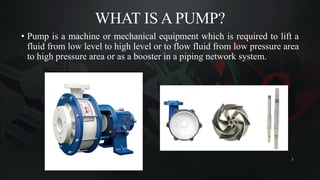
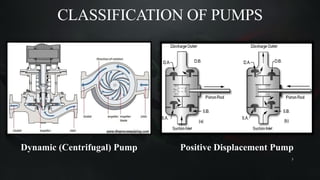
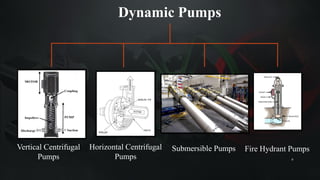
The document presents a mini project on troubleshooting pumps conducted by Om A. Zavare under the guidance of Prof. Harshada Jadhav at Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University. It covers what pumps are, their classifications, common types, troubleshooting techniques, and emphasizes the importance of systematic maintenance to prevent issues. The conclusion highlights the differences between centrifugal and reciprocating pumps regarding maintenance and application suitability.