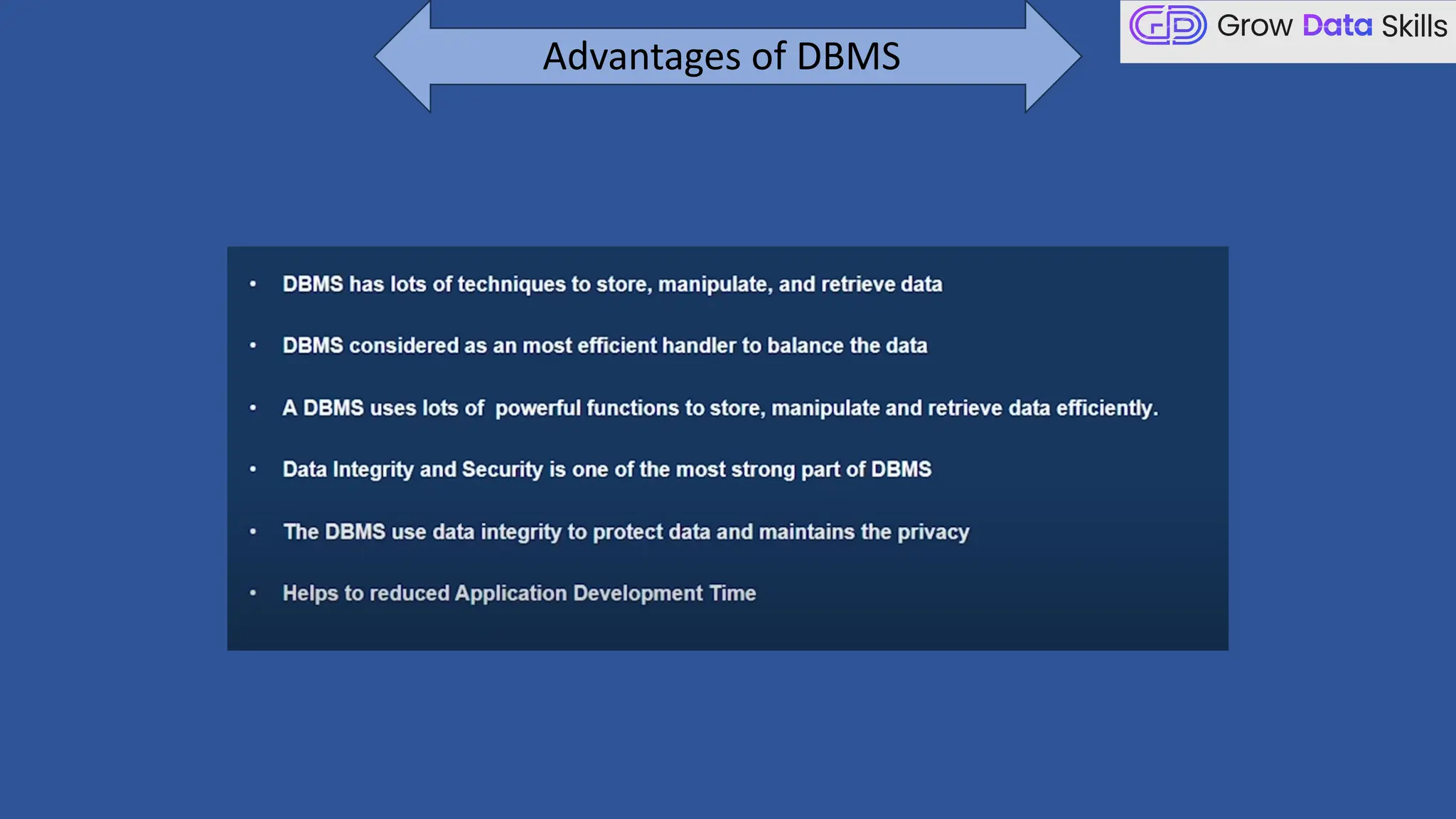
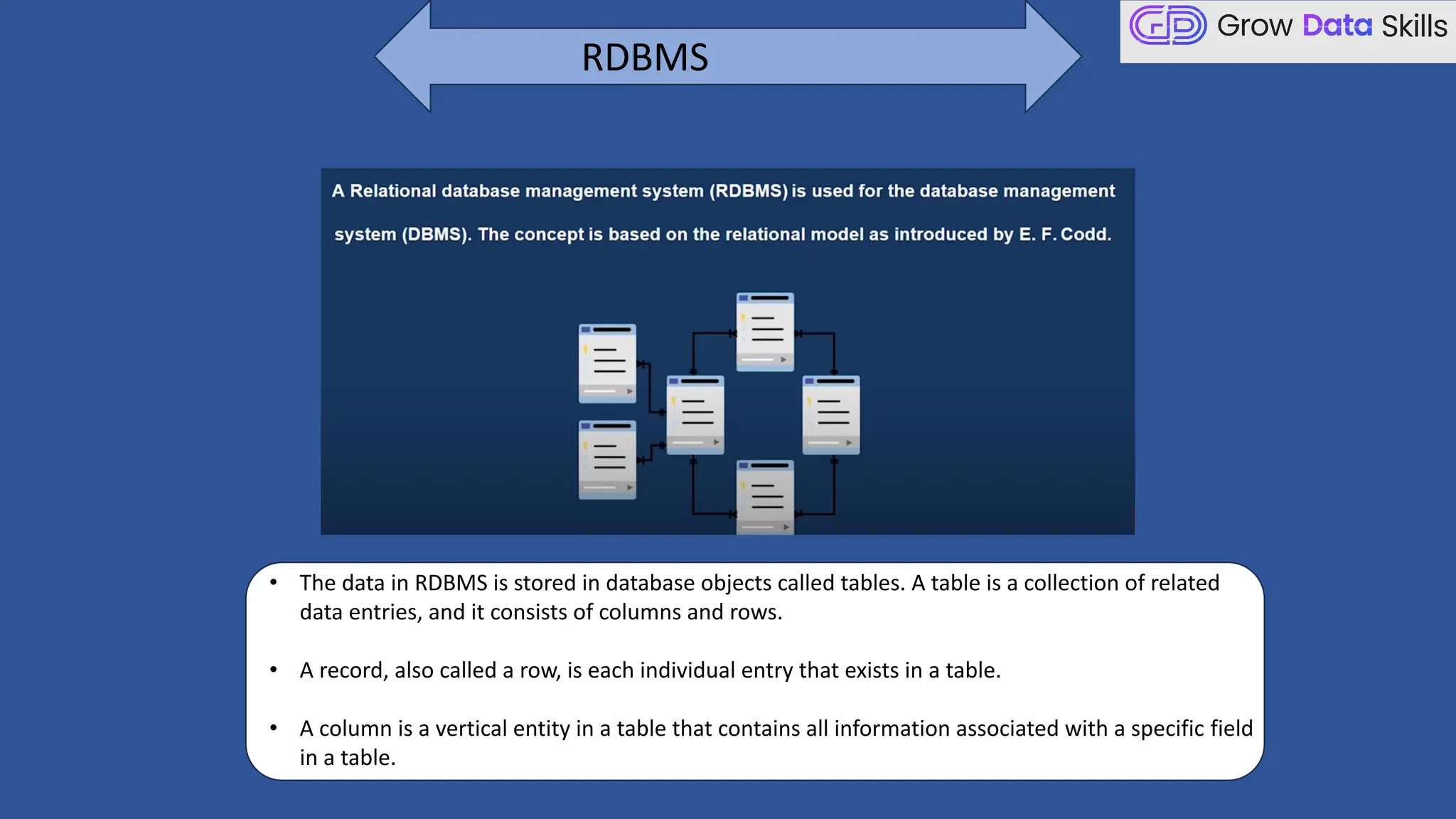
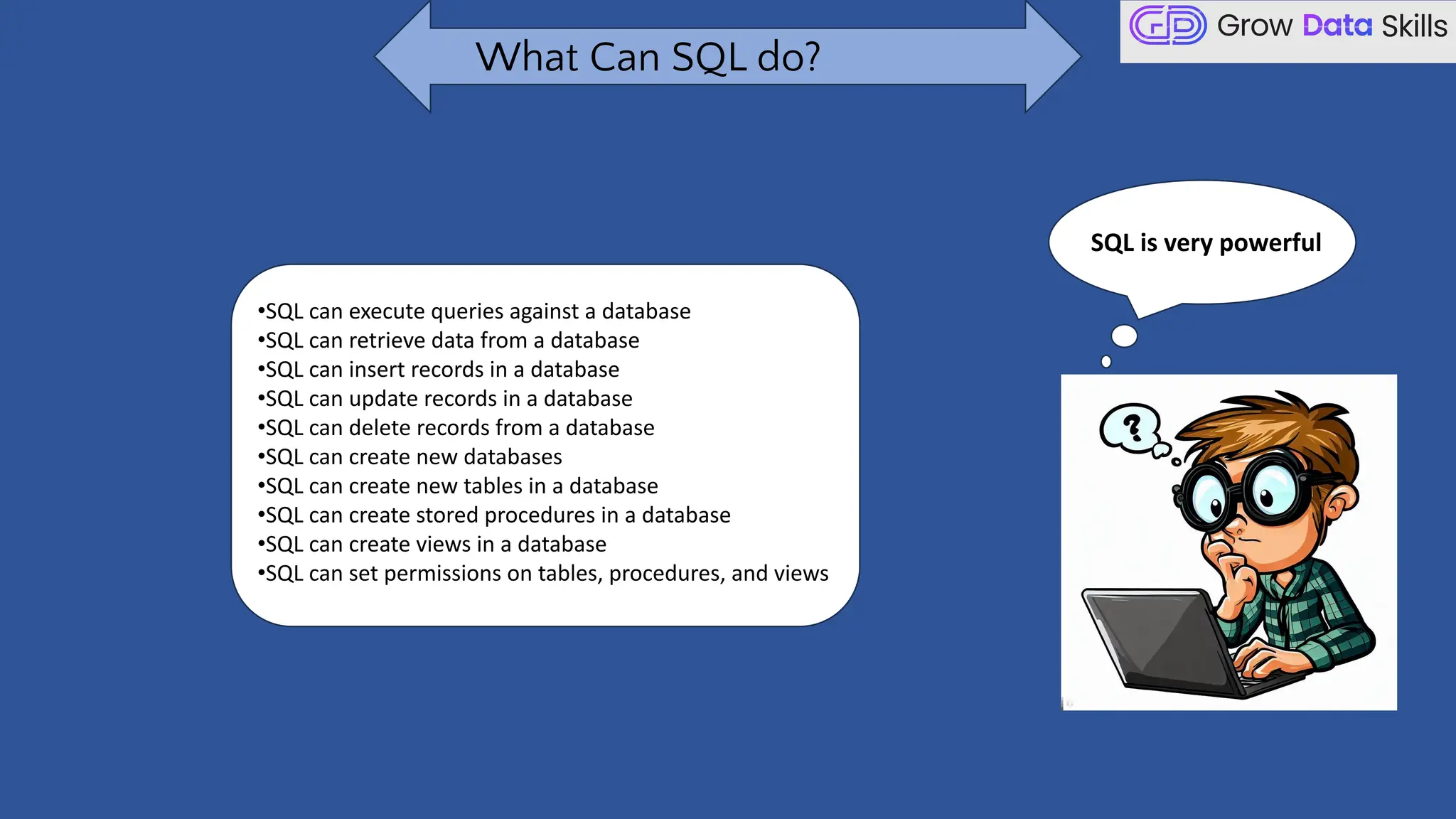
