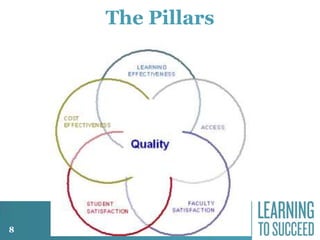
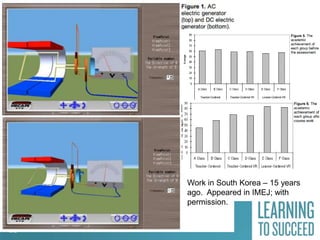
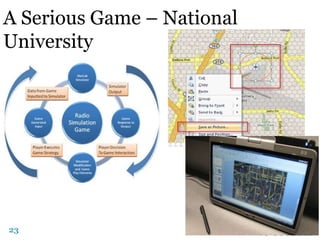
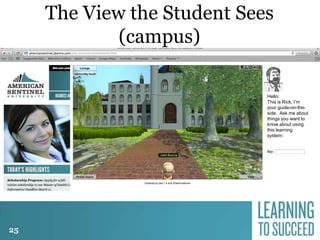
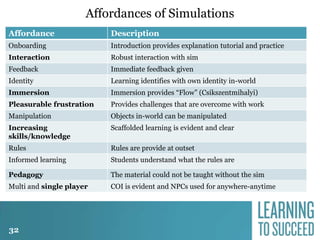
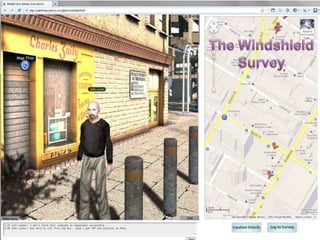
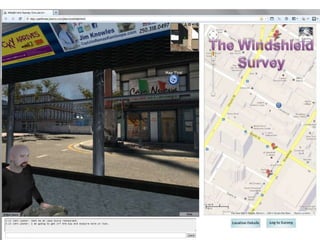
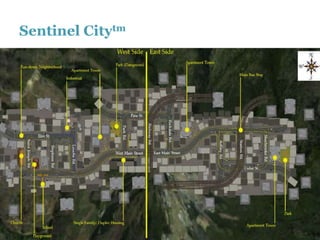
The document discusses the history and future of online education. It begins with a brief overview of the speaker's background and experience in online learning. It then provides a high-level history of online education, noting that online learning started in the 1990s with asynchronous learning networks and grew through research and organizations like the Sloan Consortium. The document outlines concerns about a "quiet crisis" in online education and discusses changing dimensions in online learning like new technologies, widespread acceptance, and increased competition. It advocates for a focus on affordable, high-quality online education and learning through simulations, videos, mobile access, and competency-based models.