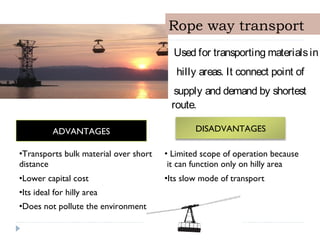
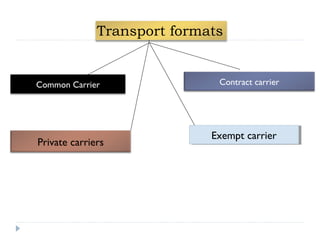
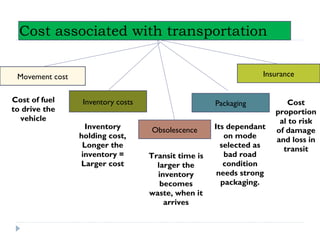
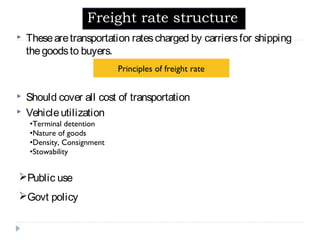
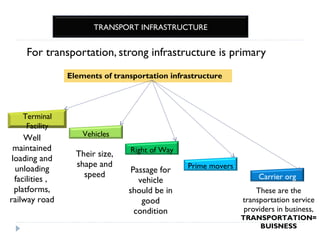
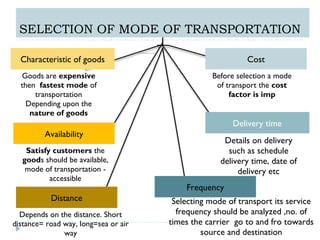
The document details the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of various transportation modes, notably air transport and ropeway transport. It highlights factors influencing transportation costs, including product-related aspects and operational considerations. Additionally, it discusses the significance of transport infrastructure and the challenges faced, particularly in rural areas of India, affecting transportation efficiency and costs.