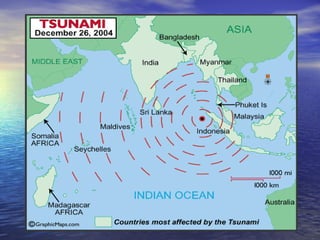
The 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake occurred on December 26, 2004 off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia with a magnitude of 9.3. It triggered a series of devastating tsunamis that affected countries around the Indian Ocean. Over 225,000 people were killed in 11 countries, making it one of the deadliest natural disasters in history. Indonesia, Sri Lanka, India, and Thailand were the hardest hit. The earthquake generated tsunami waves as high as 30 meters that caused widespread damage when they reached coastal areas.