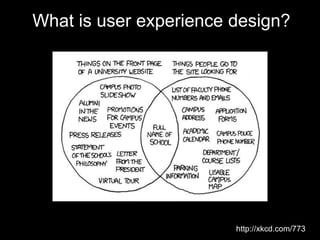
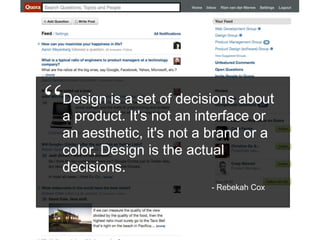
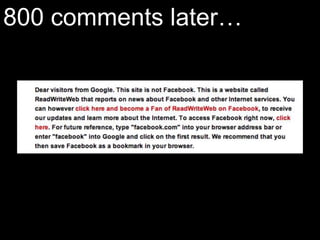
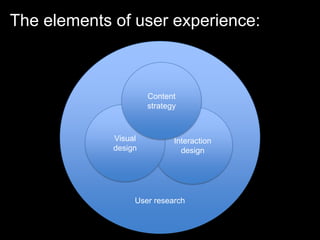
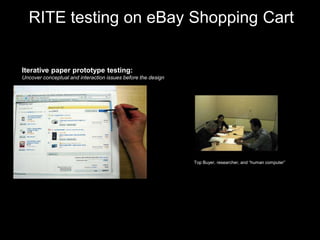
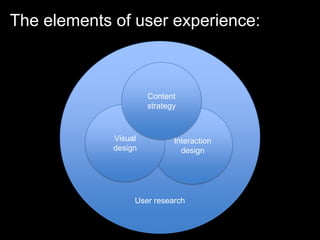
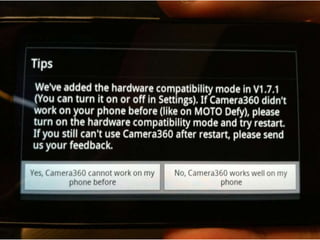
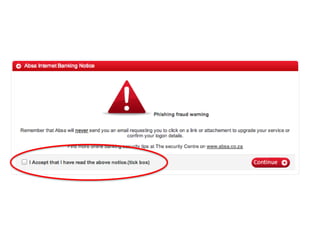
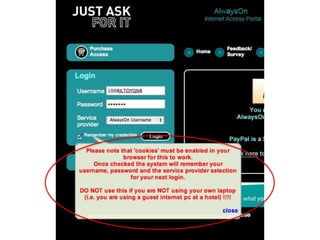
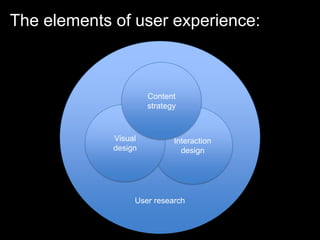
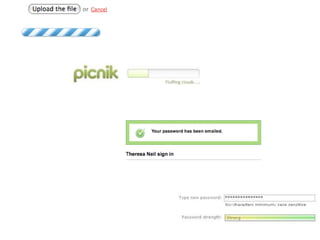
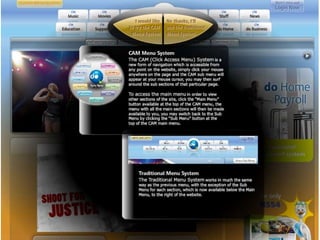
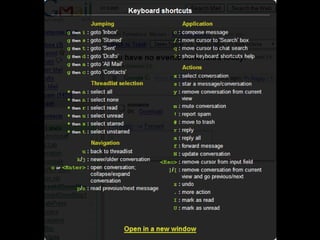
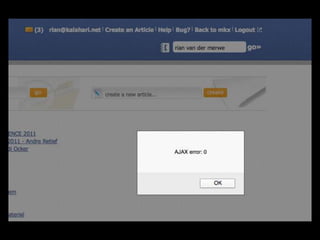
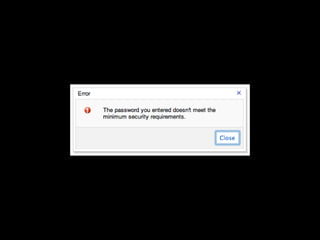
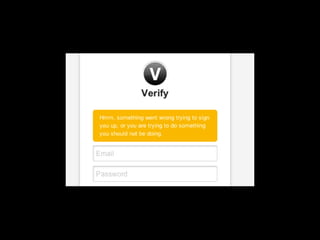
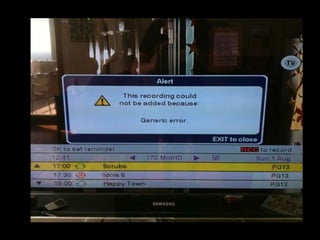
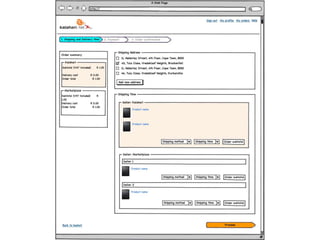
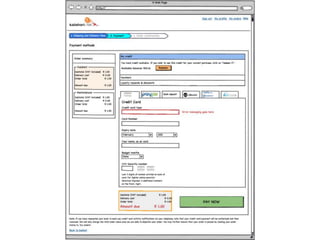
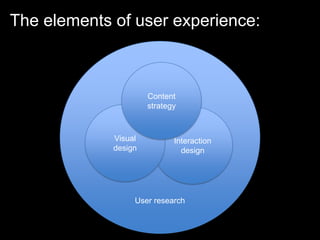
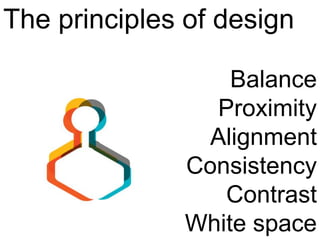
