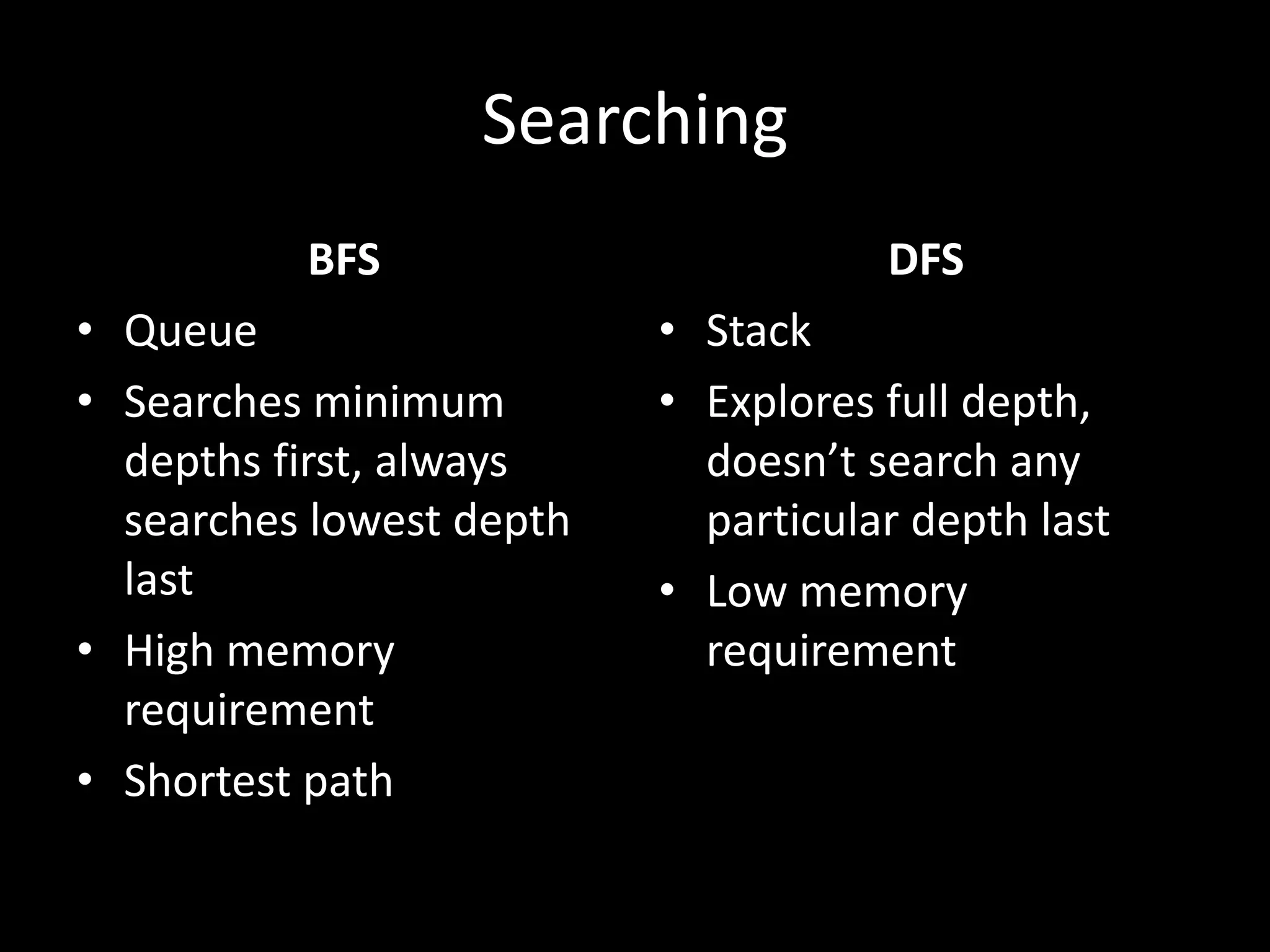
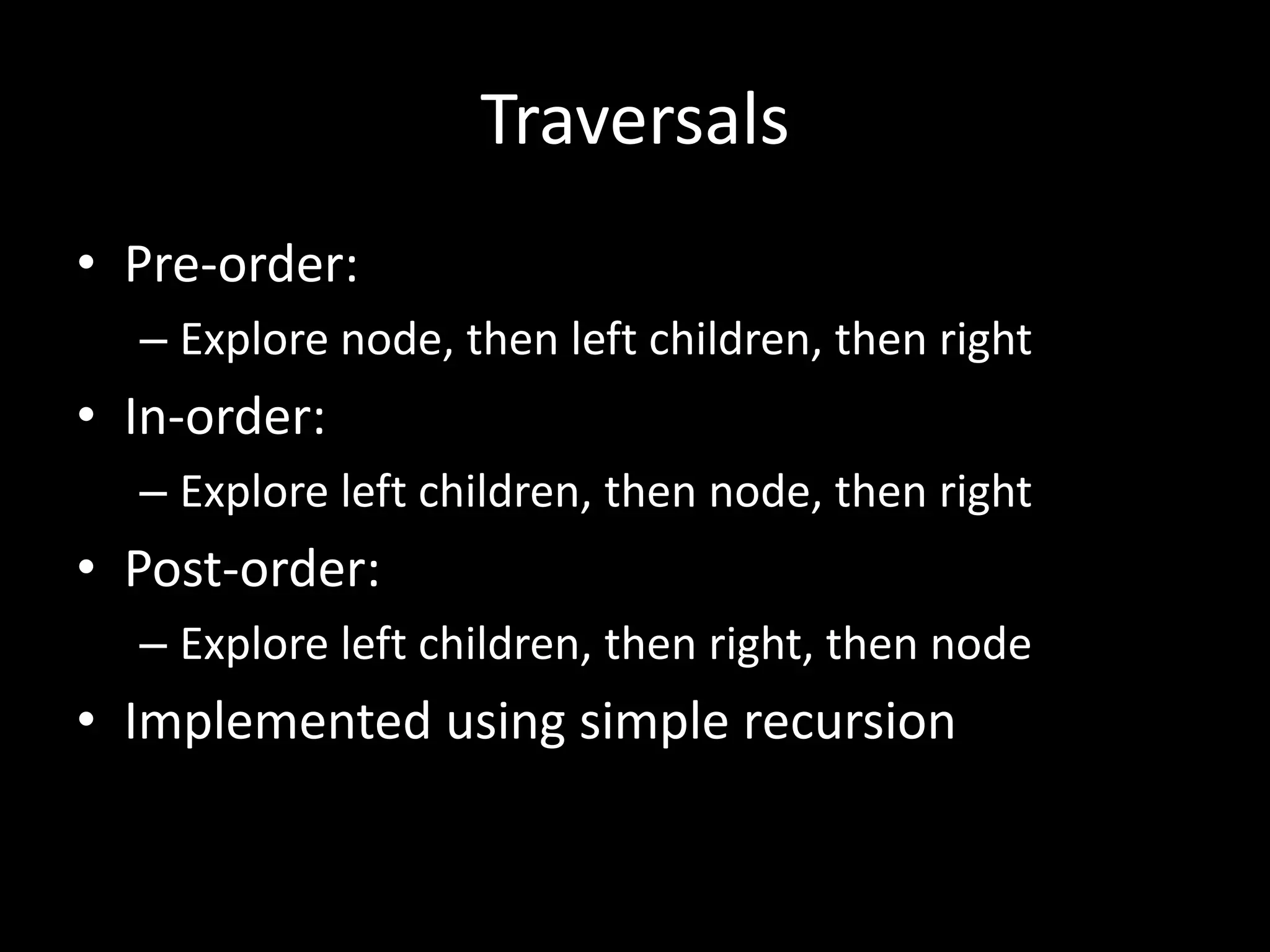
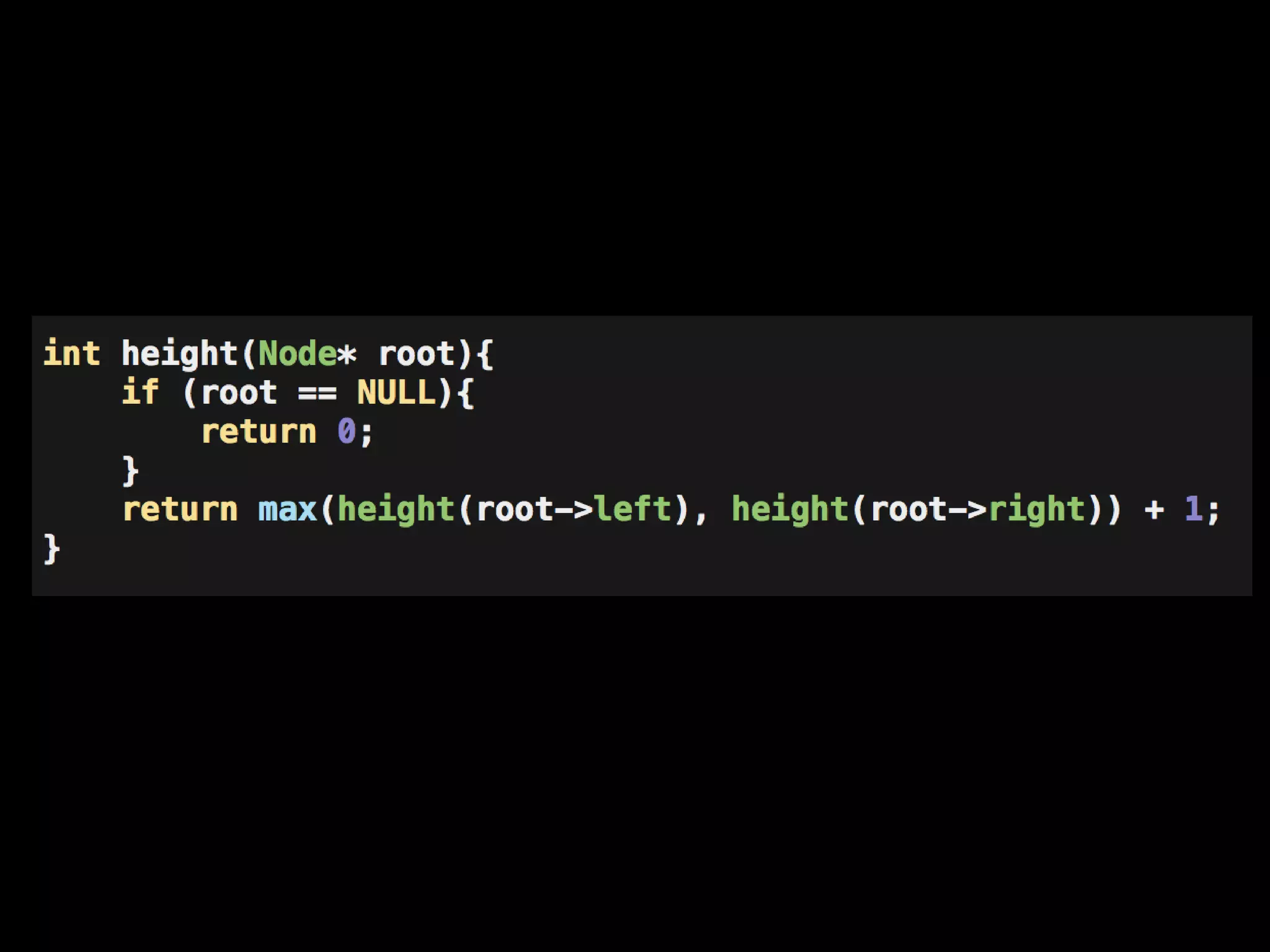
