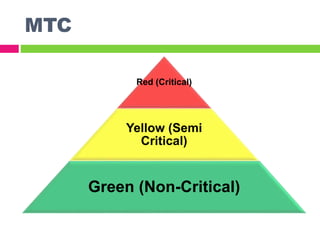
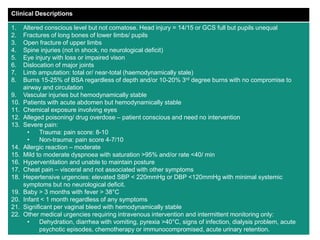
This document provides an overview of triage in emergency departments. It defines triage as a process used to assess patients' severity of injury or illness upon arrival to prioritize treatment. The document outlines several challenges emergency departments face and the goals of triage to provide appropriate care in a timely manner. It then describes common triage systems and levels (critical, semi-critical, non-critical), the roles of triage officers, and the process involving assessment, priority assignment, and initial treatment or transport. The Malaysian Triage Category is presented as an example, detailing its levels and clinical descriptions to guide triage decisions.