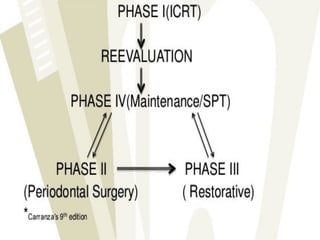
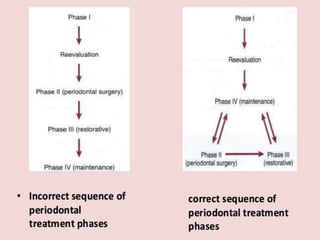
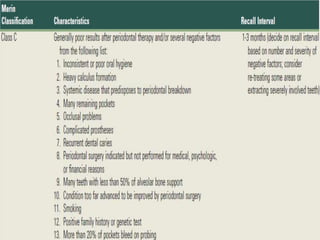
The document outlines the key components and goals of a treatment plan, including:
1. A treatment plan is created after diagnosis and prognosis to establish a blueprint for case management including all procedures needed for oral health.
2. The goals are to reconstruct a healthy dentition that meets functional and aesthetic needs, considering long term needs like prosthetics and implants.
3. The master plan coordinates all short and long term goals to create a well-functioning dentition in a healthy environment.