This document proposes improvements to the query performance of triple stores that store RDF data in a relational database. It explores storing RDF triples in different orders in three tables and developing a query rewriting scheme. It also looks at optimizing the physical schema through graph clustering techniques that aim to reduce the number of disk accesses by grouping related triples closer together. The paper presents an implementation of these techniques over a million triples and shows they can yield significant performance benefits on complex queries.

![Triple-Triple RDF Store with Greedy Graph Based Grouping
Abstract platform, on which the state of the art is evaluated and its
Triple stores, based on relational databases, have progress towards the vision is assessed. Efficiently querying
received wide attention amongst database such Triple stores presents many challenges. Since RDF is
researchers and Semantic web enthusiasts. essentially a graph based data format, queries involve
Improving the query performance on very large multiple joins and become really slow when scaling to
RDF datasets is a challenging problem, which billion triples. If the 'Semantic Web' vision is to be
needs to be addressed for efficient implementation incorporated, then we require very fast query retrieval
of such triple stores. In this paper, we explore techniques since the long response times of these systems
promising approaches to address the problem. We would be unacceptable to a normal Internet user.
explore the possibility of storing the RDF triples
in different orders in three tables and develop a In this paper, we explore promising new ideas for Triple
query rewriting scheme for the same. We also look store implementation. In particular, we take the Triple-Triple
at optimization of the physical schema by graph idea (explained later) to its logical conclusion, and develop
clustering techniques that aim to bring related SPARQL to SQL query rewriting mechanisms for the same.
triples closer to each other on disk. We also We further enhance the Triple-Triple idea by introducing a
present experimental results from the computationally feasible clustering scheme that attempts to
implementation of the scheme over a million reduce the number of disk pages accessed, by moving related
triples. Our results show that our scheme can subjects/objects/properties closer to each other on disk. In
yield significant performance benefits on complex fact, this clustering scheme can be applied to any general
queries. indexing scheme for the Triple stores.
1. Introduction Section 2 details related work in this area. Section 3 presents
In the recent years, RDF[1] stores or Triple stores, that can various approaches that were considered for improving the
store information about (subject, property, object) triples of query performance. Section 4 presents a query rewriting
Ontologies, have received significant attention from database technique corresponding to the Triple-Triple idea. Section 5
researchers. Many efforts have been made to implement identifies and analyzes the benefits of grouping related
RDF stores using relational databases, and devising efficient triples in the same data block, to reduce the number of disk
schemes for accessing information from such stores. These IO operations. Section 6 presents the experimental results
efforts are focussed towards the larger vision of the and Section 7 concludes.
'Semantic Web'. To realize this vision, RDBMS based Triple
stores should be able to store , and query enormous amounts 2. Related Work
of triples that describe web pages on the Internet. [3] establishes the validity of using relational databases to
store and query ontologies. The paper extends SQL with a
The Billion Triple challenge [2] serves as a common set of ontology related operators, that can help obtain more](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-2-2048.jpg)
![pertinent results for ontology driven applications . At the spo, osp , pos, to help lookups based on each of the three
same time, the applications can also benefit from the elements in the Triple. However, it works with its own query
efficient storage and retrieval mechanisms in a RDBMS. language rather than using the general purpose SPARQL and
Simplistically, the baseline physical model for storing RDQL. Adabi et al [5] pursue an interesting path, arguing
ontologies in RDF format, using a RDBMS consists of two towards having a table for each property, with the associated
tables – Symbol table and a Triple table (refer figure 1). An subject and object that are related by that property. Such a
ontology describing the elements of the Web, contains URLs vertical partitioning approach tends to reduce the query
and URIs, which are long strings (lex field in SymbolTable). response time by incorporating fast linear merge joins, when
To avoid redundancy and wastage of disk space, these each table is sorted by the subject or object. However, such
elements are assigned unique integer identifiers (hash field in an approach inherently assumes that the queries are property
SymbolTable). This mapping from the element to the bound. A non-property bound query would require us to
identifiers is stored in the Symbol table. The Triples table query across all the tables. Hexastore [6] furthers the
has three columns – s (subject), p (property), o (object) – as multiple indexing approach taken by Kowari, by storing the
per RDF conventions and each tuple in the table represents a three elements of a triple, in six different orders. For
RDF triple. The table has a compound primary key on all the example, the spo ordering is stored as a sorted list of
three columns. Such a naive representation of the triples, subjects, with each subject pointing to another sorted list of
enables us to analyze clearly, where the benefits come from, properties defined for that subject. Each property in such
when evaluating much more sophisticated physical schema. sorted properties list points to a sorted list of objects defined
Figure 1 Baseline Physical model
for that subject, property pair. Thus, all joins can be
Many research efforts have attempted to propose alternate converted into fast linear merge joins. Hexastore occupies
physical schema and improved SPARQL to SQL query five times more space than a single triples table. However,
rewriting techniques, to improve query performance over the this is acceptable with the ever falling storage costs.