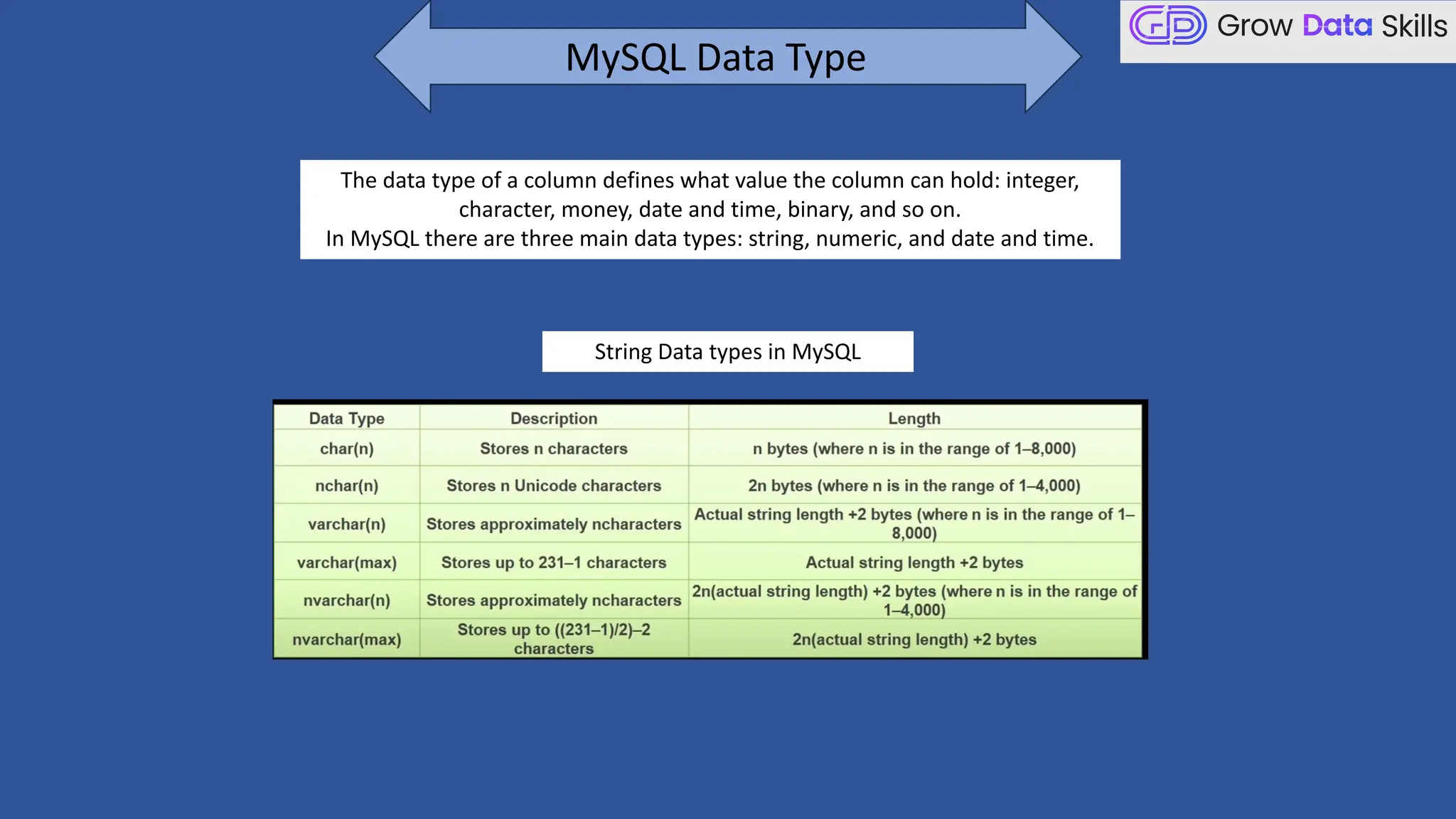
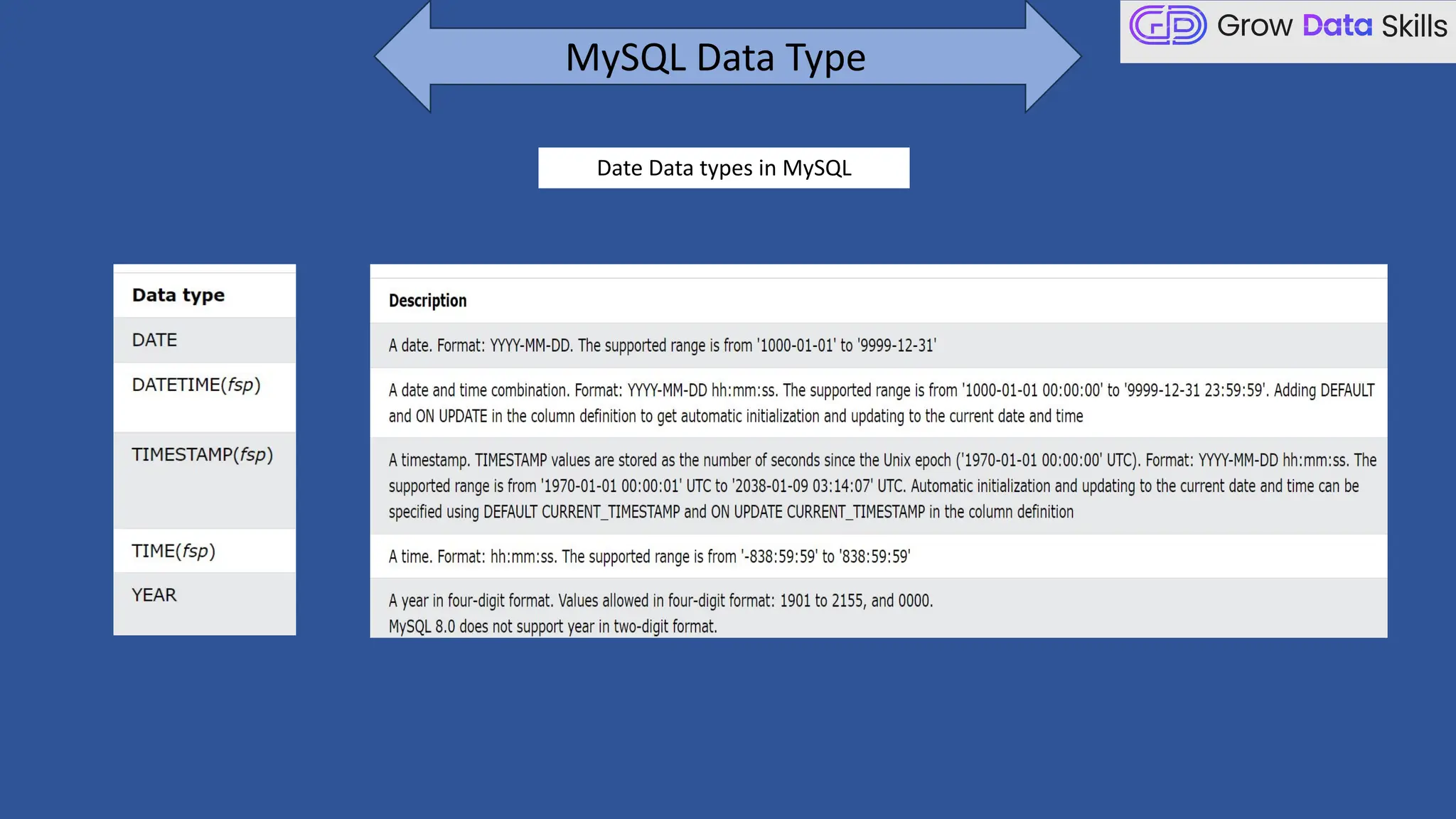
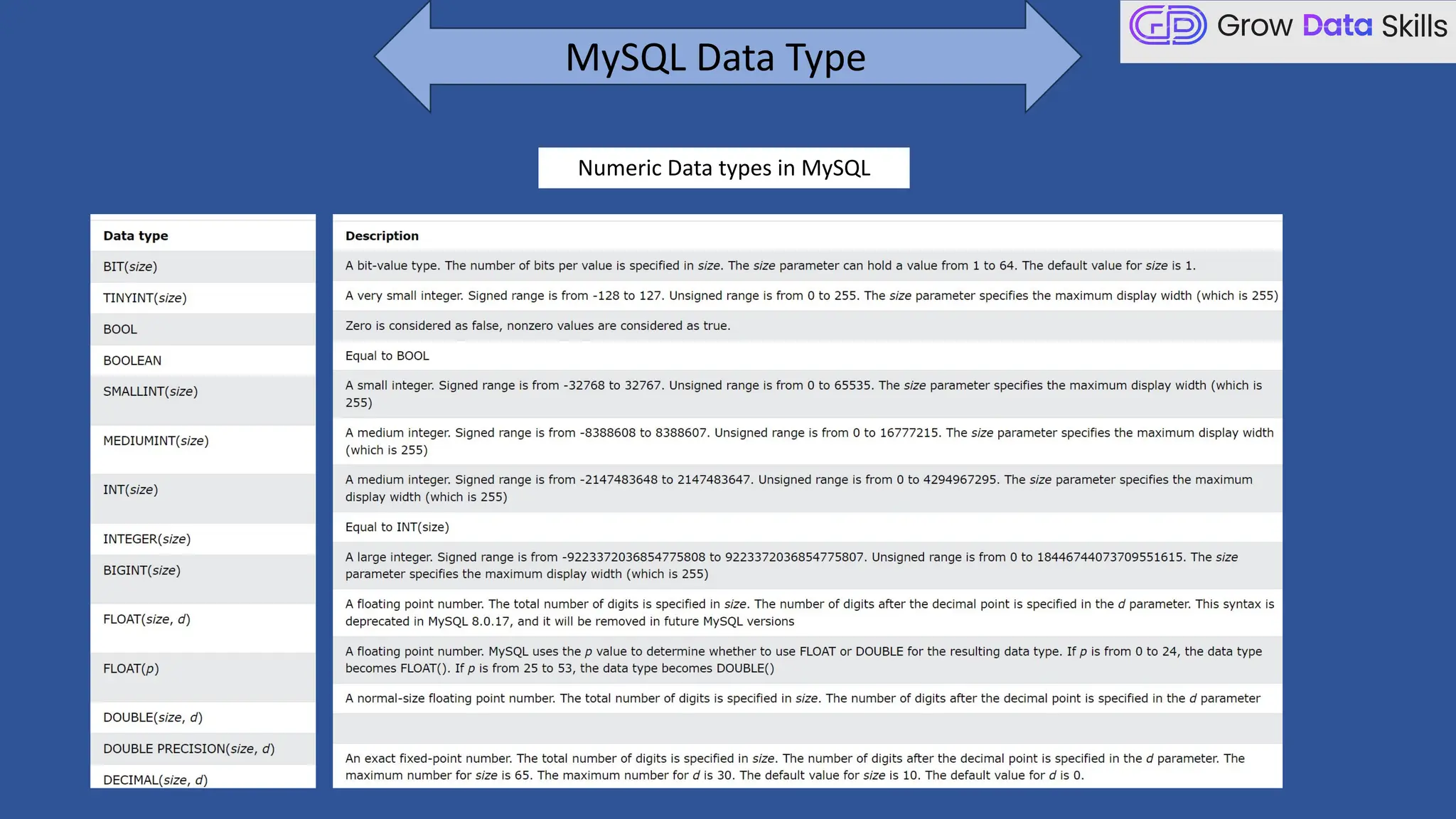
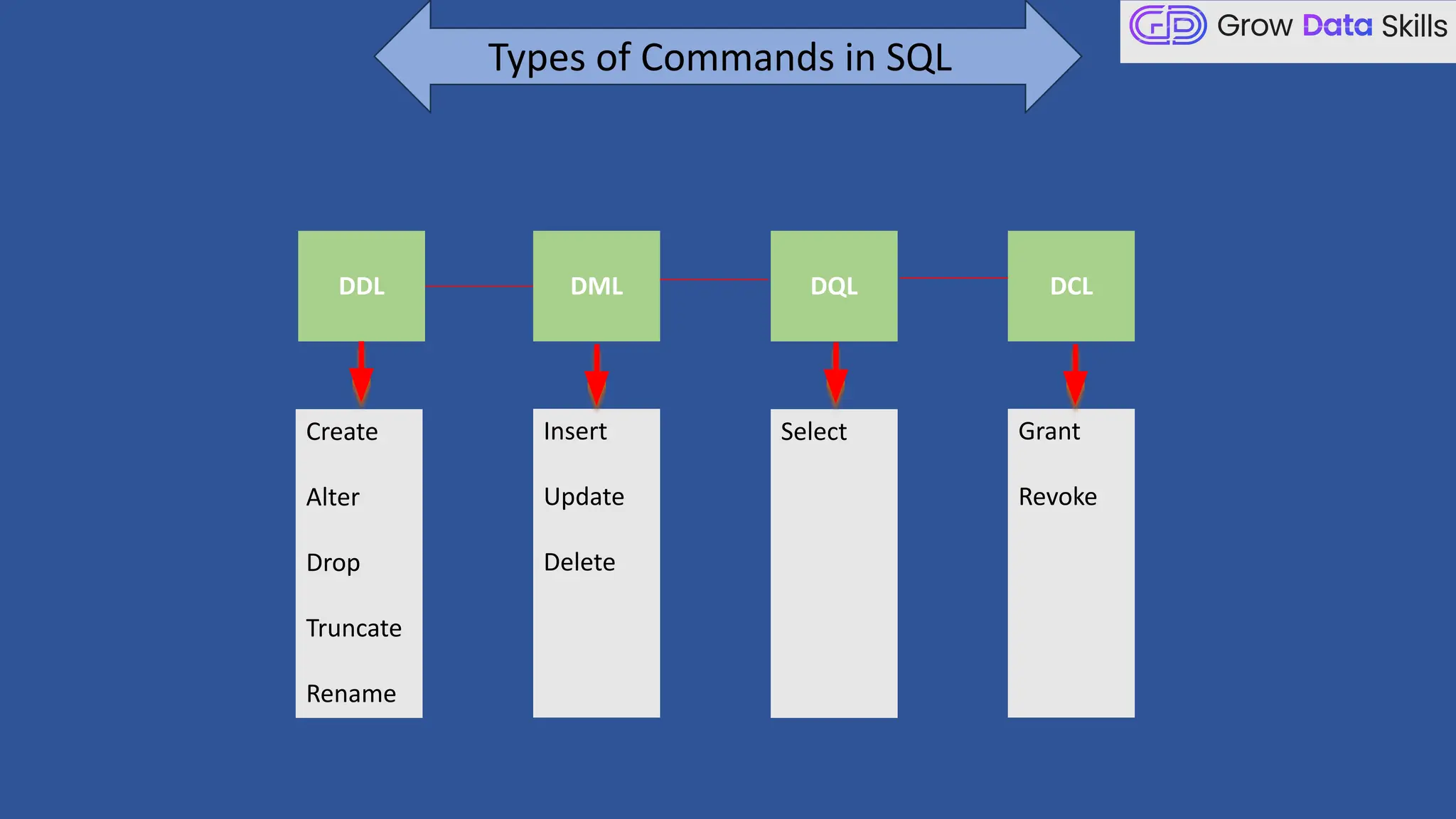
