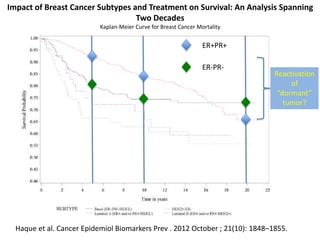
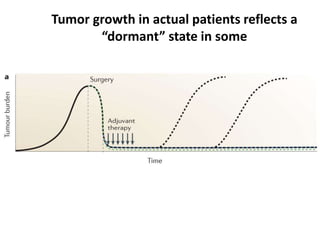
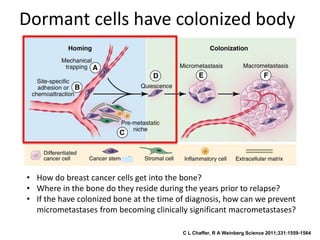
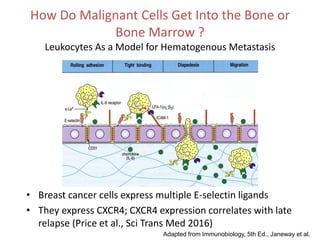
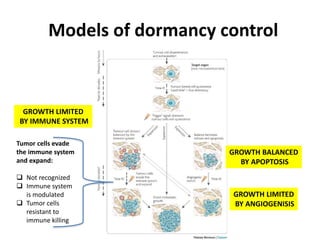
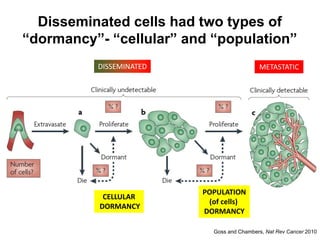
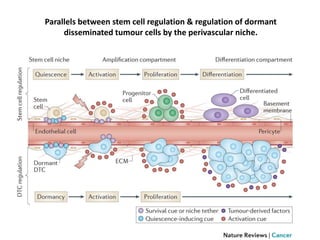
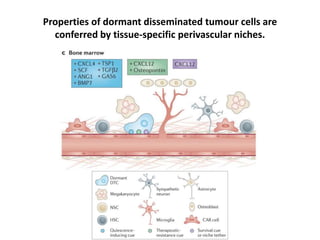
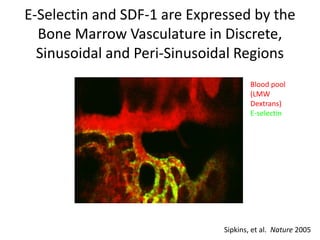
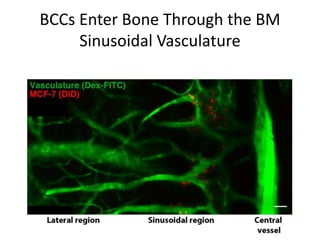
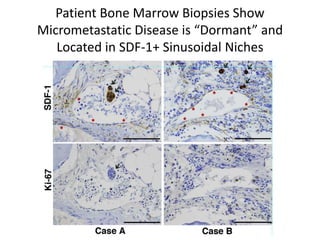
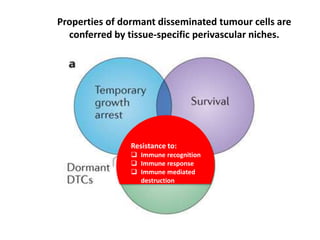
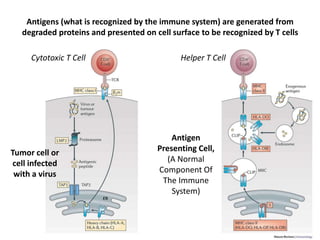
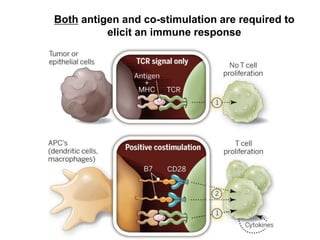
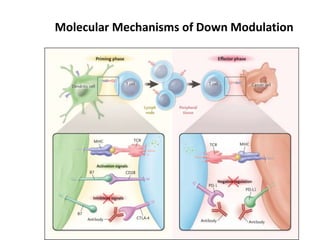
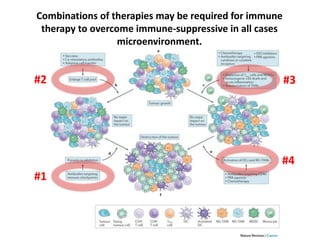
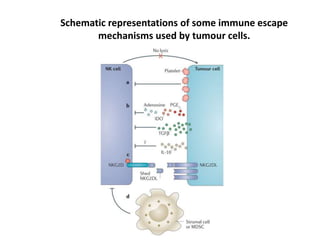
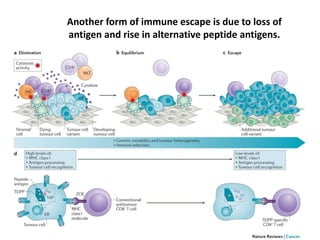
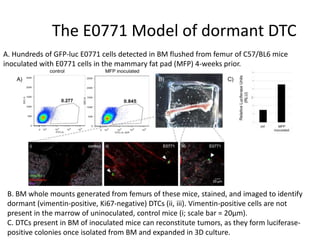
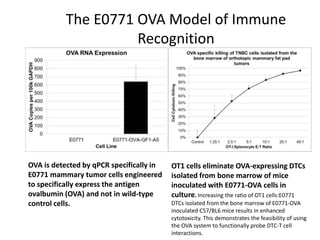
The document discusses tumor dormancy in breast cancer, focusing on how dormant tumor cells colonize the bone and evade immune detection over time. It explores the mechanisms behind the immune escape of disseminated tumor cells (DTCs) and the importance of their microenvironment for potential therapies. The research aims to understand DTC behavior to develop non-toxic strategies to prevent their progression into clinically significant metastasis.