baseline model. This is based on the realization that the
baseline model can be used as a simple logical data model 3. Promising Directions
alone. Kowari metastore [4] proposes a RDF store based on We will now explore some promising directions in which we
AVL trees with each triple stored in three different orders – can further improvements from the baseline physical model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-3-2048.jpg)
![We will detail each idea and also present some motivation installation.
for pursuing [or abandoning] the idea. We also present
concrete and motivating examples for our arguments, using 3.2 Triple-Triple
MySql. One promising idea is to create three redundant copies of the
triples table with the compound primary keys – spo, pos,
3.1 Applicability of Spatial Indexes osp, such that each table has tuples sorted on subject ,
Potentially faster query execution times can be achieved if property and object in the order of occurrence in the primary
the joins between the triples are materialized in euclidean keys of the tables. Figure 2 presents the Triple-Triple
Figure 2 TripleTriple Physical model
space, in terms of fast minimum bounding rectangle (MBR) physical model. From here on, we will refer a table by its
operations. For example, simply storing each triple as a (s,p), primary key i.e. spo table will denote the triples table with
(p,o) line segment will materialize subject-subject joins as a (s,p,o) as the compound primary key. For the spo table, the
MBRcontains operation between the line segment triples will be clustered based on subjects and then clustered
(s,minhash) (s,maxhash) and the start point of each triple line on properties and then on objects, Such, a clustering ensures
segment. Minhash and maxhash are the minimum and that the triples are stored in sorted order in disk and hence
maximum integer ids from the symbol table. However, the fast linear merge joins can be applied. Note that this scheme
support for R-Tree operations remain limited in commercial requires only 3 times extra space than a triples table,
DBMS. MySql does not support spatial joins. Postgresql described in the baseline model. Hence, this approach is
does not support R-Trees. Only Oracle Enterprise, supports definitely promising. The primary compound index is also
spatial joins. We were unable to pursue this direction further, useful for any query that involves a prefix of the compound
due to non availability (or rather infeasibility) of an Oracle key. For example, spo table can answer select queries based](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-4-2048.jpg)
![on s, sp, spo columns, using the primary index. for each join operation – spo or pos or osp. Also, we must be
able to support selects on any combination of the three triple
Though MySql does not support merge joins [7], the idea elements. These decisions are listed in Table 1.
still would yield faster execution times since the sorted
nature of the data ensures efficient use of the index. Operation Method
Remember that, even with a secondary index, if the relevant
subject-subject join spo JOIN spo
tuples are spread across the table in different blocks, the end
performance could be worse than a table scan. For the property-property join pos JOIN pos
Semantic web vision, MySql plays a pivotal role since many object-object join osp JOIN osp
web sites are powered by MySql. This gives enough
subject-object join spo JOIN osp
motivation to continue exploring the idea using MySql. For
Subject select spo
example, a simple three table join on 25K triples, using
Triple-Triple yields very encouraging benefits over the Property select pos
baseline model. In Figure 3, Triples_s denotes spo table, Object select osp
Triples_p denotes the pos table and Triples_o denotes the
subject-property selects / spo [no need for a
osp table. Triples tables denotes the baseline triples table.
