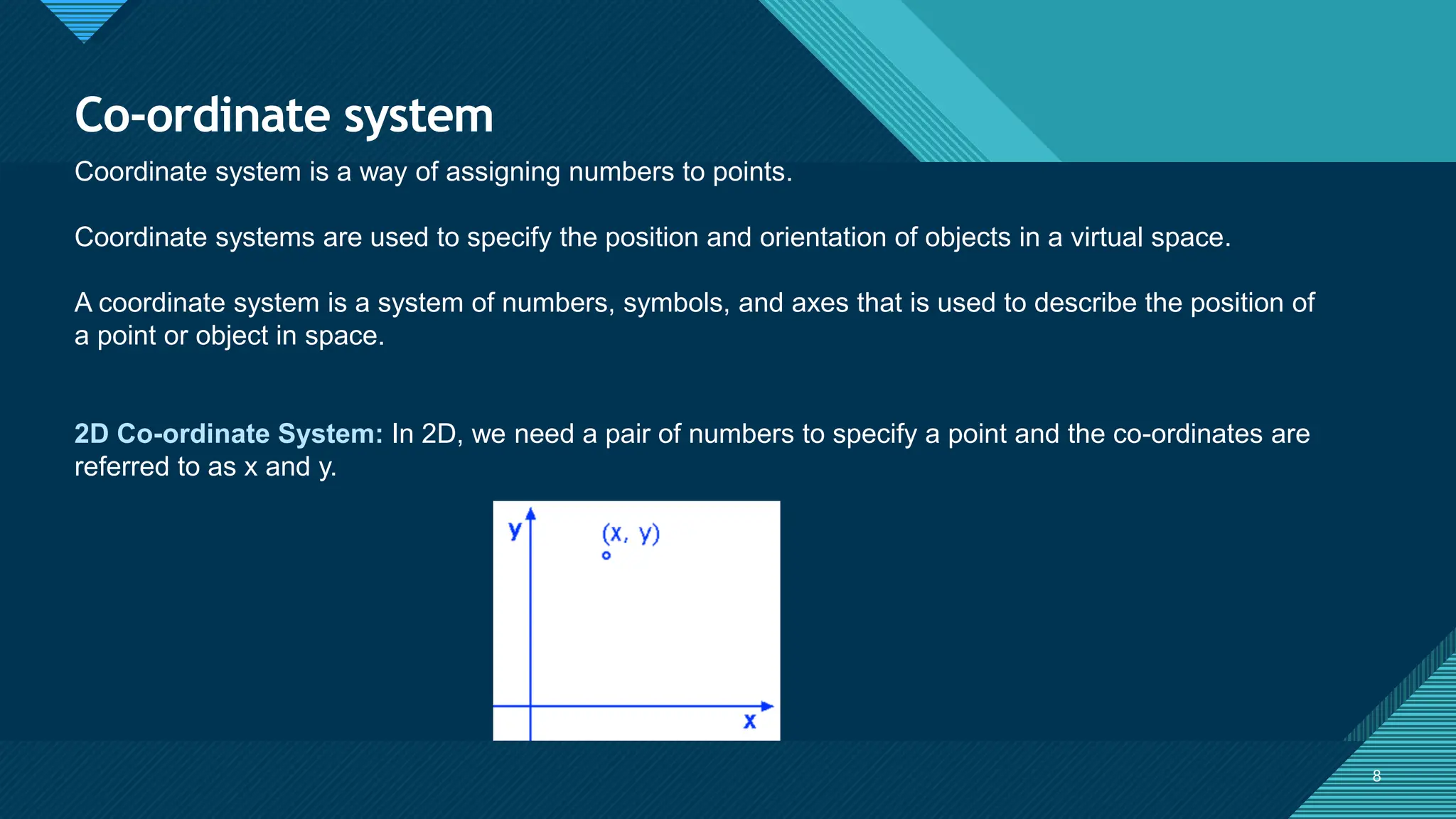
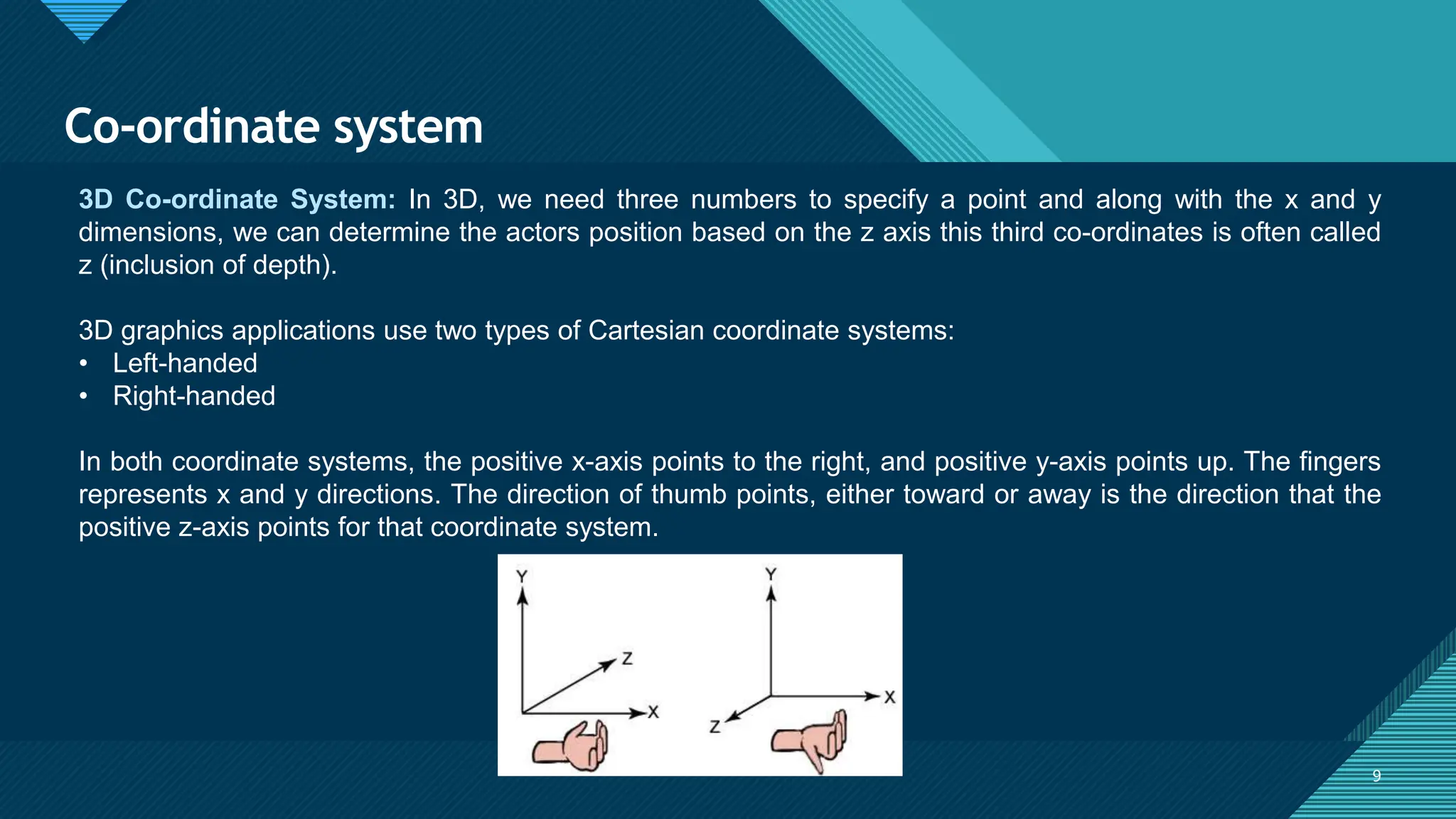
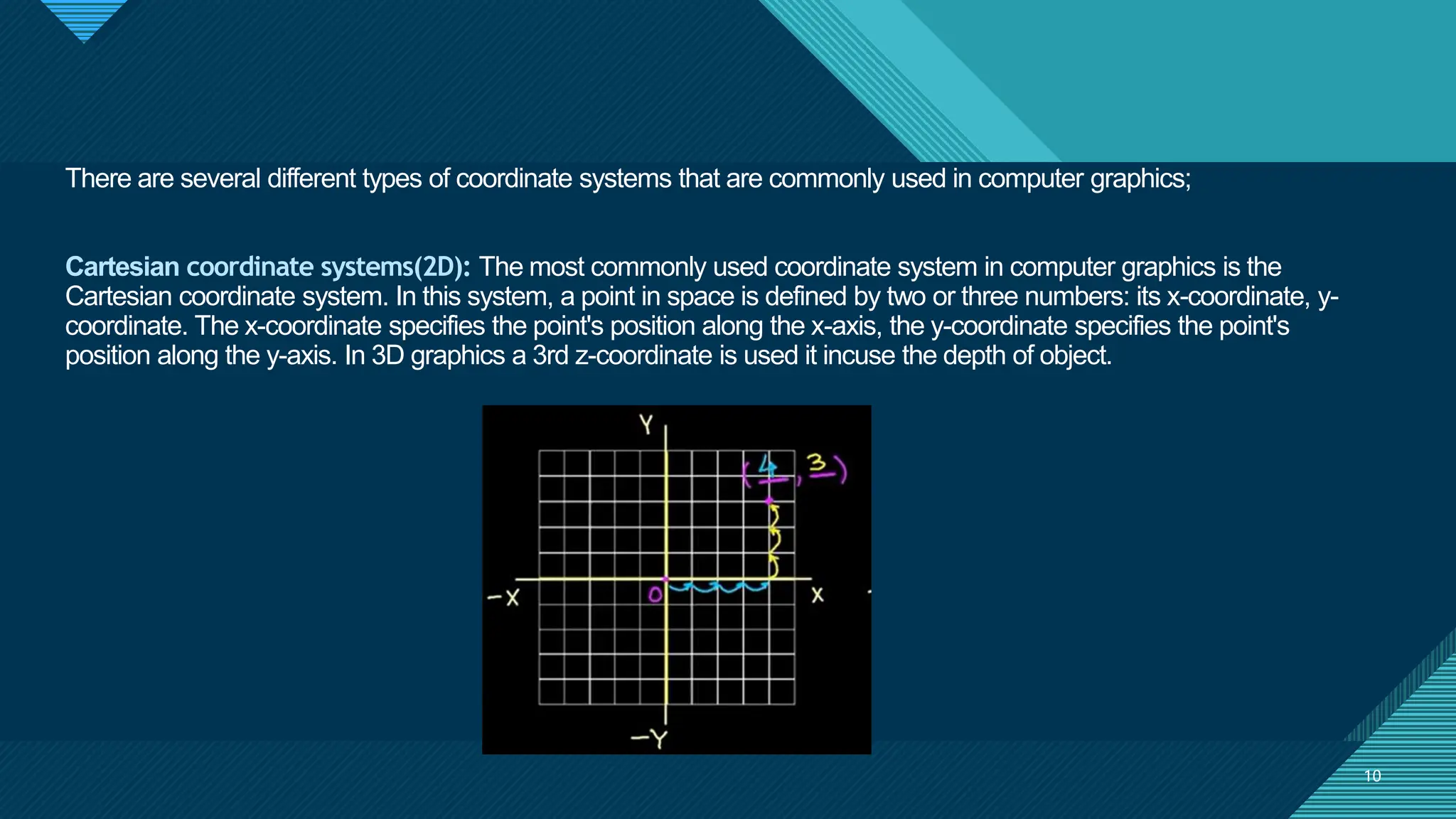
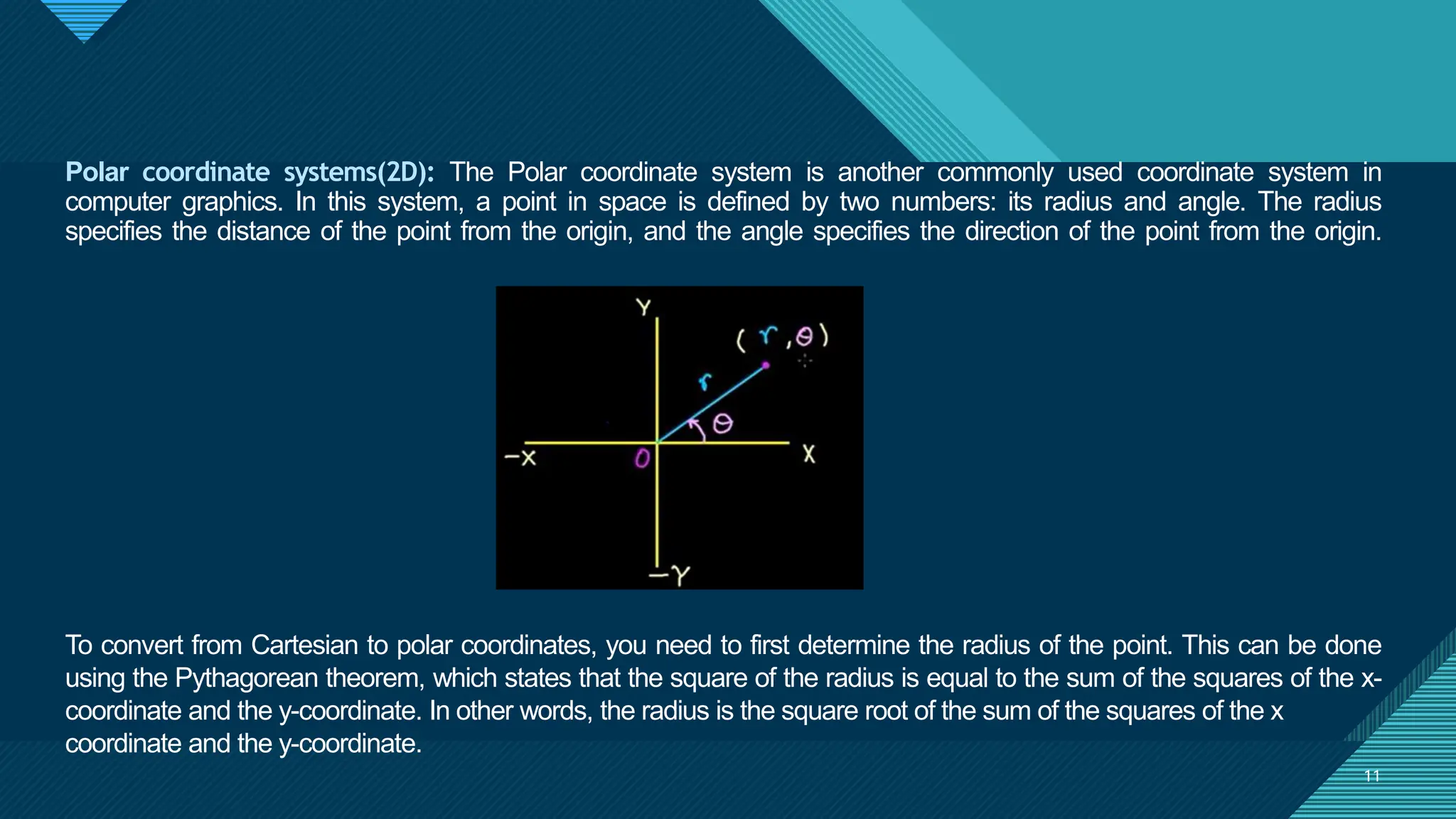
The document provides an overview of computer graphics, detailing its definition, applications, and basic terms such as images, objects, pixels, and resolutions. It discusses various coordinate systems used in 2D and 3D graphics, including Cartesian, polar, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Additionally, it covers file formats for graphics, their characteristics, and how they store digital images, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of formats like TIFF, BMP, JPEG, GIF, PNG, and PCX.