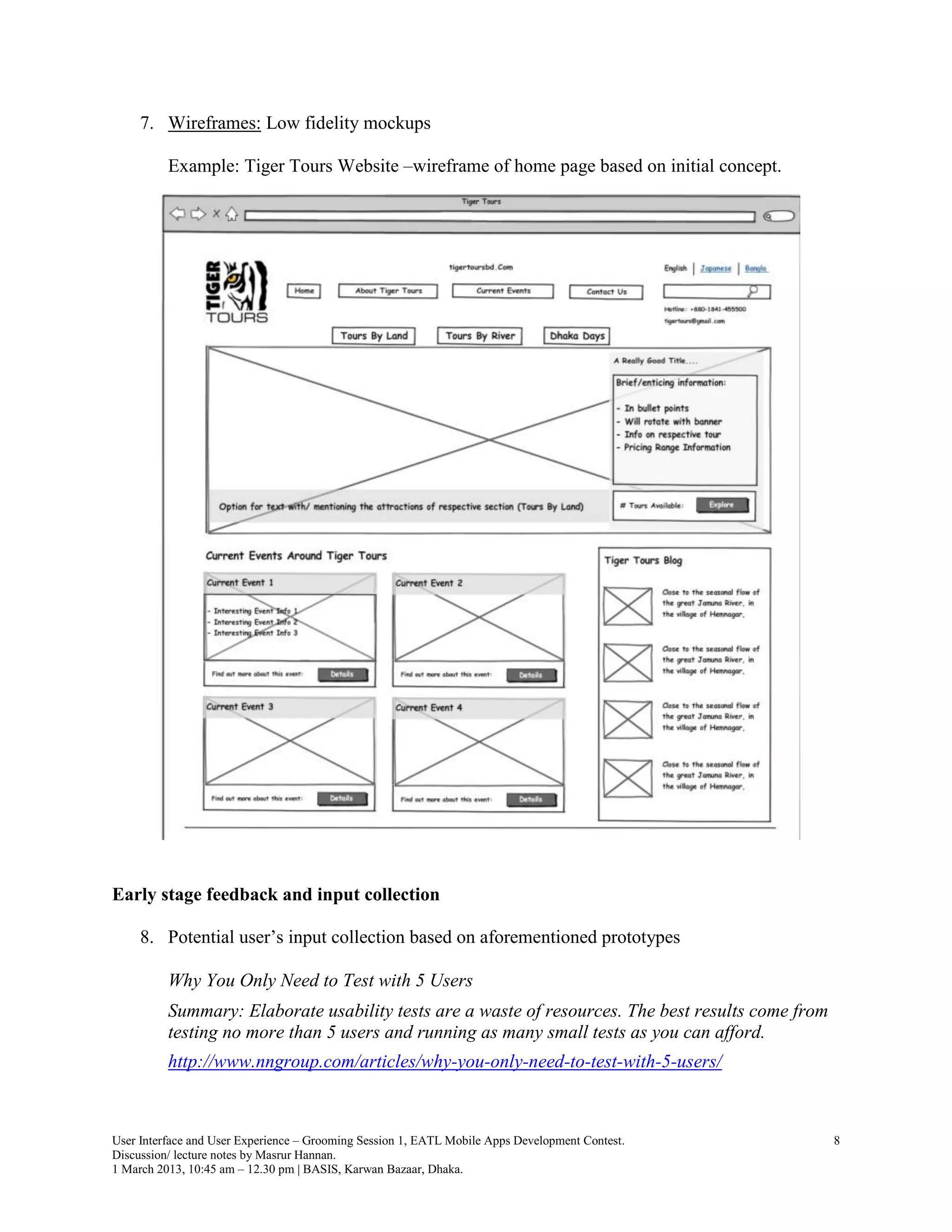
The document outlines a grooming session for user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design related to a mobile apps development contest, conducted by industry professionals. Key principles discussed include human-computer interaction, usability design, and various methodologies for designing effective user experiences. The session emphasized the importance of user research, iterative design, and evaluation techniques to ensure products are user-friendly and meet user needs.






![My approach matches and is somewhat based on Jesse James Garrett’s FIVE planes of user
experience design. However, considering local (Bangladesh) context – I have tried some
simplification.
Initial Research
1. Information ecology: identifying the context, content and users
Goals, funding, politics,
culture, technology,
resources, constraints….
Data types, volumes, Audience, tasks, needs,
content objects, existing information seeking
structures…. behavior, experience….
Figure 1.1: Three inter-dependent components of an information ecology
[Information Architecture for the World Wide Web: Designing Large-Scale Web Sites, 2006, page 25]
Mobile app context: Anticipated environment, time of use, devices of users
Ultimate goal: recognizing the Real Challenge and Opportunity
2. Needfinding exercises: user (potential and existing) interviews, card sorting exercises
amongst small segment. Some quick approaches:
Open, unbiased questions: What values and goals do people have?
Story of experiences on task and need related issues
What do people do now – learn from Observations
https://class.coursera.org/hci/lecture/preview : Week 1 – Needfinding
Concept finalization
3. Inspiration research: review similar existing products and services: local and global, big
and small
4. Ideation and concept finalization: based on information ecology, needfinding exercises
and inspiration research
User Interface and User Experience – Grooming Session 1, EATL Mobile Apps Development Contest. 6
Discussion/ lecture notes by Masrur Hannan.
1 March 2013, 10:45 am – 12.30 pm | BASIS, Karwan Bazaar, Dhaka.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ui-uxlecturenotes-masrurhannan-eatlappcontestgroomingsession-1march2013atbasis-130303020422-phpapp02/75/User-Experience-UX-design-discussion-notes-1-EATL-mobile-app-dev-contest-grooming-session-1-1st-march-2013-at-BASIS-7-2048.jpg)