property-subject select separate pso]
Nodes table will denote the symbol table. All following
examples in the paper will use the same conventions to subject-object selects/ osp [no need for a
denote the corresponding tables. object-subject selects separate sop]
mysql> select * from Triples_s t_s, Object-property selects/ pos [no need for a
Triples_o t_o , Triples_p t_p where
property-object selects separate ops]
t_s.s = t_o.o and t_s.s = t_p.p;
Empty set (0.28 sec)
Subject-property-object Any table
mysql> select * from Triples t_1, select
Triples t_2, Triples t_3 where t_1.s =
t_2.o and t_1.s = t_3.p; Table 1 : Answering queries using Triple-Triple
Empty set (2 min 10.83 sec)
Hence, to our understanding, the three possible orderings –
Figure 3 Benefits of TripleTriple over baseline
spo, pos, osp – are sufficient for handling the same set of
queries that the Hexastore handles. The only missing piece in
In comparison to the Hexastore, the Triple-Triple stores only
building a complete Triple-Triple store is to define
three possible orderings of the elements in a triple. We
mechanisms to convert sparql to sql queries, using the
explore if these orderings are sufficient for answering the
appropriate tables for each triple. We explore this problem in
same range of queries answered by the Hexastore. The only
the next section.
possible joins are subject-subject joins, object-object joins,
property-property joins and subject-object joins, with all
3.3 Applicability of Secondary Indexes
joins being equijoins. Hence, mechanisms for using the
It is tempting to create secondary indexes on other columns ,
Triple-Triple should judiciously choose which table to use](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-5-2048.jpg)
![that do not form a prefix of the primary key of the triples is adopted. Since all joins of t1 are subject joins, we safely
table (both in the baseline and the Triple-Triple idea). For choose spo table for t1. Since all the joins involving t4 are
example, the spo table can have secondary indexes on po and subject joins, we choose spo table for t4. However, t3
o, to speed up the selects on those columns. However, initial presents a difficulty. For the t1,t3 join to be efficient , we
experiments showed no improvement in the query response need to use spo table for t3. For the t3,t4 join to be efficient,
times, since the bulk of the benefit was from the primary we need to pick the osp table for t3. Clearly, only one of
index or the values were split across multiple disk pages so these options is possible. In general, a sparql to sql compiler
that the secondary index did not make sense. For example, for the Triple-Triple has to make these hard decisions
there are relatively very few properties in the data, when dynamically during runtime. From our experiments, we
compared to subjects or objects. Hence, a secondary index noticed that the MySql optimizer (or any other DBMS) does
would not be beneficial here. Also, along the similar lines, not do a good job in choosing the right join order for the
secondary index on the lex field of the symbol table did not tables and substantial performance gains can be achieved by
yield significant benefits. Hence, we stick with the Triple- simply rewriting the query by explicitly specifying a join
Triple baseline model. order. These are hard search problems and thus, even in the
context of the Triple-Triple, the sparql compiler cannot be
4. Add-Join expected to do a very good job in optimizing the choice of
Converting SPARQL to a SQL query on the baseline is tables.
straight forward. When deciding which tables to use for each
triple in the Triple-Triple store, we can be faced with Hence, we adopt a method we term as Add-Join, which tries
interesting tradeoffs. For example, consider the SPARQL to achieve the best of both worlds, by using multiple triples
query in figure 4. tables for a single triple in the SPARQL query. In effect, we
SELECT ?label ?producer ?comment add extra joins to the resulting sql query. But, as we show,
WHERE { the cost of such additional joins is no way prohibitive and
t1 dataFromProducer9:Product444
rdfs:label ?label . can be traded off in return for a deterministic simple sparql-
t2 dataFromProducer9:Product444 sql compilation technique. For example, in the above
rdfs:comment ?comment .
t3 dataFromProducer9:Product444 example, we use two tables for t3 triple – t3_o [which is a
bsbm:producer ?p . osp table] and t3_s [which is a spo table]. We join t1 with
t4 ?p rdfs:label ?producer
} t3_s and t3_o with t4, and finally join t3_s and t3_o on all
Figure 4: Tradeoff in SQL conversion three columns. The final join is very fast since it involves all
three columns, so that the primary index can be used. In
The triples involved in the sparql query are marked t1, t2, t3 effect, all of the joins in the query can use the clustered
and t4. It is easy to observe that t1 joins t2,t3,t4 on the primary index. Figure 5 shows that the additional joins are
subject and t3 joins t4 using a subject-object join. Our task is not prohibitively expensive, using the same example.
to select one of the three triple tables – spo, pos, osp – Also, when rewriting the query for the Triple-Triple, we
judiciously so that all joins make use of the primary index must ensure that we have as few rows to start with as
and hence the fastest access path to access the relevant data possible. Since, MySql uses a single-sweep multi join](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-6-2048.jpg)
![algorithm [8], this would ensure that we try to match as few method described above.
