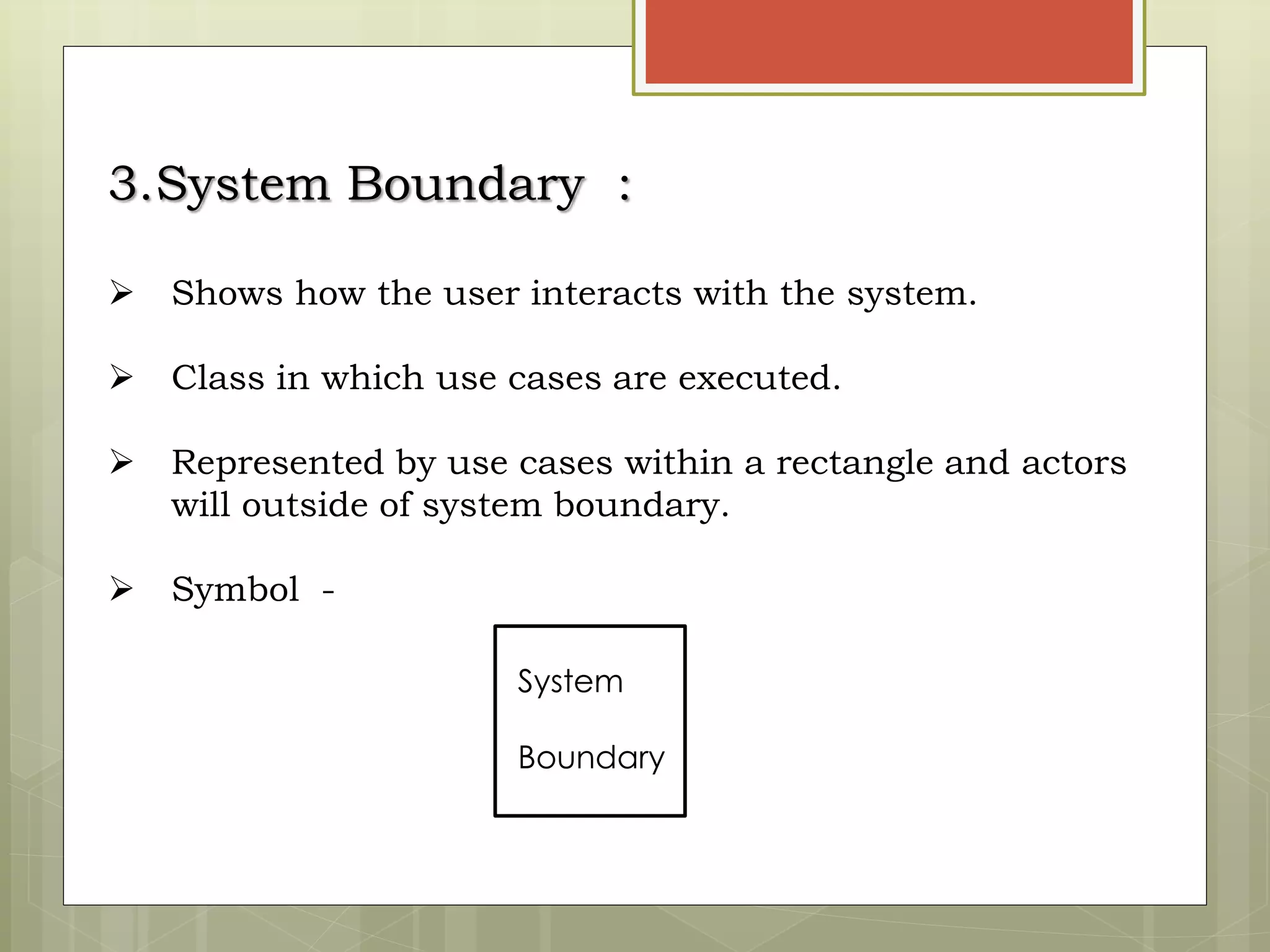
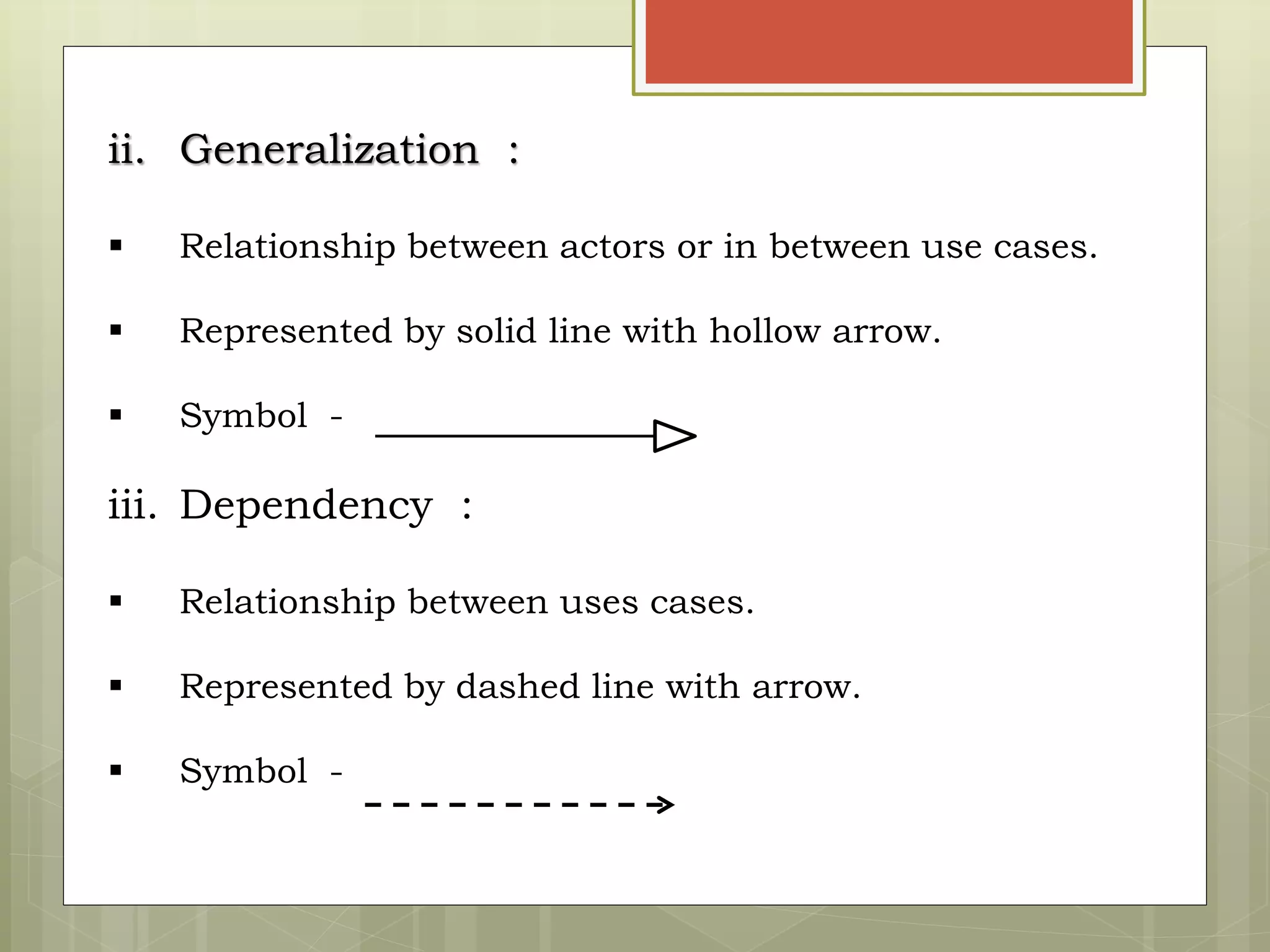
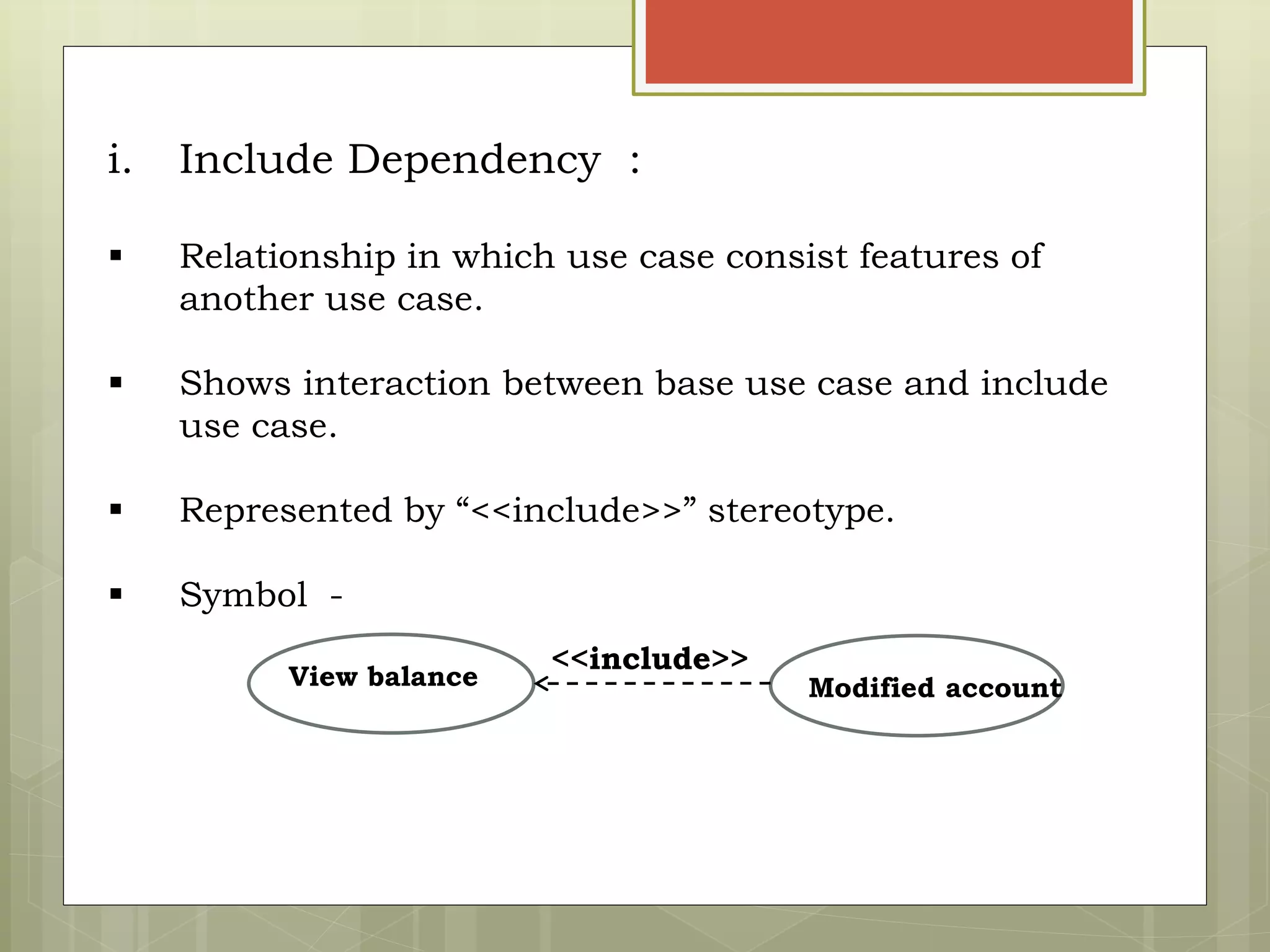
