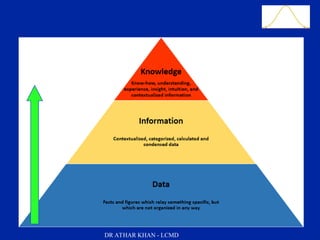
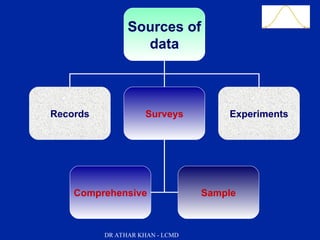
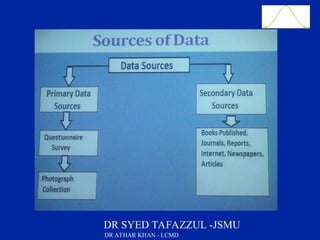
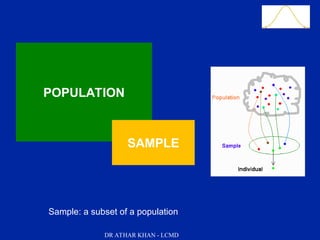
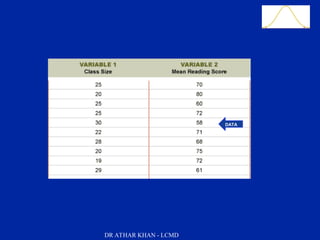
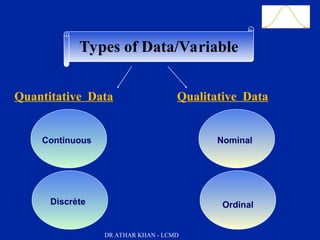
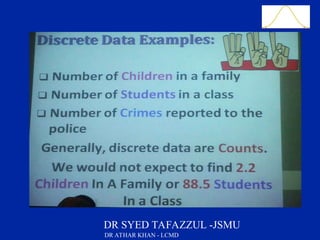
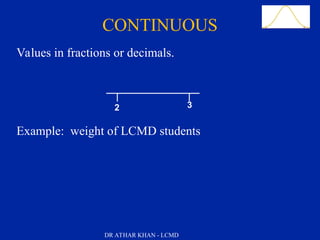
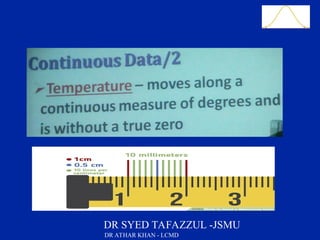
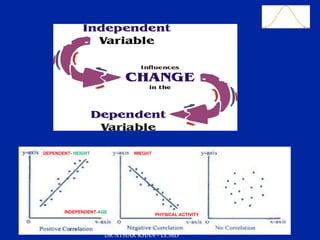
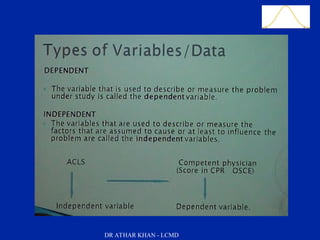
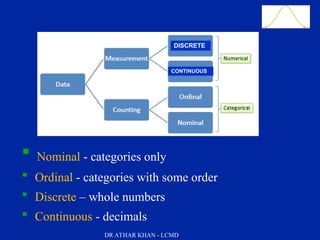
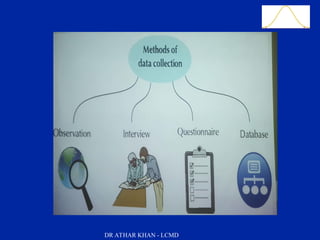
This document is a slide presentation about data and its types given by Dr. Athar Khan. The presentation defines different types of data including nominal, ordinal, discrete, and continuous data. It provides examples of each type of data and discusses how quantitative data can be transformed into qualitative data. The objectives are to classify data, describe how different types of data are measured, and discuss techniques for data collection.