tuples as possible in each stage of the multi join. 5. Graph Based Grouping
AddJoin : We observe that the further benefits can be achieved only
select * from Triples_s as t1 through physical optimizations. One interesting observation
STRAIGHT_JOIN Triples_s as t3_s
STRAIGHT_JOIN Triples_o as t3_o we make is that the selects on the triples table can be
STRAIGHT_JOIN Triples_s as t4 where
improved if the related tuples are brought closer to each
t1.s = 1280067686087321383 and t1.s =
t3_s.s and t3_o.o = t4.s and t3_s.s = other on disk. For example consider the spo table with
t3_o.s and t3_s.p = t3_o.p and t3_s.o =
t3_o.o; selects using po, p, o on it. This is a common scenario when
0.2 sec triples with different properties are joined on the subject.
Use spo for t3: Remember that we introduce additional joins only for the
select * from Triples_s as t1 joins between triples and selects using bound input values.
STRAIGHT_JOIN Triples_s as t3
STRAIGHT_JOIN Triples_s as t4 where
t1.s = 1280067686087321383 and t1.s = By bringing the subjects with common properties and
t3.s and t3.o = t4.s;
0.17 sec objects, closer to each other, we, in effect, reduce the
Figure 5 Cost of additional joins number of disk pages across which the result of the select
Hence, in addition to joins, we can also involve multiple operation is distributed. Thus, such a scheme would result in
triple tables for a single triple, when there is an initial select direct reductions in the I/O cost for the operation. The same
operation on the triple. For eg: Though a triple joins on s, it scenario can be applied to other two tables as well, bringing
might involve a select on p as a bound input value. In those together related properties and objects respectively.
cases, selecting p using a spo table may not be efficient.
Hence, we introduce an additional pos table for the triple and The integer identifiers assigned to the elements of the triples,
perform the select upon it, and later joining the pos and spo determine the order in which the triples appear on disk.
tables. We now present the algorithm to convert SPARQL to Right now, these ids are assigned randomly. Hence, we
SQL, based on Add-Join method. cannot use general purpose clustering schemes based on
euclidean distances, to group the related triples together.
Query Rewriting method: Also, without the Triple-Triple, it would be impossible to
Step 0. Convert the SPARQL query to sql, on the baseline give equal priority to each of subject, property and object.
Step 1. Identify the triples that have bound values for its This is because the first element of the compound primary
elements i.e. the input for the sql query. key determines the order on disk and hence a clustering
Step 2. In the explicit join order that we intend to provide, scheme has to choose between the three elements. Another
start with the triple with bound input values and follow it approach is to abandon the primary keys all together and
with triples that join with that triple. define a physical representation that brings together related
Step 3. For selects on the non join attributes, insert entries triples close to each other , based on all three columns.
for 'Nodes' as necessary in the explicit order. However, such a scheme would compromise on having data
Step 4. Once, the explicit ordering is done, introduce in sorted order. The Triple-Triple idea lends flexibility by
additional triple tables for each triple, as per the Add-Join allowing us to optimize with respect to subject, property and](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-7-2048.jpg)
![object using the spo, pos and osp tables respectively. formulated as an optimization problem as described in figure
Hence, the integers Ids need to be assigned intelligently in 6. The formulation can be suitably generalized to P-graphs
order to leverage these benefits. We now define metrics and O-graphs also. The problem is an instance of the
which quantify the strength of the relationship between two Knapsack constrained Maximum Weighted cluster problem
elements. S-score, P-score and O-score denote the metrics [9].
for interrelating subjects, properties and objects respectively.
