This document provides an overview of Android including:
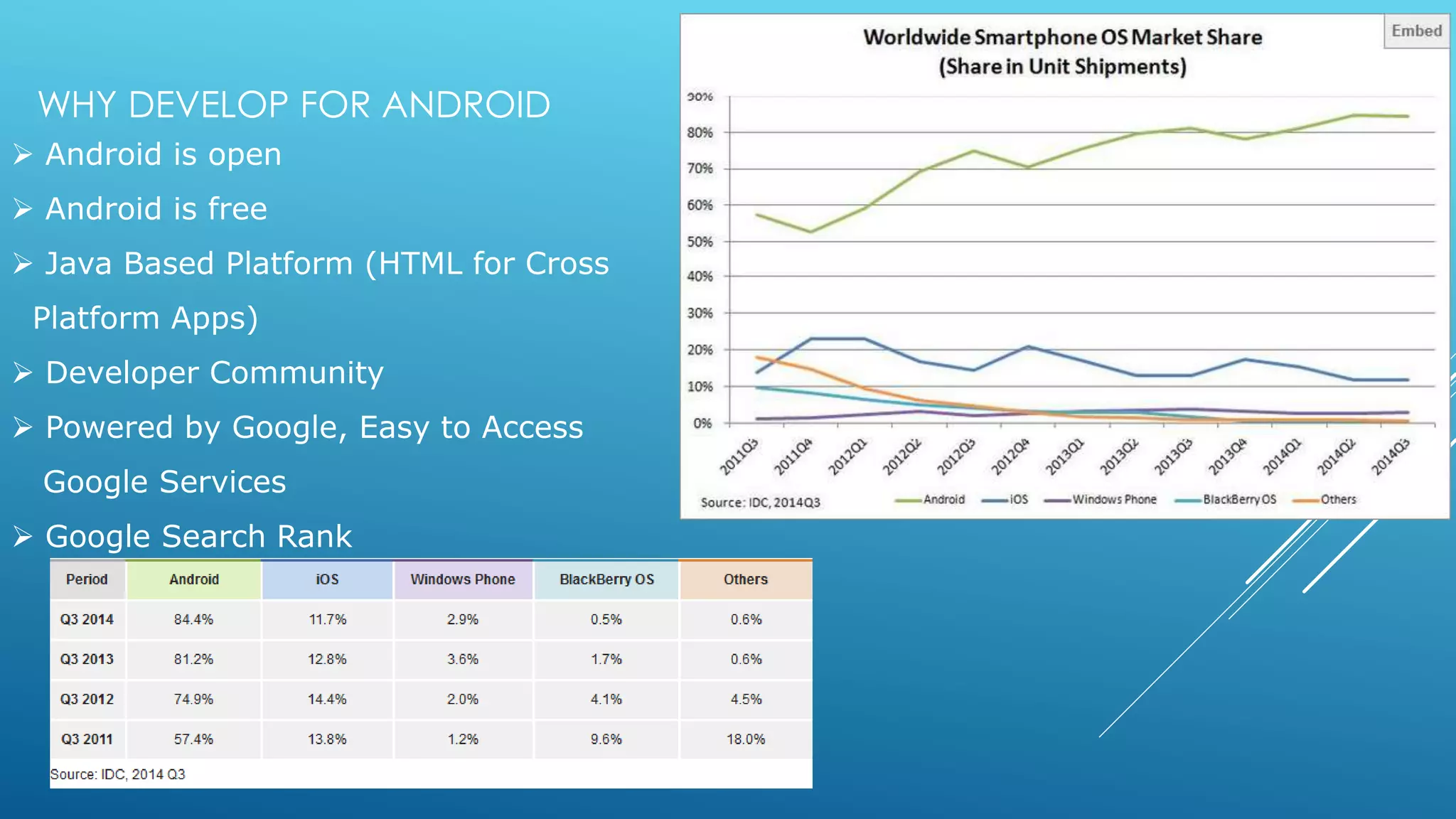
- Android's history beginning in 2005 when Google acquired Android Inc. and the Open Handset Alliance was announced in 2007.