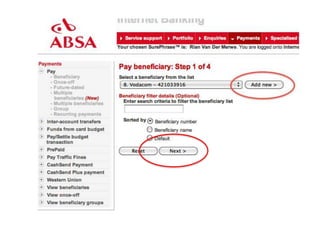
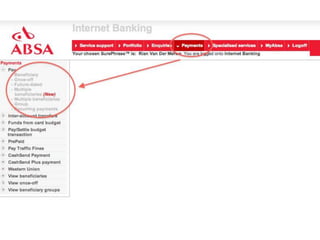
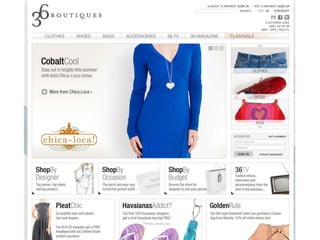
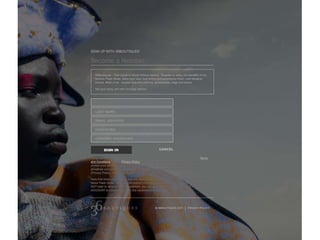
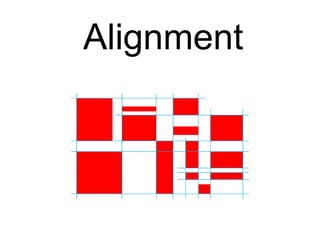
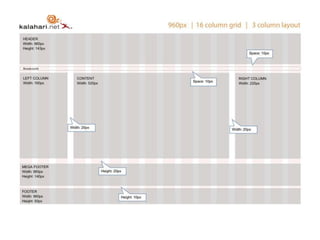
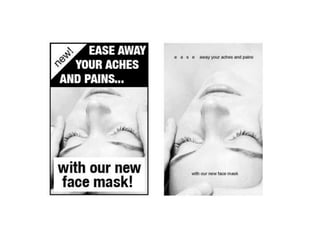
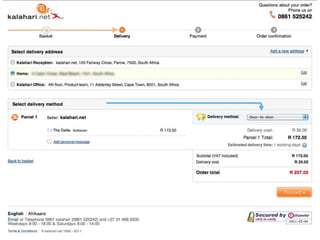
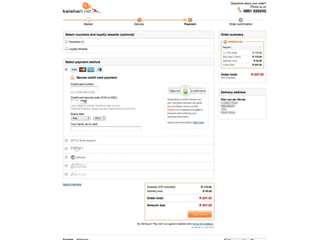
User experience design (UXD) focuses on enhancing user satisfaction by improving the usability, accessibility, and pleasure derived from interaction with products and services. It integrates various disciplines, including engineering, marketing, and design, to meet user needs efficiently and effectively. Essential elements of UXD include user research, content strategy, visual design, and interaction design, all aimed at creating seamless and enjoyable user experiences.