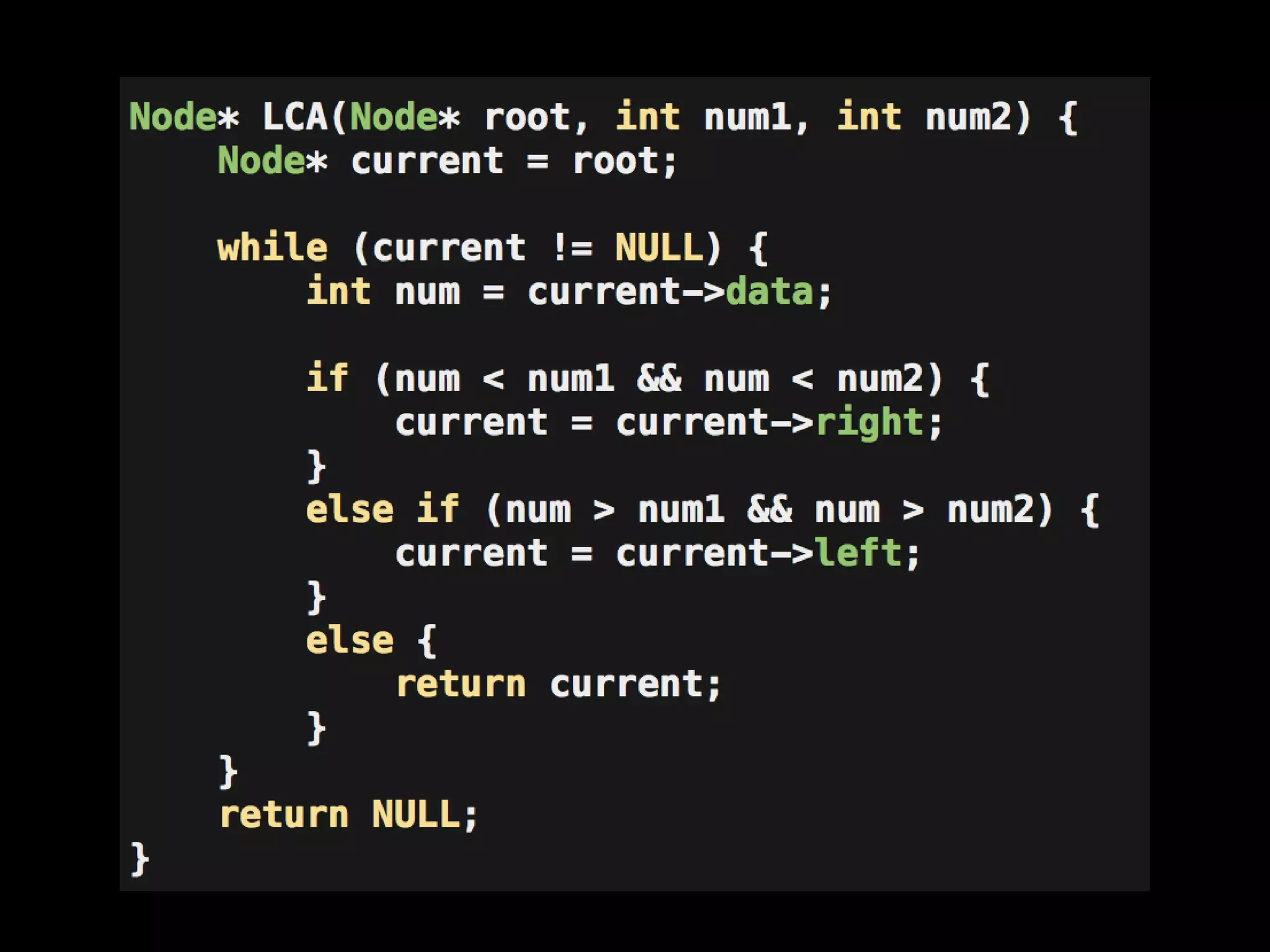
This document discusses different types of trees and graphs. It defines properties of trees including that trees are connected graphs with n-1 edges and no cycles. It describes binary search trees where all descendants to the left of a node are smaller and all to the right are greater. The document also covers heaps, tree traversals, common tree algorithms and their strategies, and briefly mentions graphs.