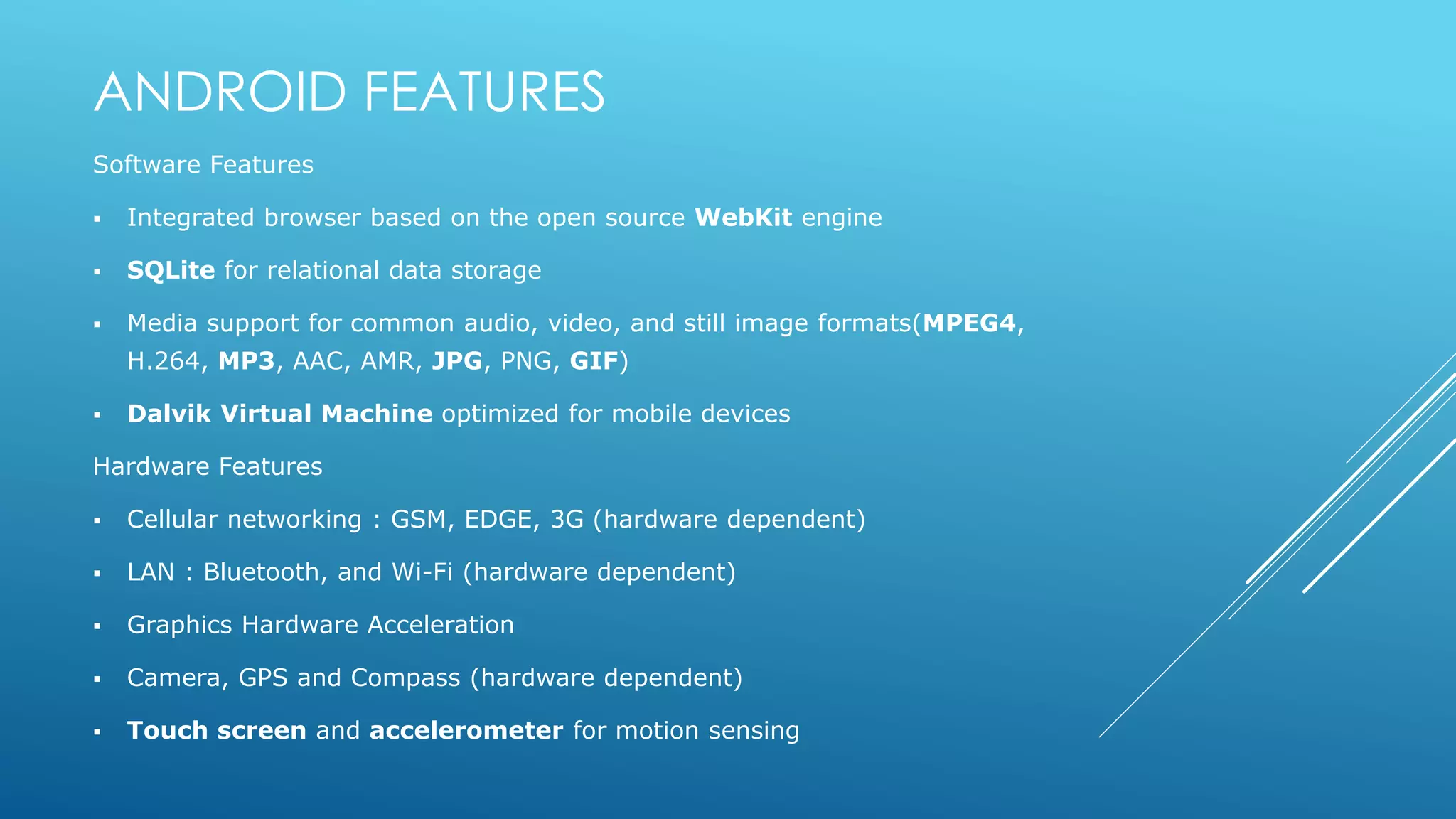
- Android's key features including an integrated browser, SQLite database, media support, and hardware features like cellular networking and cameras that vary by device.
