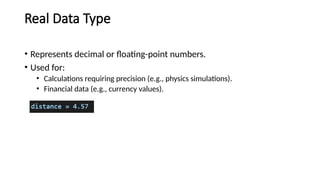
The document discusses the importance of data types in programming, specifically integer, real, and boolean types, along with their characteristics and examples of usage. It emphasizes the role of library functions in simplifying programming tasks and describes how selecting the correct data type can enhance efficiency and accuracy. Additionally, it includes practical programming exercises demonstrating the use of these data types.








![Examples
name = "Alice"
print(len(name)) # Output: 5
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
print(len(numbers)) # Output: 4
number = 3.14159
print(round(number)) # Output: 3
print(round(number, 2)) # Output: 3.14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/programming-250203165955-549c6302/85/programming-in-computer-science-cambridge-pptx-11-320.jpg)
