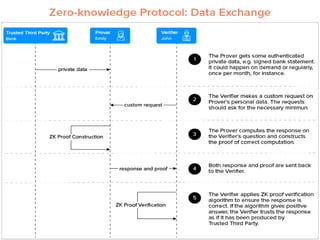
Zero-knowledge proof is an encryption method that allows one party to prove knowledge of a statement without revealing the information itself, introduced by MIT researchers in the 1980s. It requires interactive input from a verifier and has properties of completeness, soundness, and zero-knowledge. Current real-life applications of zero-knowledge proofs include platforms like Zcash and innovations by banks like ING, but adoption in blockchain is still slow due to various challenges.