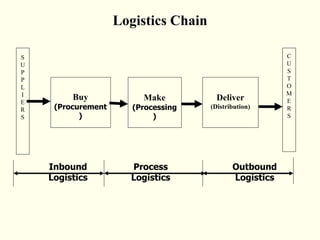
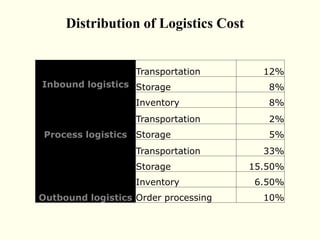
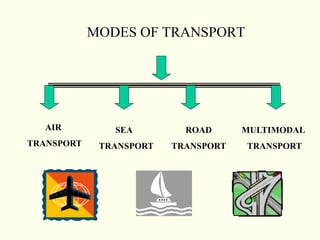
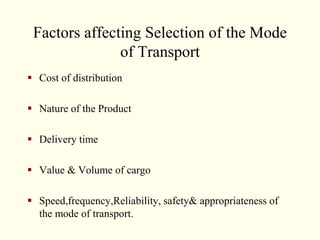
This document discusses various aspects of logistics planning for export distribution. It covers determining the optimal transportation mode based on cost and other factors. Modes discussed include air, sea, road, and multimodal transport. It also describes the roles of clearing and forwarding agents and how they assist with transportation arrangements, documentation, and other logistics services. Containerization is presented as an efficient method for cargo distribution.