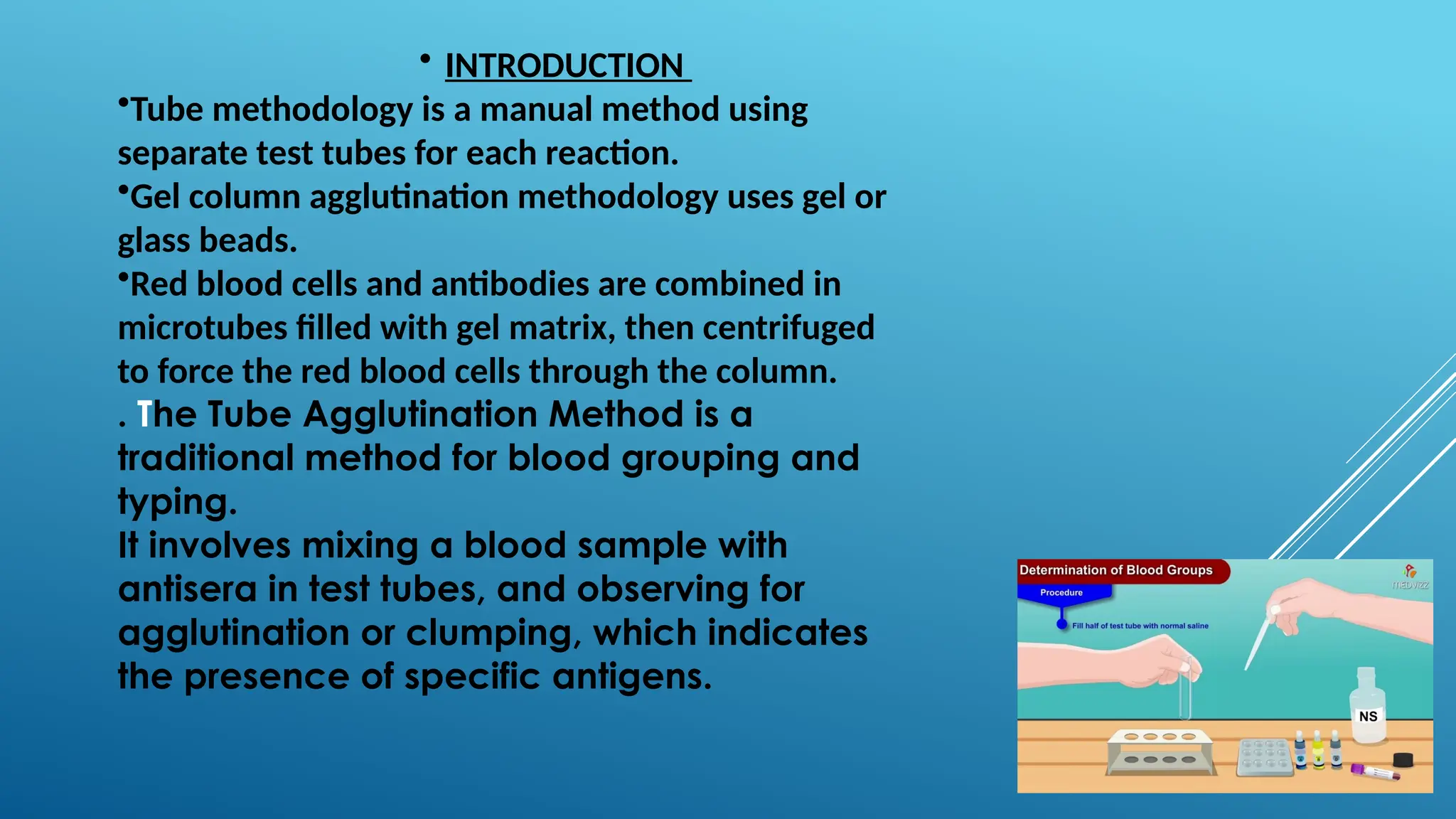
The document outlines two blood typing methodologies: the traditional tube method and the gel column agglutination method. The tube method, which uses test tubes for mixing blood samples with antisera, is more reliable and sensitive for determining blood groups compared to the slide method, requiring specific reagents and a centrifuge to observe agglutination. The document provides a detailed procedure for conducting the tube method, including preparation of reagents and reading results to interpret blood types.