The formulation aims to extract the cluster from the graph
S-score(s1, s2) = Number of triple pairs t1,t2 with (t1.s=s1 such that the sum of all the edge weights in the cluster is
and t2.s=s2) and ( t1.p = t2.p or t1.o = t2.o) maximal, subject to the constraint that there can be at most B
triples on a block. For MySql, which uses 16Kb data blocks,
defines the S-score for two subjects s1 and s2. P-score and B = 16Kb/12 = 1300. Once, such a maximal cluster is
O-score are defined similarly. Once, we have these metrics extracted, we assign consecutive ids to all the elements of
computed, we build three graphs S-graph, P-graph, O-graph the cluster. We then repeat the algorithm, pruning the graph
that depict relationships between subjects, properties , removing the assigned edges. However, in practice, this
objects using S-score, P-score, O-score as edge weights problem is NP hard and grows computationally unrealistic,
respectively. The S-graph will have a vertices for each with large data sets which involve thousands of subjects. The
subject and S-score between two subjects as the edge weight. S-graph is also very dense and this complicates the solution
Note that no subject or object occurs as a property. Hence, further. For example, a 25K triples database, contains 2367
the problem of assigning ids to properties can be solved subjects, 200K edges. Hence, when we scale to a billion
independent of the other two elements. However, some triples, the graph construction itself may become a very long
subjects also occur as objects. But, there can be only one id process. There are other graph clustering tools such as
that can be assigned to that element. We therefore prune out MCL[10] and Graclus [11], for unsupervised learning from
the O-graph by removing all vertices and edges graphs. Though, these tools do not solve the exact problem
corresponding to such overlapping subjects. as described above, they attempt to provide clusters from the
graph based on connected components. Attempts at
Let S denote a cluster and Si denote a
subject belonging to S. hierarchical clustering using the MCL algorithm, yields only
Objective :
3 clusters, reflecting on the dense nature of these graphs and
Max : ∀i ∀ j Σ Sscore( Si, Sj ),i!= j
Constraints: non applicability of standard graph clustering techniques.
Σ numTriples(Si) <= B
where numTriples(Si) denote the number
of triples with subject Si Hence, we attempt to develop computationally feasible
B denotes the number of triples per
greedy algorithms for the problem. One such greedy
block
algorithm is described in Figure 7. The algorithm greedily
Figure 6 : Optimal clustering of subjects constructs parts of the relationship graphs and assigns
identifiers based on such partial graphs. The algorithm
Each disk page can be viewed as a cluster or group and the closely approximates the optimal solution for certain parts of
problem of finding the most related subjects can be the graph. Nonetheless, it is suboptimal since we ignore the](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-8-2048.jpg)
![strength of the relationships between the discovered subjects queries that cause scalability problems for applications.
