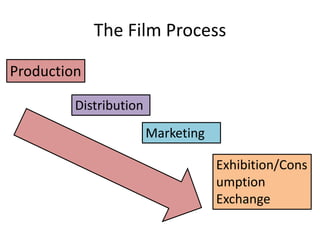
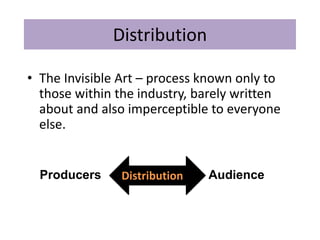
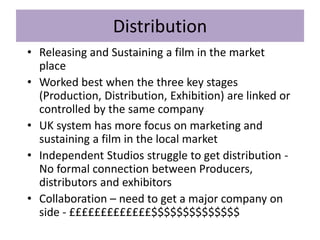
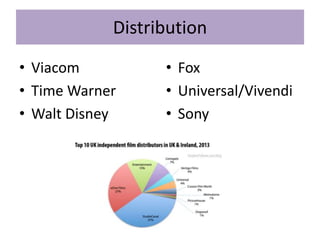
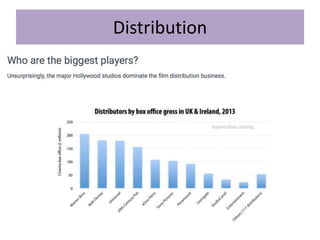
The key stages of the film process are production, distribution, marketing, and exhibition/consumption.
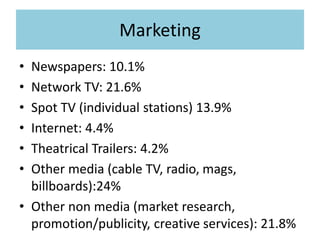
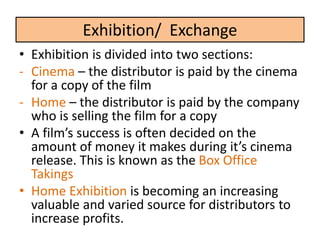
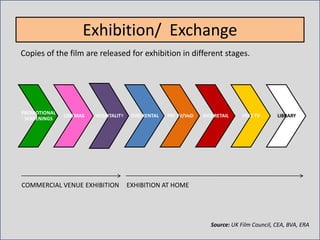
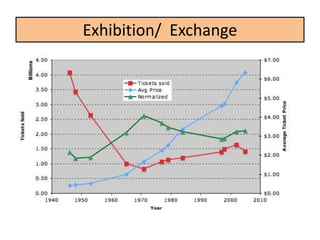
During production, a production company creates the film through pre-production, production, and post-production. Distribution involves releasing and sustaining the film in the marketplace through techniques like wide release, platform release, and limited release. Marketing employs strategies such as trailers, advertisements, publicity events, and product tie-ins to promote the film. Finally, exhibition makes the film experience available to audiences through cinema screenings and home media like DVDs, streaming, and TV broadcasts.