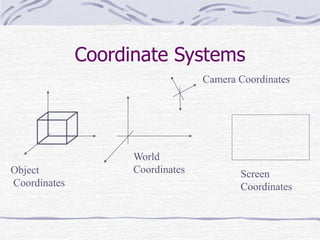
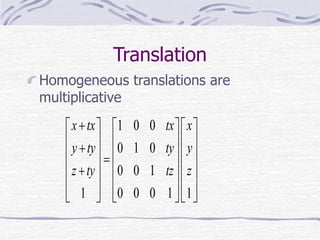
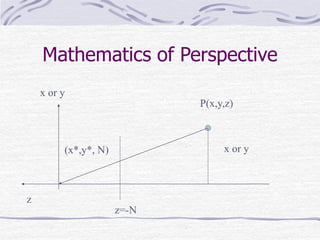
This document discusses computer graphics and the role of linear algebra in creating 2D images from 3D mathematical models. It explains that computer graphics uses transformations between different coordinate systems, such as object coordinates, world coordinates, camera coordinates, and screen coordinates, to render 3D scenes. These coordinate transformations involve affine transformations like rotation, translation, and scaling, which can be represented by homogeneous matrices. The document also describes how perspective projection is achieved through multiplication of points by a perspective matrix to give the illusion of depth.