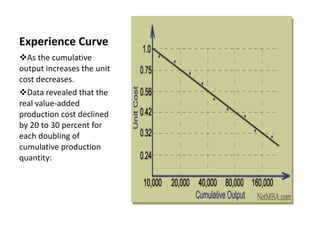
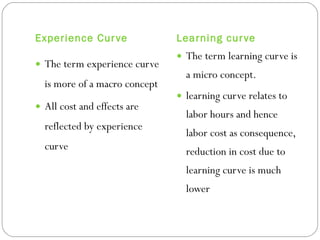
The document discusses the concept of an experience curve, which shows that the real production cost of a product declines by 20-30% for every doubling of cumulative production quantity. It notes that experience curves and learning curves are sometimes used interchangeably but have different meanings, with experience curves reflecting all costs at a macro level and learning curves specifically relating to labor hours and costs. The document also outlines some strategic, internal, and external uses of experience curves, such as determining pricing, scheduling, and estimating costs.