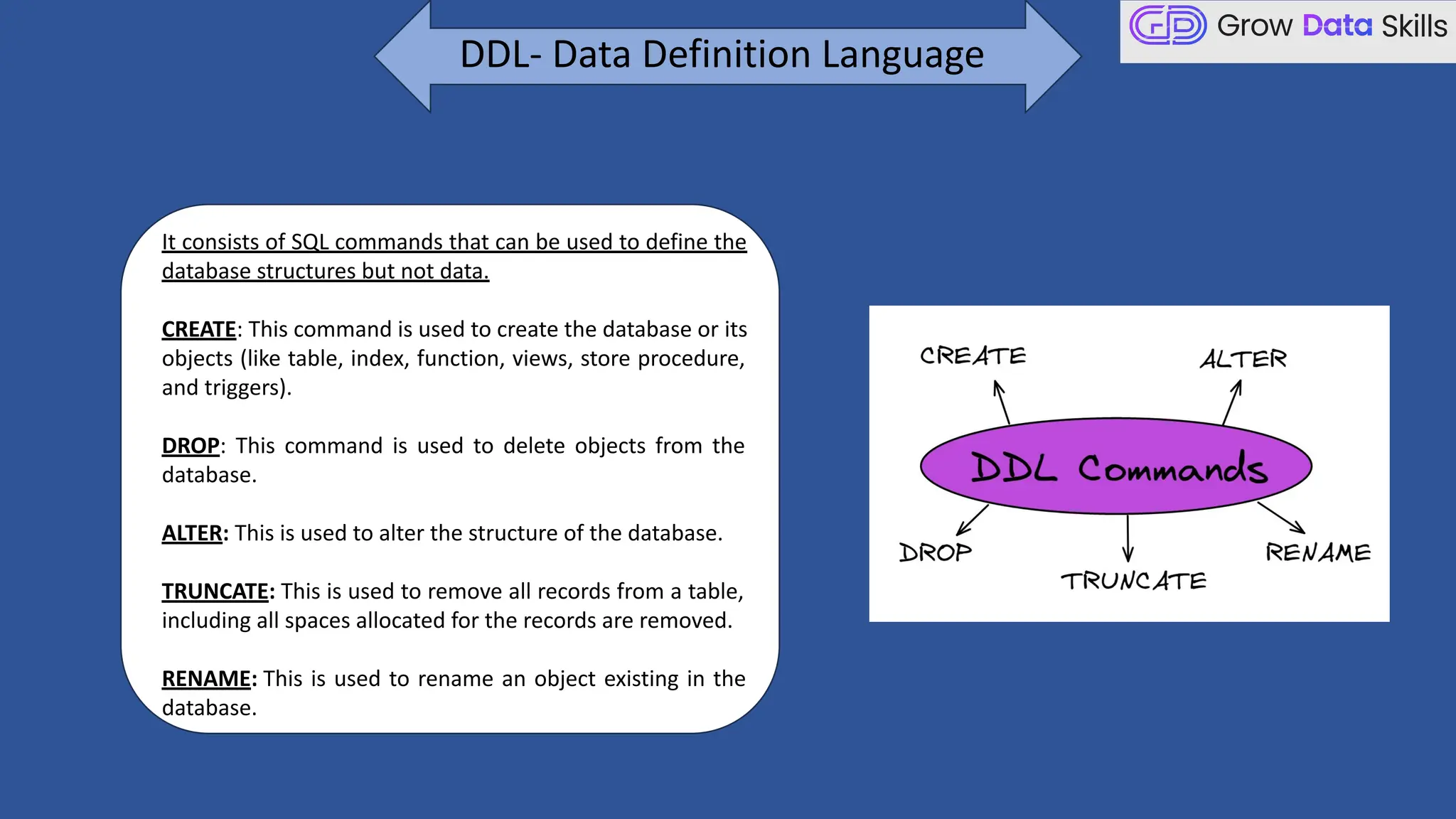
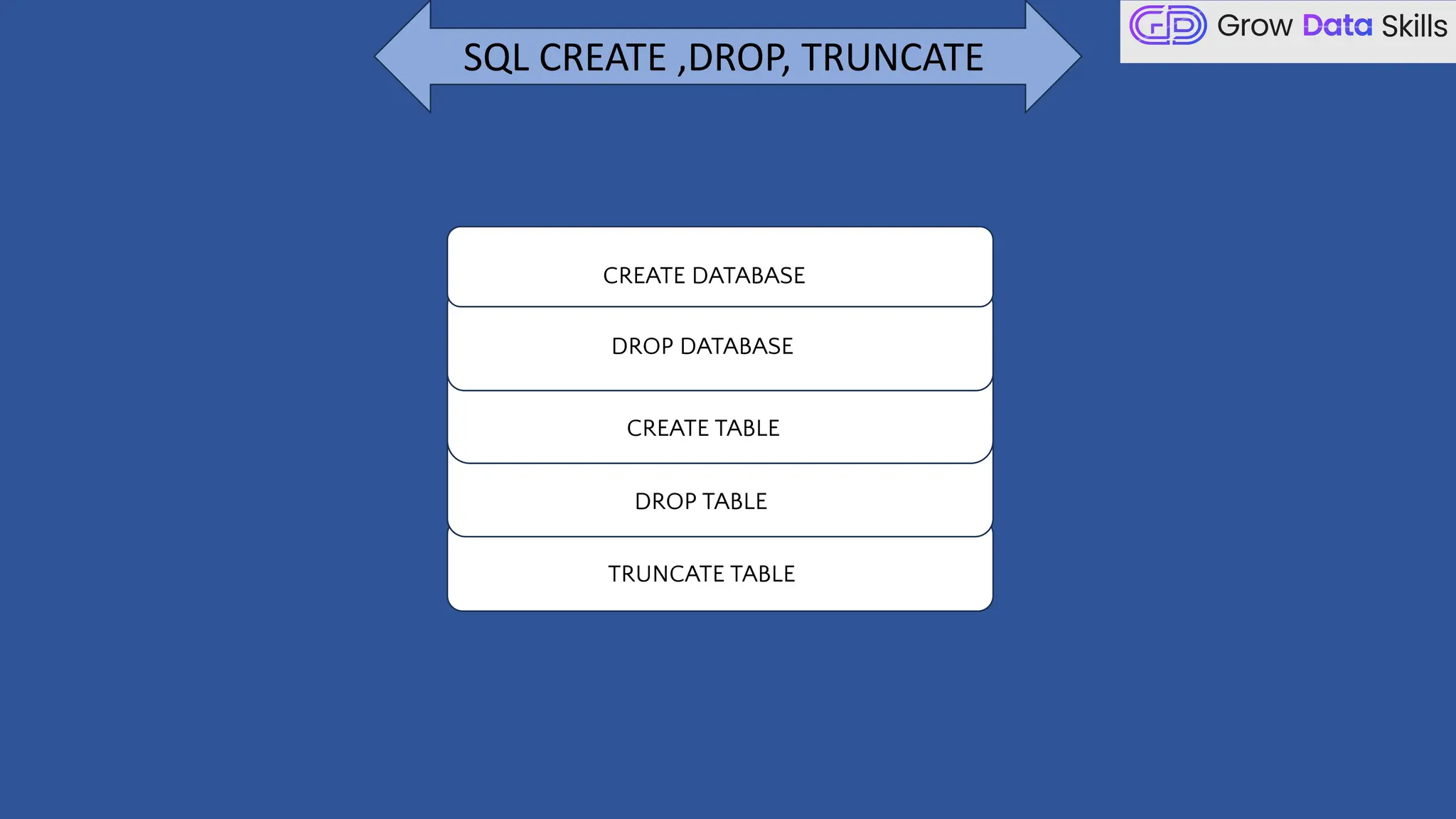
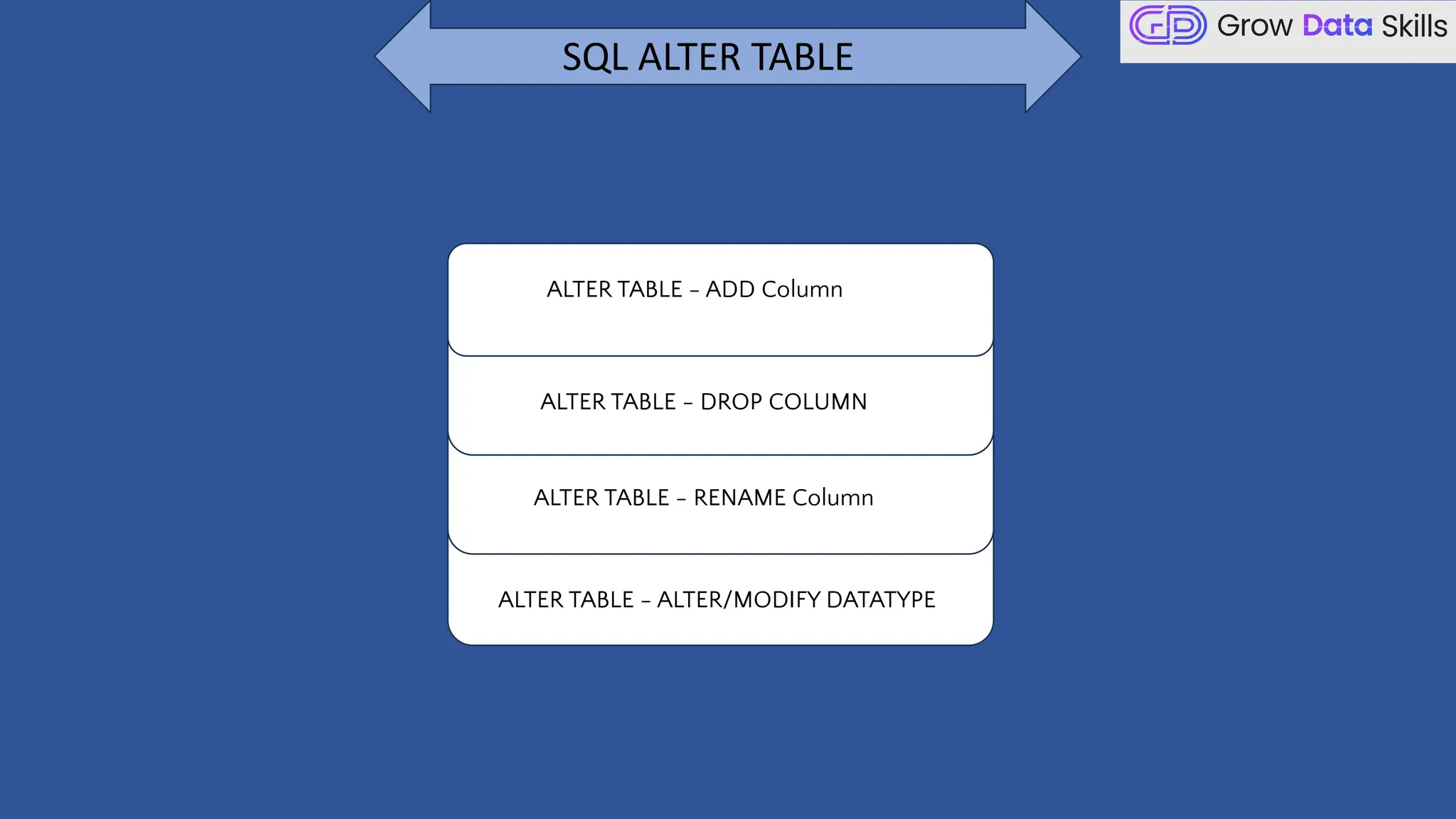
