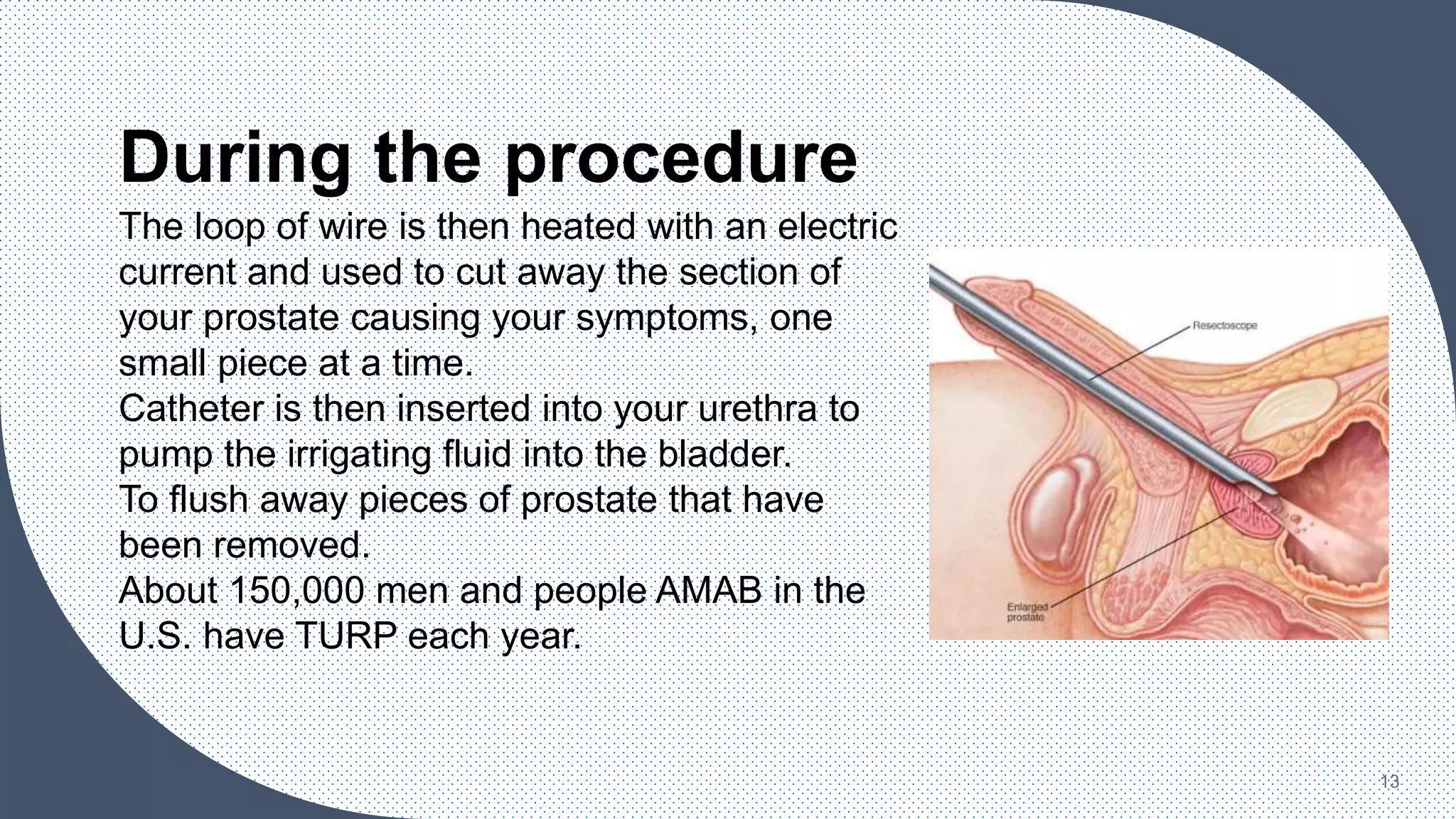
The document provides an overview of transurethral resection of prostate (TURP), a surgical procedure used to treat urinary problems caused by an enlarged prostate. It details the pre-operative preparations, procedural steps, and post-operative care, highlighting associated risks and alternative treatment options. Emphasizing the significance of patient management and surgical team roles, it serves as a guide for understanding the TURP process.