Si.
While there is a subject S [that has RDBMS MySql 5.0
not been assigned an Id] :
Assign next available id to S OS Ubuntu 8.04
compute all the subjects Si
related to S; i.e has a non zero S Processor AMD Turion TL 58
score with S
compute Sscore(S, Si) for all 32/64 bit 32
such discovered subjects
Assign ids to Si in the Processor speed 1.9 Ghz
increasing order of Sscore(S,Si) till
Σ numTriples(Si) <= B L1 cache (MB) 128
Figure 7: Greedy Grouping L2 cache (MB) 512
FSB speed (MHz) 800
In section 6, we validate the effectiveness of this algorithm.
RAM (Gb) 2
Once again, the id assignment for properties can be done in a
symmetric fashion. For the objects, we need to additionally Disk capacity (Gb) 160
ignore objects which are also subjects. Disk rotation 5400
(RPM)
6. Empirical results
Buffering (MB) 8
We present empirical results that demonstrate the validity of
the approaches proposed in this paper. Specifically, we study
Table 2 Platform details
the query performance compared to the baseline and the real
benefits of the grouping technique described in the previous
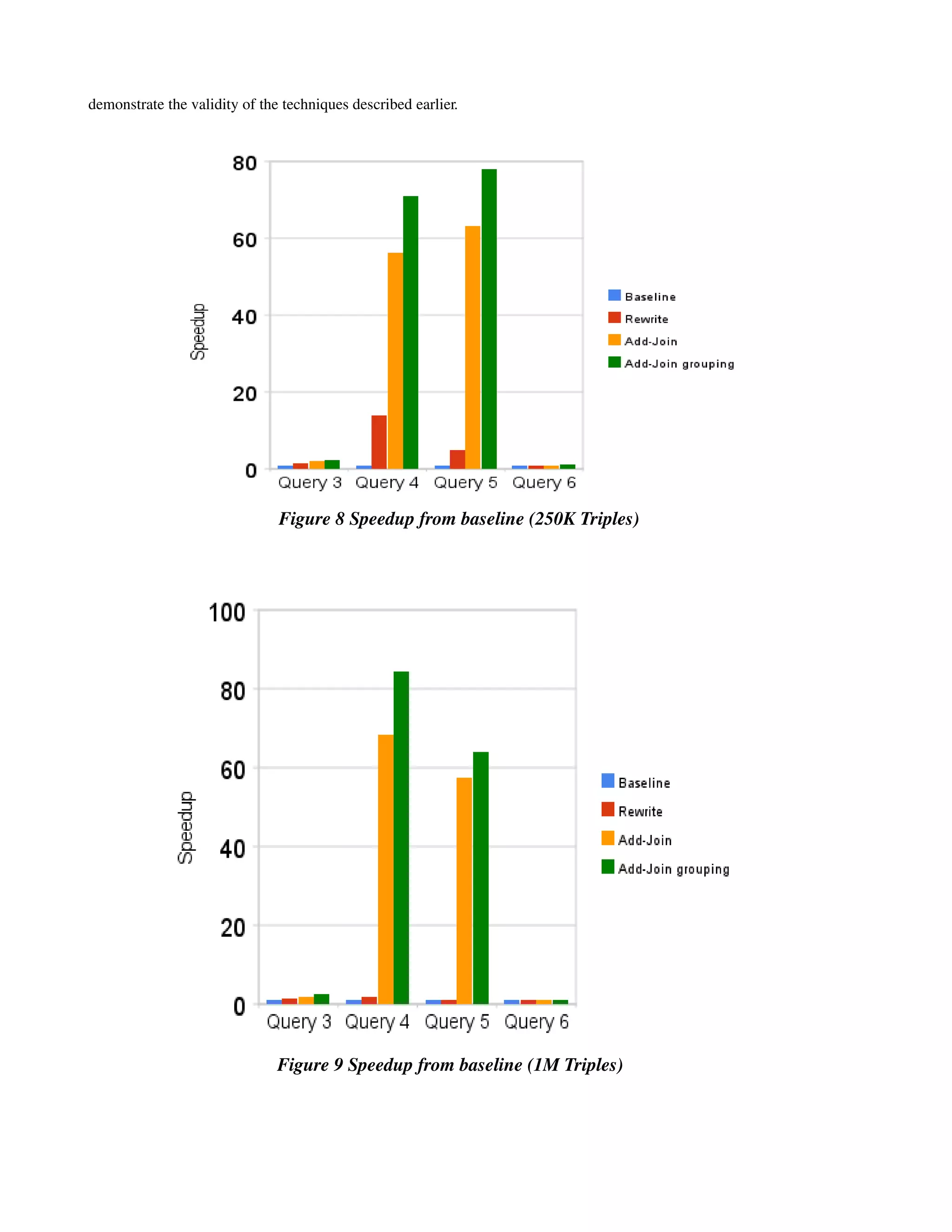
The improvements on query 3 and query 6 are not
section. Our experimental setup is detailed in Table 2.
significant. The baseline timings for those queries are not
very large in the first place and involve lesser number of
6.1 Query Performance
joins. For example, query 6 involves only one triple. Add-
For each scheme that we evaluate, we define a metric called
Join uses two triples for the query and offers the same
speed up to compare it against the baseline. Speed up is
amount of performance as the baseline. There are very
simply the query response time for the baseline divided by
significant benefits on the queries 4 and 5. The benefits due
the query response time for the scheme for the same query.
to Add-Join method account for the bulk of the benefits over
Higher the speed up better the scheme i.e. it determines how
the baseline amounting to approximately 50x improvement
many magnitudes of performance improvement is achieved
from the baseline. The direct benefits due to grouping
by the scheme. Figure 8 and 9 present the speed ups for
technique amount to 10x-20x times over the baseline, when
three schemes – Rewrite (simply rewriting the query by
compared to the Add-Join method without grouping. It
explicitly specifying the join order), Add-Join , Add-Join
remains to be seen if better grouping techniques can yield
with grouping. The results are presented for queries 3,4,5,6
significantly higher benefits. However, these results
[12]. Queries 4,5 are typical examples of the complex](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-9-2048.jpg)
![6.2 Validation of Grouping scheme
It is also important to validate the grouping scheme
presented in section 5. We expect the grouping scheme to
reduce the number of disk I/O for selects on the triples
tables. Table 3 presents the number of rows the query
optimizer expects to examine, for answering selects on the
triple tables. It can be seen that the grouping has resulted in a
decrease in the number of rows examined for the query.
