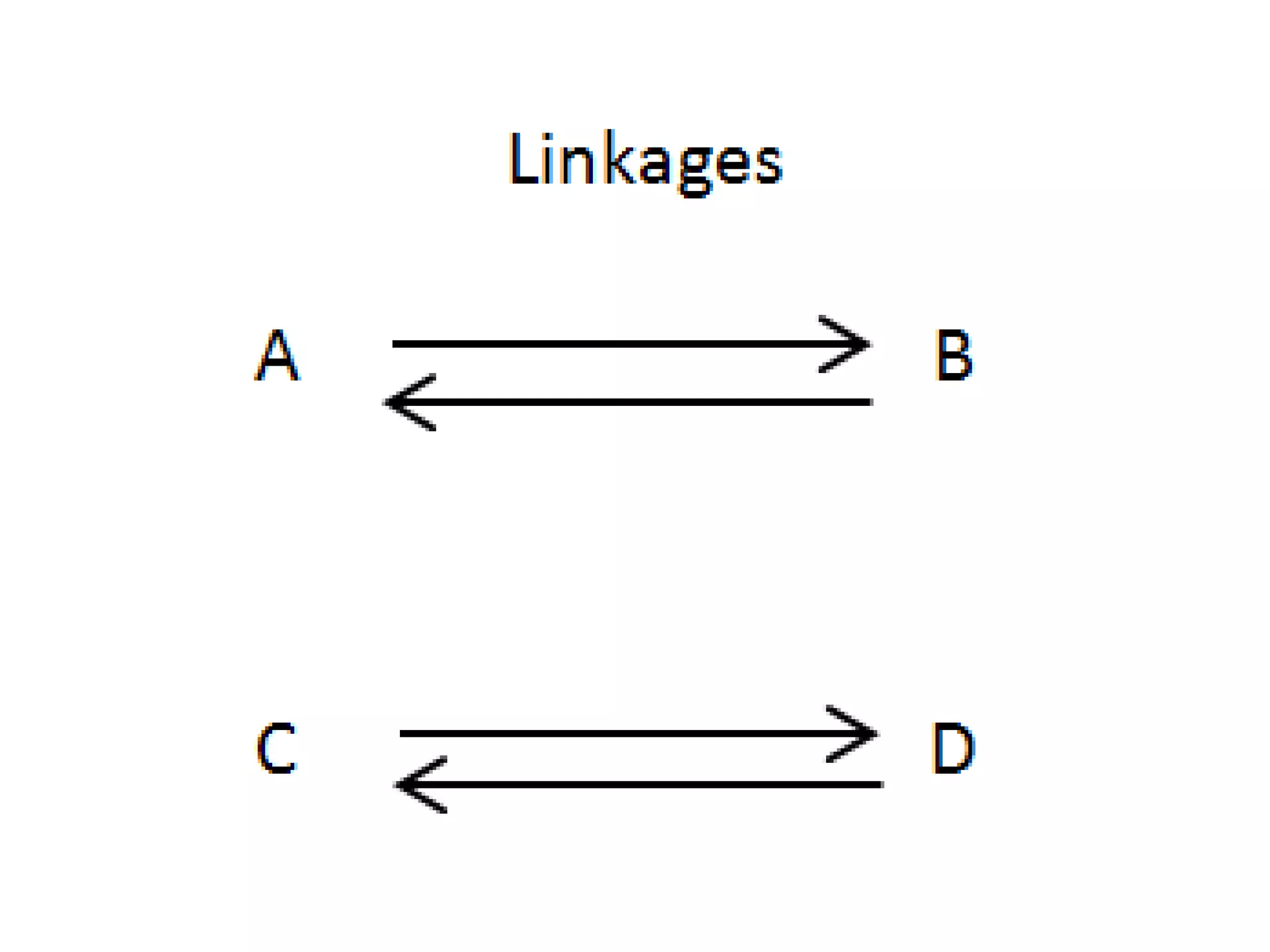
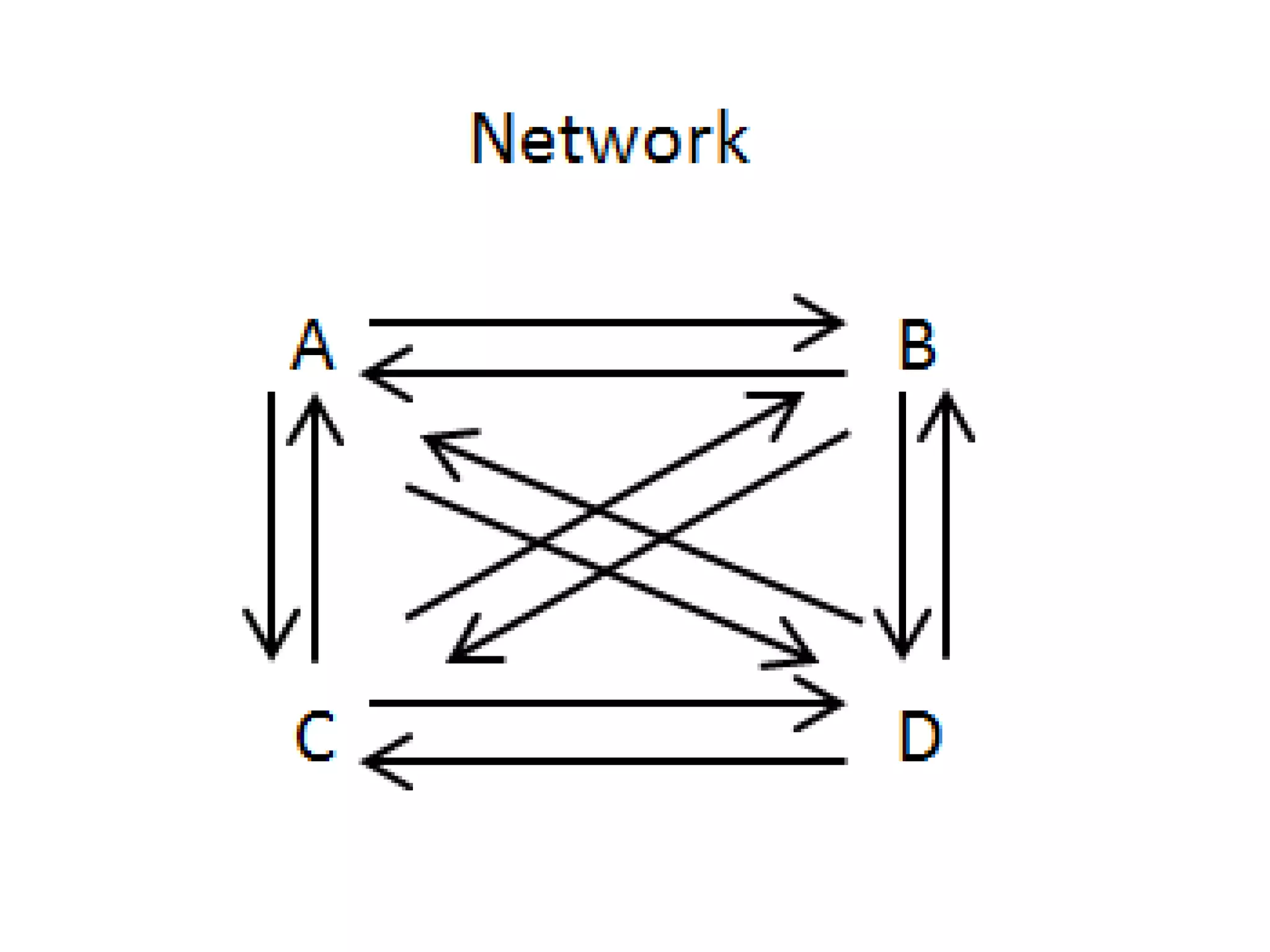
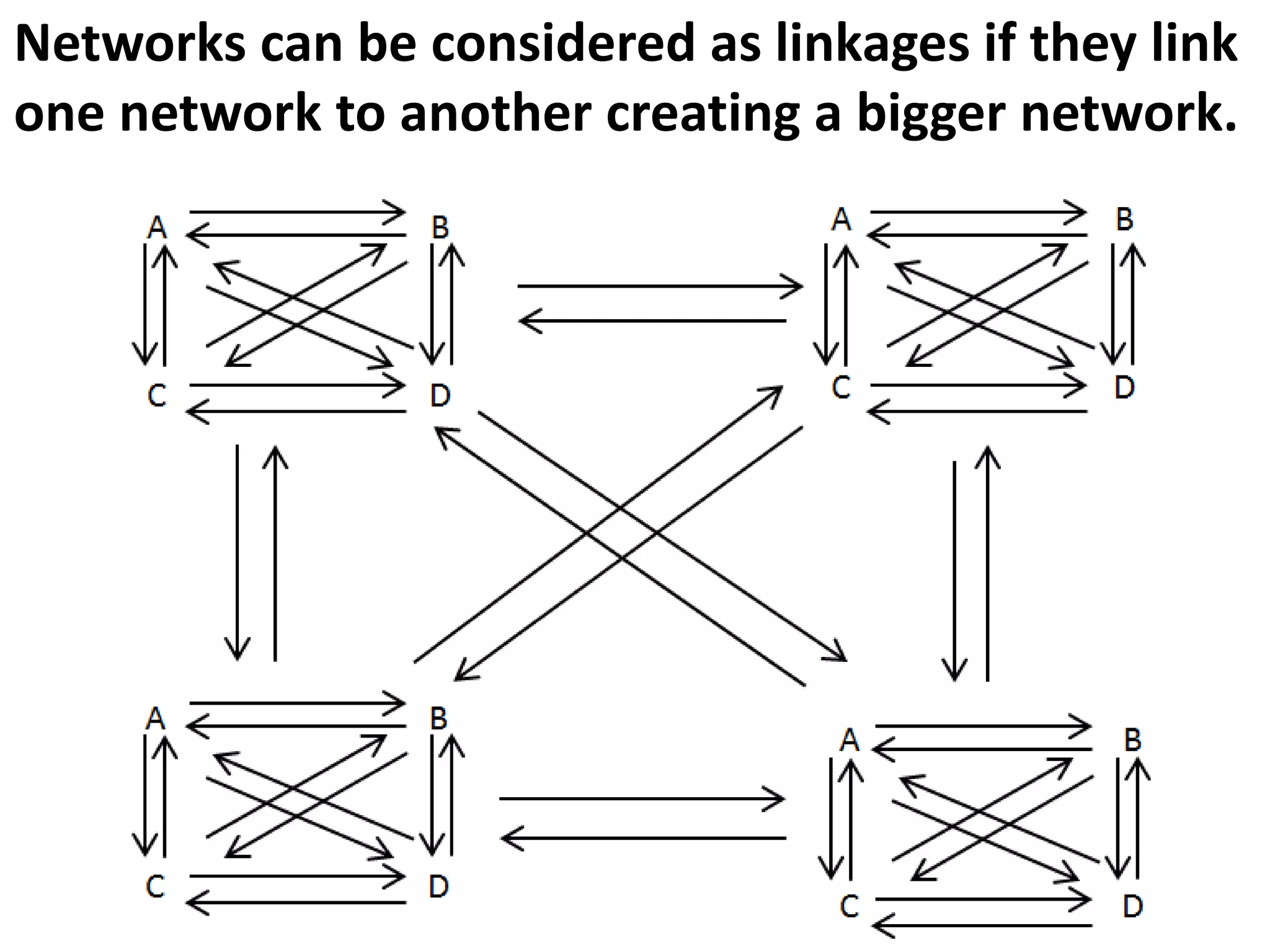
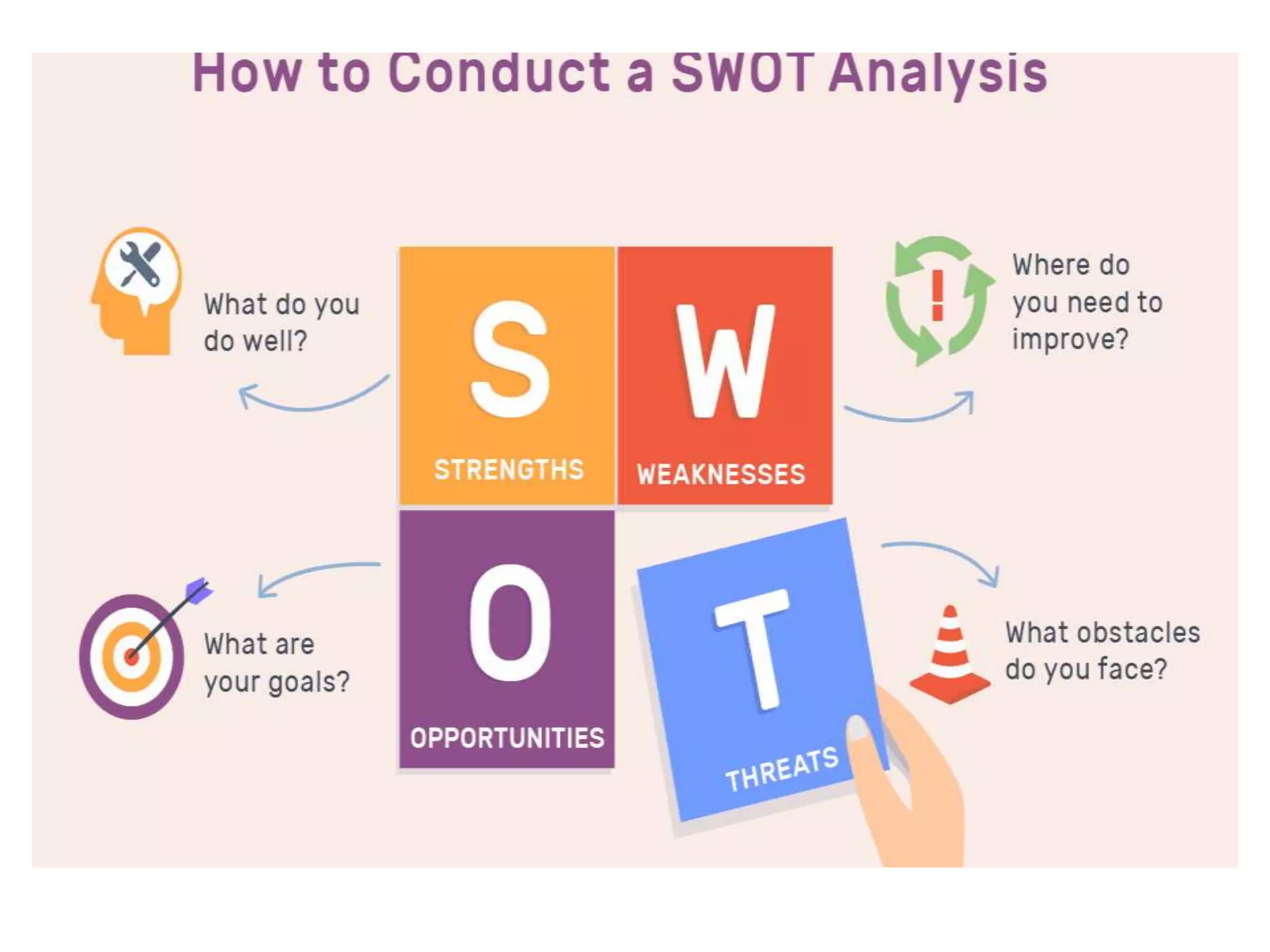
The document discusses the importance of linkages and networking for schools to collaborate with various organizations for mutual benefits, highlighting the differences in commitment levels. It categorizes social networks and family relations while emphasizing strategic analysis through SWOT analysis for informed decision-making. The text also explores intuitive thinking as a form of knowledge based on experience rather than deliberation.