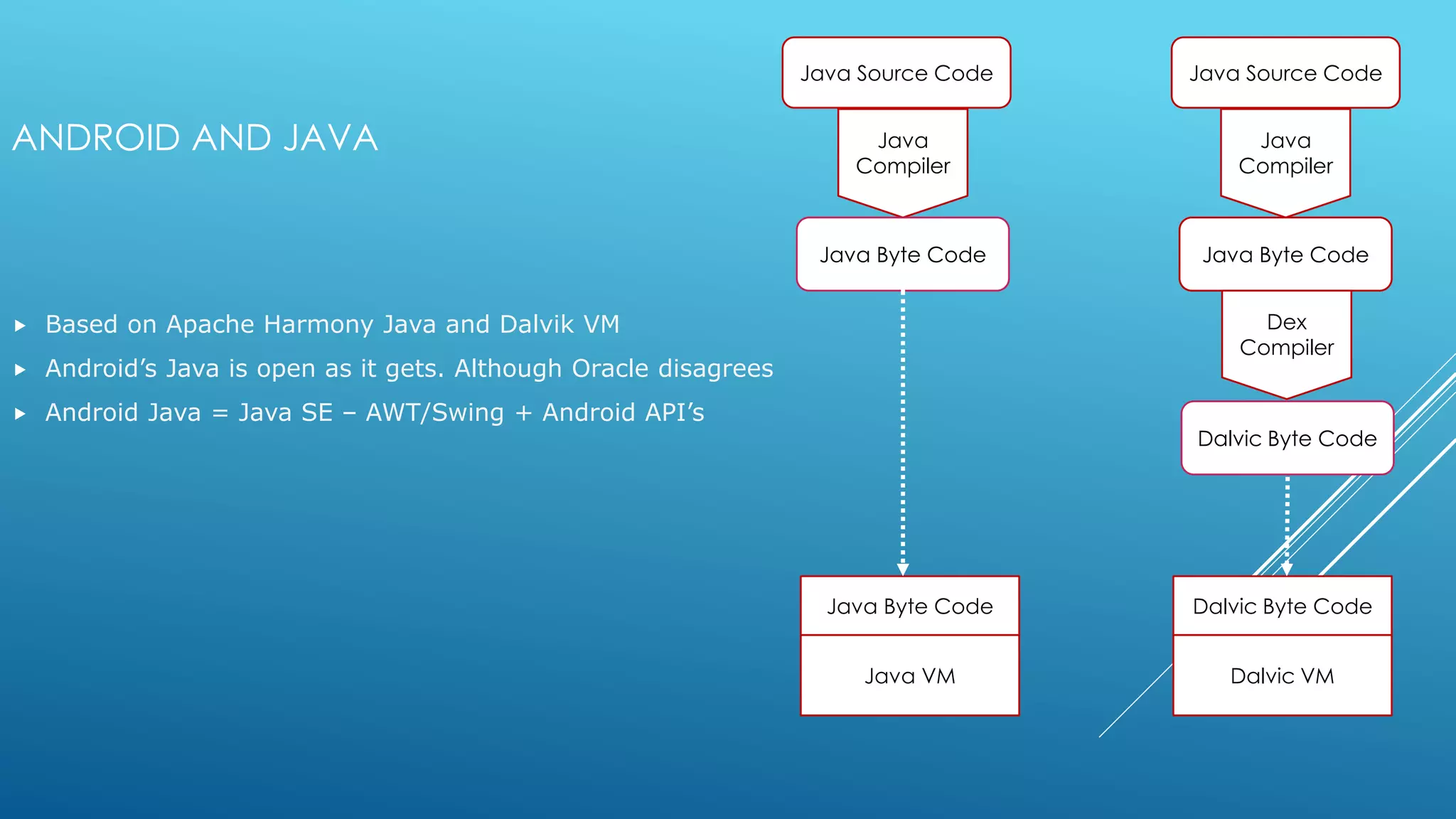
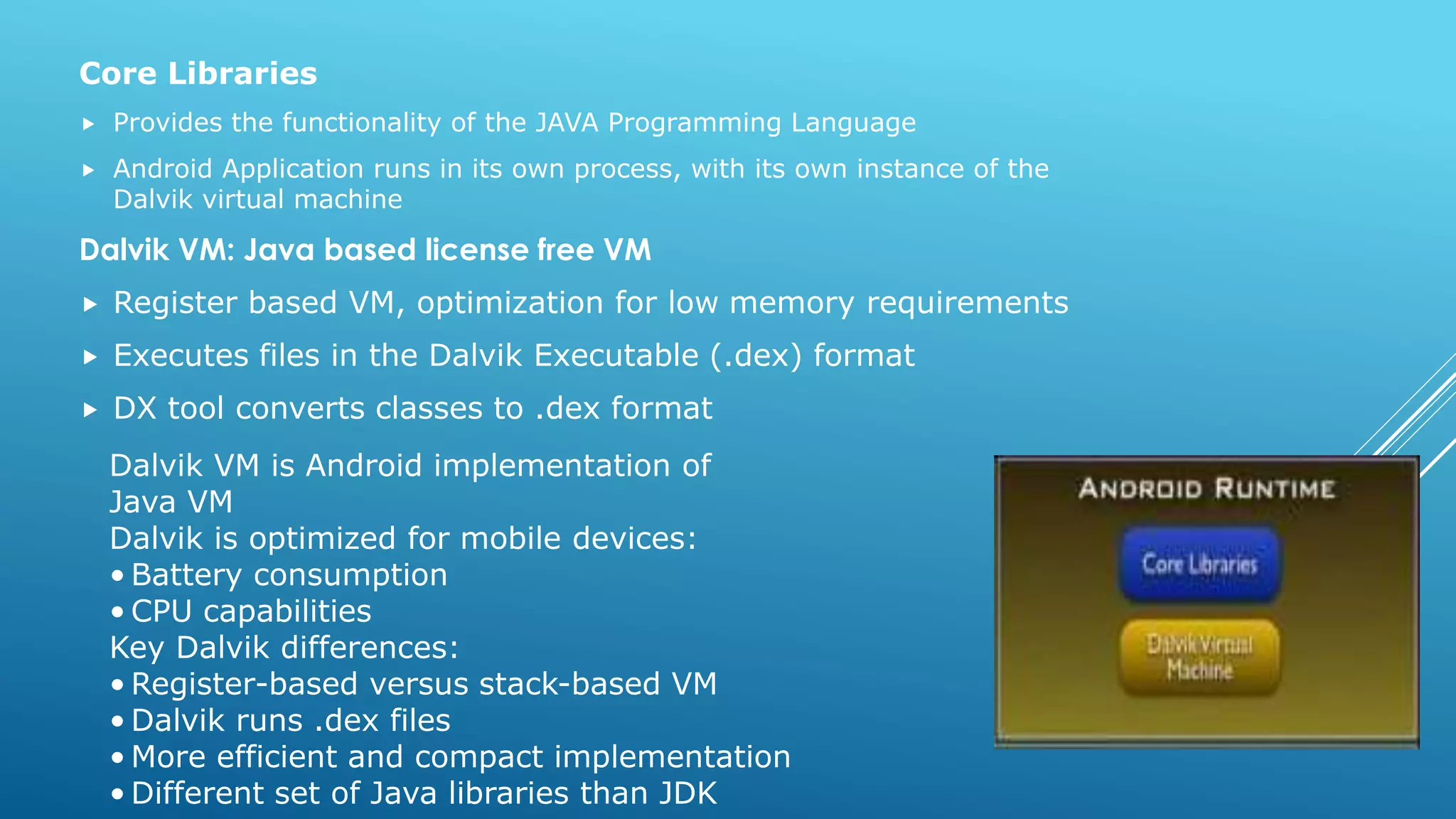
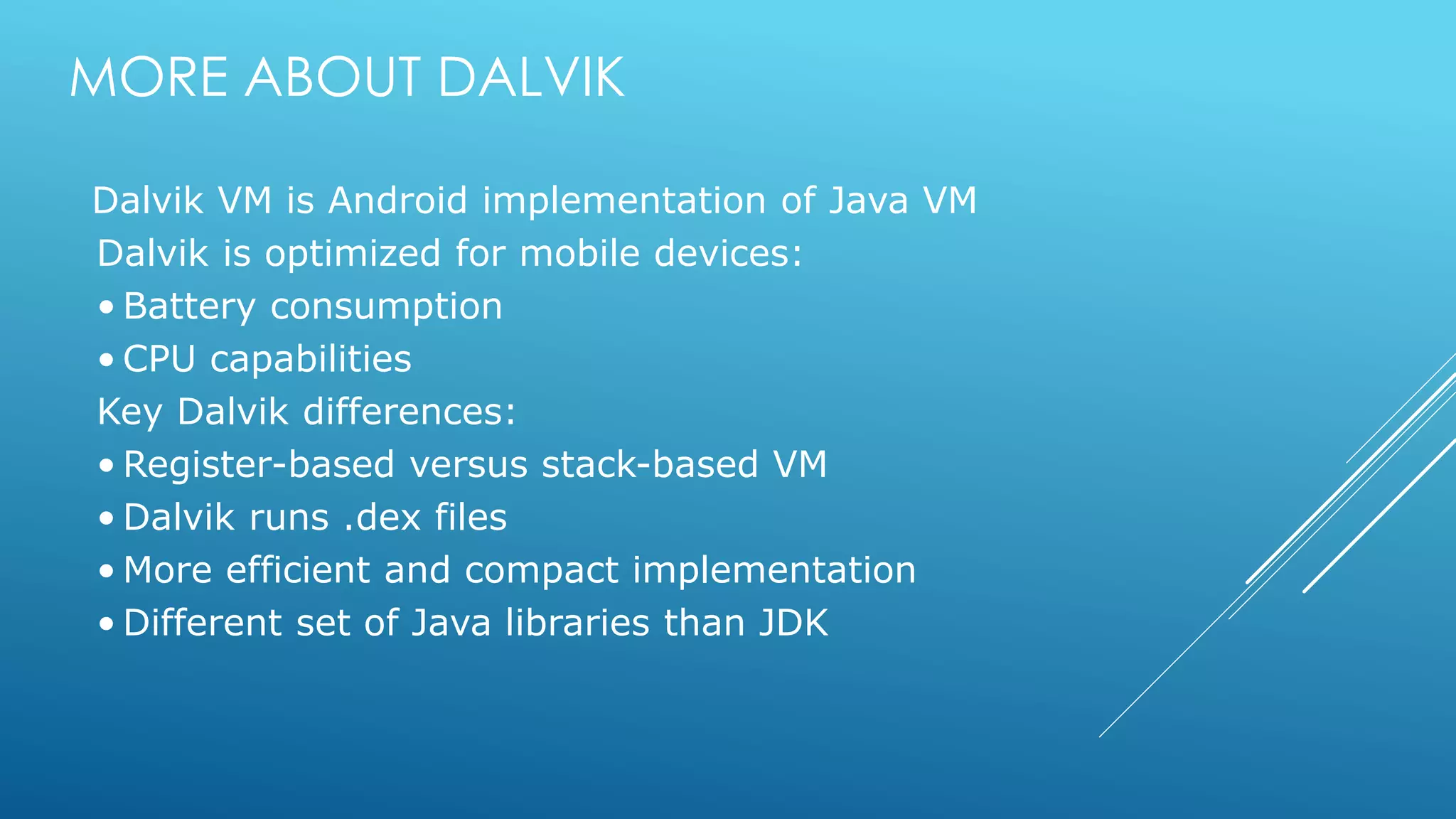
- Android is based on the Java programming language and uses the Dalvik virtual machine optimized for mobile devices.
- The Android software stack includes core libraries providing functionality like the webkit engine, SQLite, OpenGL, and more.
- Prior experience with Java and XML is recommended to develop for the Android platform.