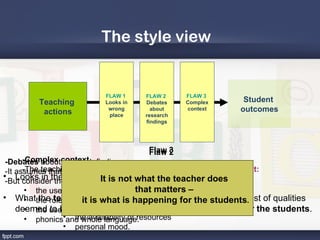
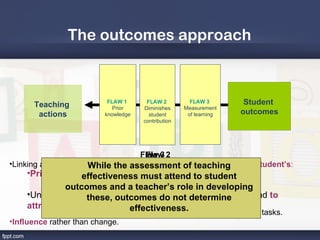
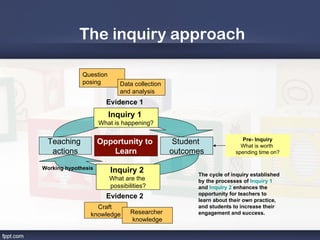
1. Effective teaching produces beneficial student learning through appropriate procedures such as quality teachers socializing with students and modeling positive behavior.
2. New teachers bring enthusiasm and creativity but need support, while mid-career teachers need leadership opportunities and veteran teachers provide wisdom and mentoring.
3. Effective teachers demonstrate caring, share responsibility, accept diversity, encourage creativity, and provide individualized instruction. Their classrooms are cheerful environments where learning is enjoyable.