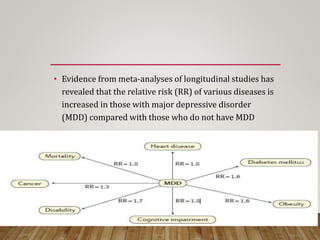
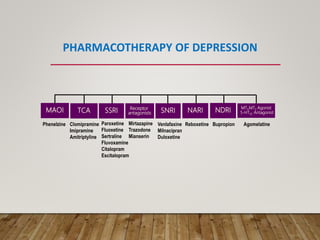
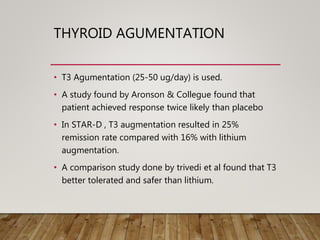
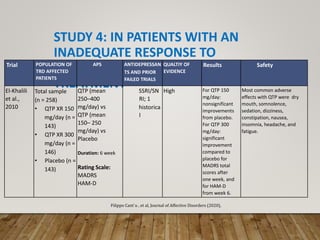
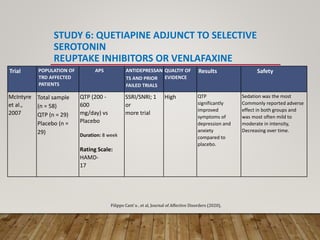
This document summarizes research on using quetiapine as an augmentation strategy for treatment-resistant depression. Six studies are reviewed that examine adding quetiapine to ongoing antidepressant treatment. The studies generally found quetiapine augmentation led to greater improvement in depression symptoms compared to placebo, especially when starting at dosages of 150-300 mg/day. The most common side effects were dry mouth, drowsiness, and weight gain. Overall, the research suggests quetiapine may be a valid option for improving outcomes for patients with treatment-resistant depression.