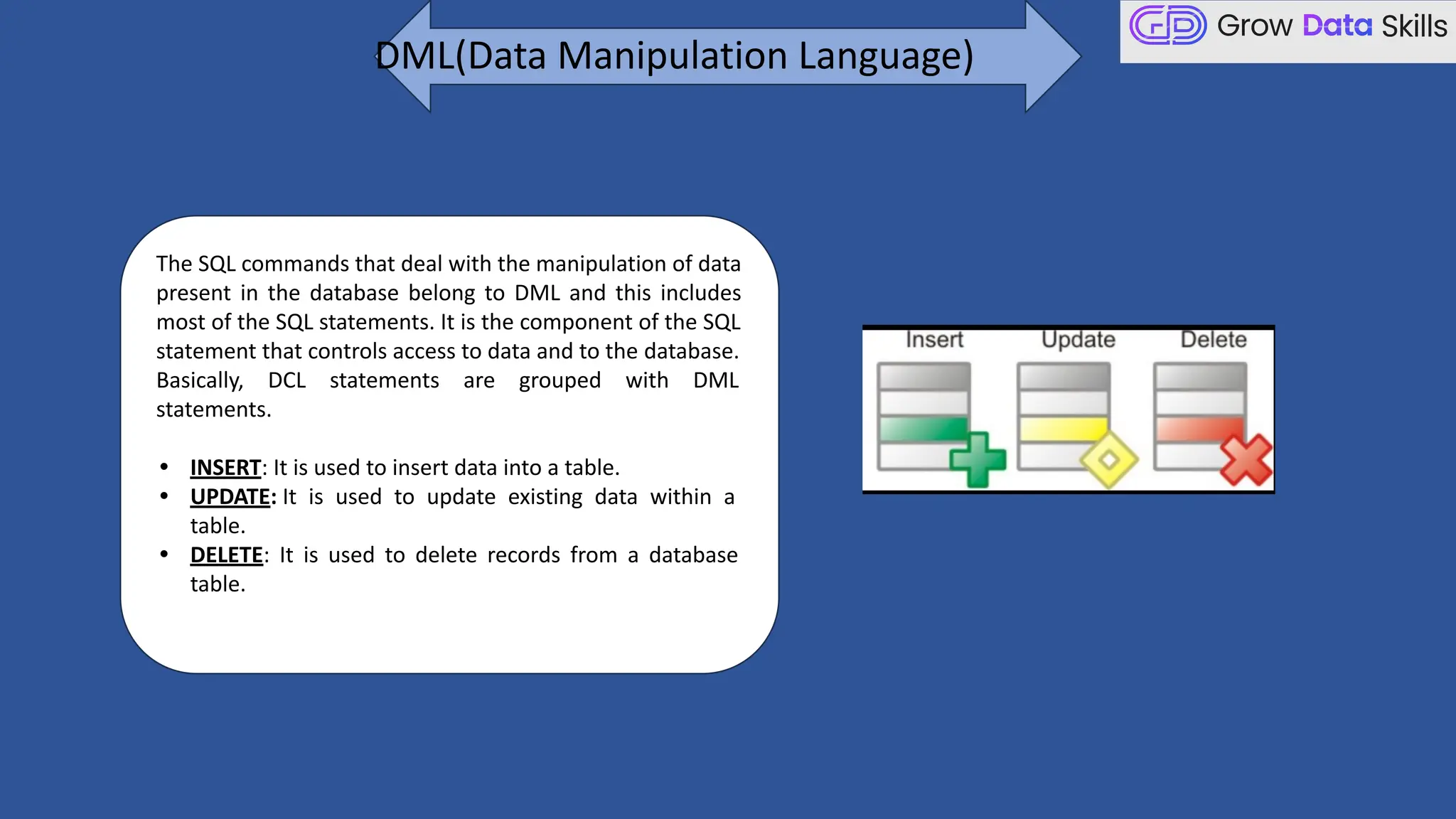
This introductory class on SQL (Structured Query Language) provides a foundational understanding of how to interact with relational databases. The session covers the basics of SQL, including its purpose, real-world applications, and different categories of SQL commands such as DDL, DML, DQL, DCL, and TCL. Students will learn the basic syntax of SQL statements with practical examples, such as using SELECT, CREATE TABLE, and INSERT INTO commands. By the end of the session, learners will be able to write simple queries to retrieve and manipulate data from a database, setting the stage for more advanced topics in subsequent classes.