Table No grouping With grouping
spo table 1000619 973866
pos table 1000619 805152 Figure 10 : Rscore
osp table 1000619 828004
The results indicate that the grouping algorithm has been
Table 3 : Expected number of rows accessed for
quite effective, increasing the interrelationship by 2x-10x
selects
times of the random Id assignment. The R-score for the pos
table is lower since there are fewer number of properties and
We also measure the amount of interrelationship between the
hence in a number of cases, a single data block is full of
triples in each block, with and without grouping, to observe
triples from the same property. In fact, the average edge
the effectiveness of our grouping algorithm. For each disk
weight for the pos table is much lower than those of the spo
block [i.e. a set of 1300 tuples] we construct S-graphs, P-
and osp tables. There are higher values for the osp table
graphs and O-graphs representing those clusters. We then
since there are far more objects than subjects, in which case,
compute the sum of all the edge weights of each such cluster
there are more number of edges in the cluster graph
and average it across all data blocks. This allows us to
constructed.
quantify the effectiveness of our grouping scheme. Ideally,
we should also be comparing our grouping scheme against
7. Conclusions and Future work
the optimal solution. However, the optimal solution is very
Thus, we have explored some promising approaches to
hard to compute as mentioned earlier and also cannot be
improving query performance in relational triple stores. An
predicted accurately since it depends on the nature of the
interesting query rewriting mechanism which introduces
triples. We divide the average edge weight for table with
additional joins to speed up query execution has been
grouping by the average edge weight for the corresponding
discussed. Optimization of the physical schema by
table without grouping to obtain a metric called the R-score
leveraging the interrelationship between the elements of a
or the relationship score for those two tables. Figure 10
triple, has been proposed. A greedy grouping algorithm
Presents the R-scores for all three triples tables for 250K and
which is simple and computationally feasible has been
1M triple tables.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-11-2048.jpg)
![proposed and validated. The results show that our approach Schiefer, Eds. Very Large Data Bases. VLDB Endowment,
is promising and can be potentially combined with other 1054-1065.
techniques in literature to yield faster RDF stores. As a part [4] David Wood, “Kowari: A Platform for Semantic Web
of future work, we intend to compare the performance of the Storage and Analysis”,In XTech 2005 Conference
system with the Hexastore and potentially enhance the [5] Abadi, D. J., Marcus, A., Madden, S. R., and
Hexastore with our grouping algorithm. As mentioned Hollenbach, K. 2007. Scalable semantic web data
earlier, we would like to develop better grouping algorithms management using vertical partitioning. In Proceedings of
by leveraging parallel computing techniques to overcome the the 33rd international Conference on Very Large Data Bases
computational issues. We believe that better grouping (Vienna, Austria, September 23 - 27, 2007). Very Large Data
algorithms can yield significantly higher performance. Bases. VLDB Endowment, 411-422.
Another key observation we make, is that no physical [6] Weiss, C., Karras, P., and Bernstein, A. 2008. Hexastore:
schema will perform best for all types of queries. Hence, sextuple indexing for semantic web data management. Proc.
with the cheap availability of storage, multiple physical VLDB Endow. 1, 1 (Aug. 2008), 1008-1019. DOI=
schema can co exist within the same RDF store and the http://doi.acm.org/10.1145/1453856.145396
SPARQL compiler can judiciously employ them based on [7] Nested-Loop Join Algorithms
the type of the query. http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/nested-loop-
joins.html
8. References [8] Using Explain syntax
[1] Resource Description Framework http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.0/en/using-explain.html
http://www.w3.org/RDF/ [9] Anuj Mehrotra and Michael A Trick, “Cliques and
[2] http://iswc2008.semanticweb.org/calls/call-for-semantic- Clustering: A Combinatorial Approach”,
web-challenge-and-billion-triples-tracks/ [10] MCL : An algorithm for clustering graphs,
[3] Das, S., Chong, E. I., Eadon, G., and Srinivasan, J. 2004. http://www.micans.org/mcl/
Supporting ontology-based semantic matching in RDBMS. [11] Graclus
In Proceedings of the Thirtieth international Conference on http://www.cs.utexas.edu/users/dml/Software/graclus.html
Very Large Data Bases - Volume 30 (Toronto, Canada, [12] Class project website
August 31 - September 03, 2004). M. A. Nascimento, M. T. http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~jsequeda/cs386d/project.html
Özsu, D. Kossmann, R. J. Miller, J. A. Blakeley, and K. B.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vinoth-chandar-termpaper-120428123405-phpapp01/75/Triple-Triple-RDF-Store-with-Greedy-Graph-based-Grouping-12-2048.jpg)