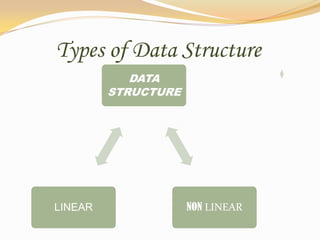
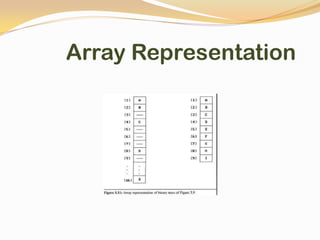
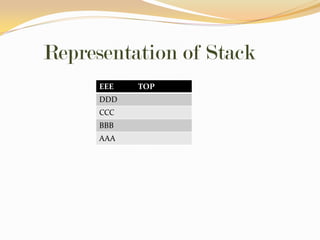
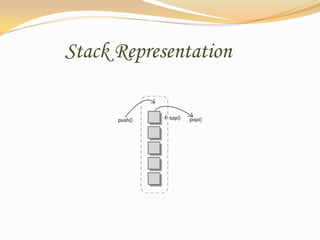
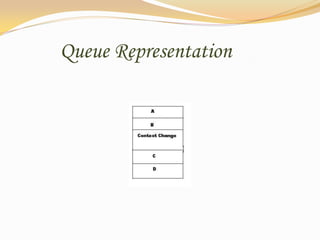
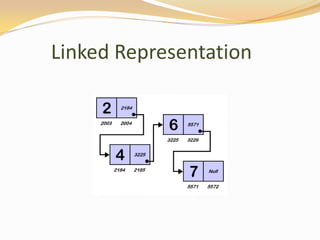
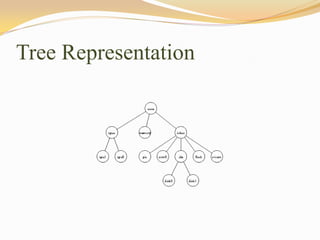
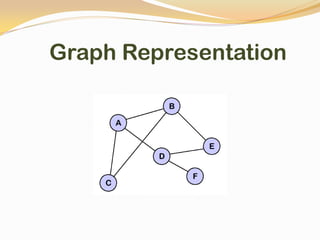
This document discusses data structures and their types. It defines data structures as the logical or mathematical organization of data in computer memory or on disk. The main types are linear data structures like arrays, stacks, queues, and linked lists, and non-linear structures like trees and graphs. Common operations on data structures include traversing, searching, inserting, deleting, sorting, and merging. Algorithms manipulate data in these structures to solve problems.