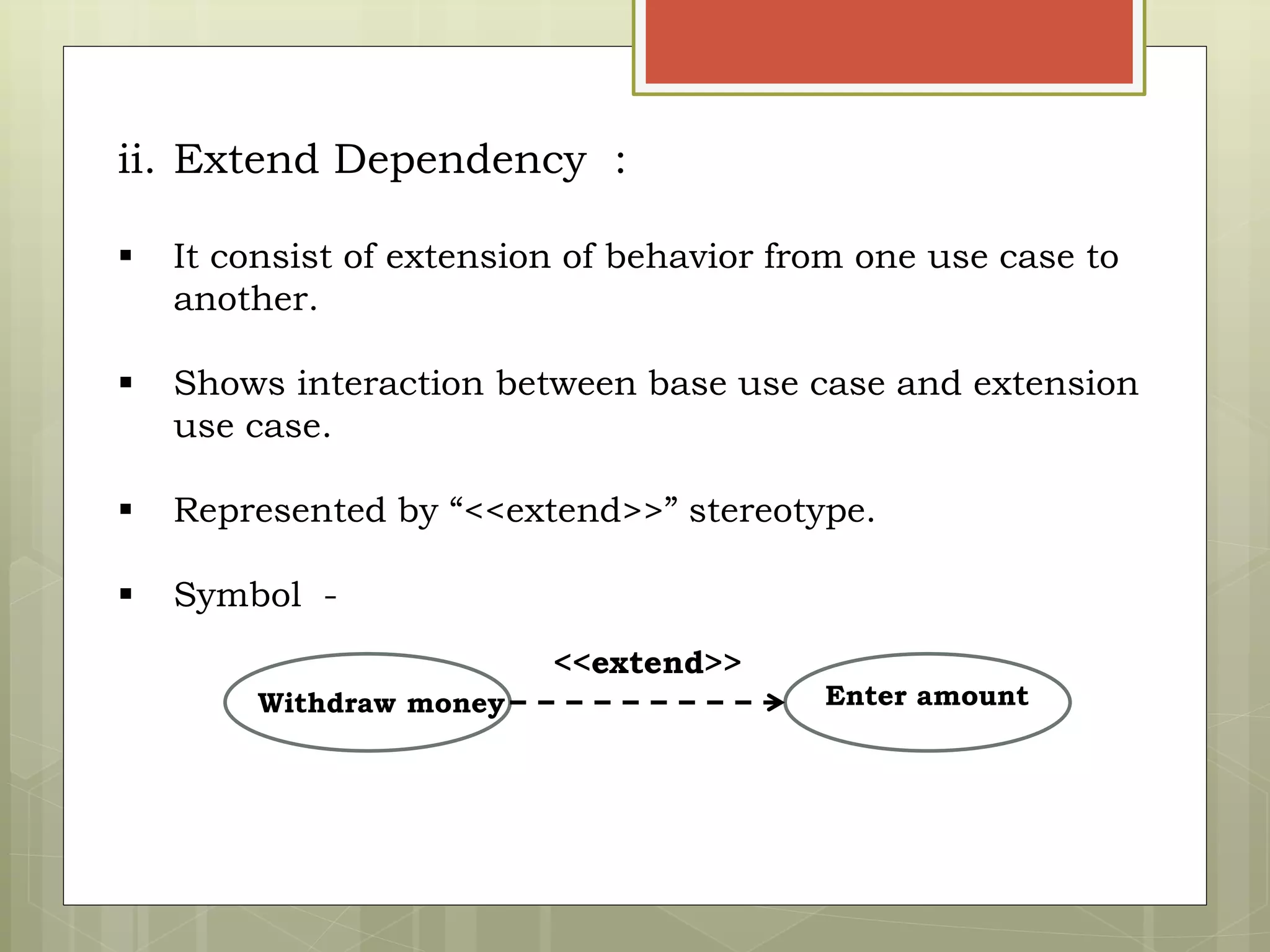
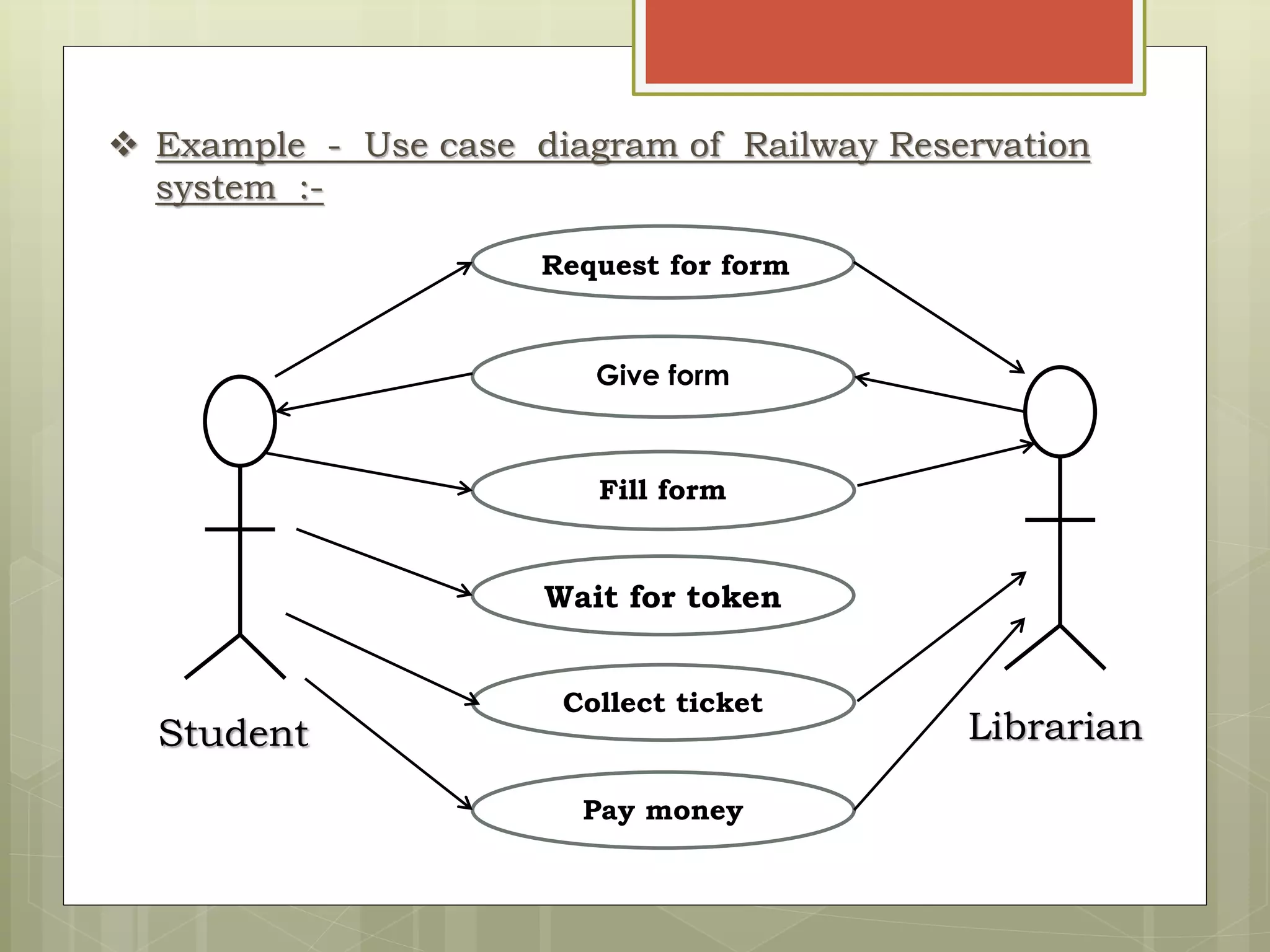
This document defines and explains the key elements of a use case diagram including actors, use cases, the system boundary, and communication lines. It provides examples of primary and secondary actors, describes use cases as sequences of actions performed by the system, and explains different types of relationships between use cases such as include and extend dependencies. Finally, it includes an example use case diagram for a railway reservation system to demonstrate these concepts.