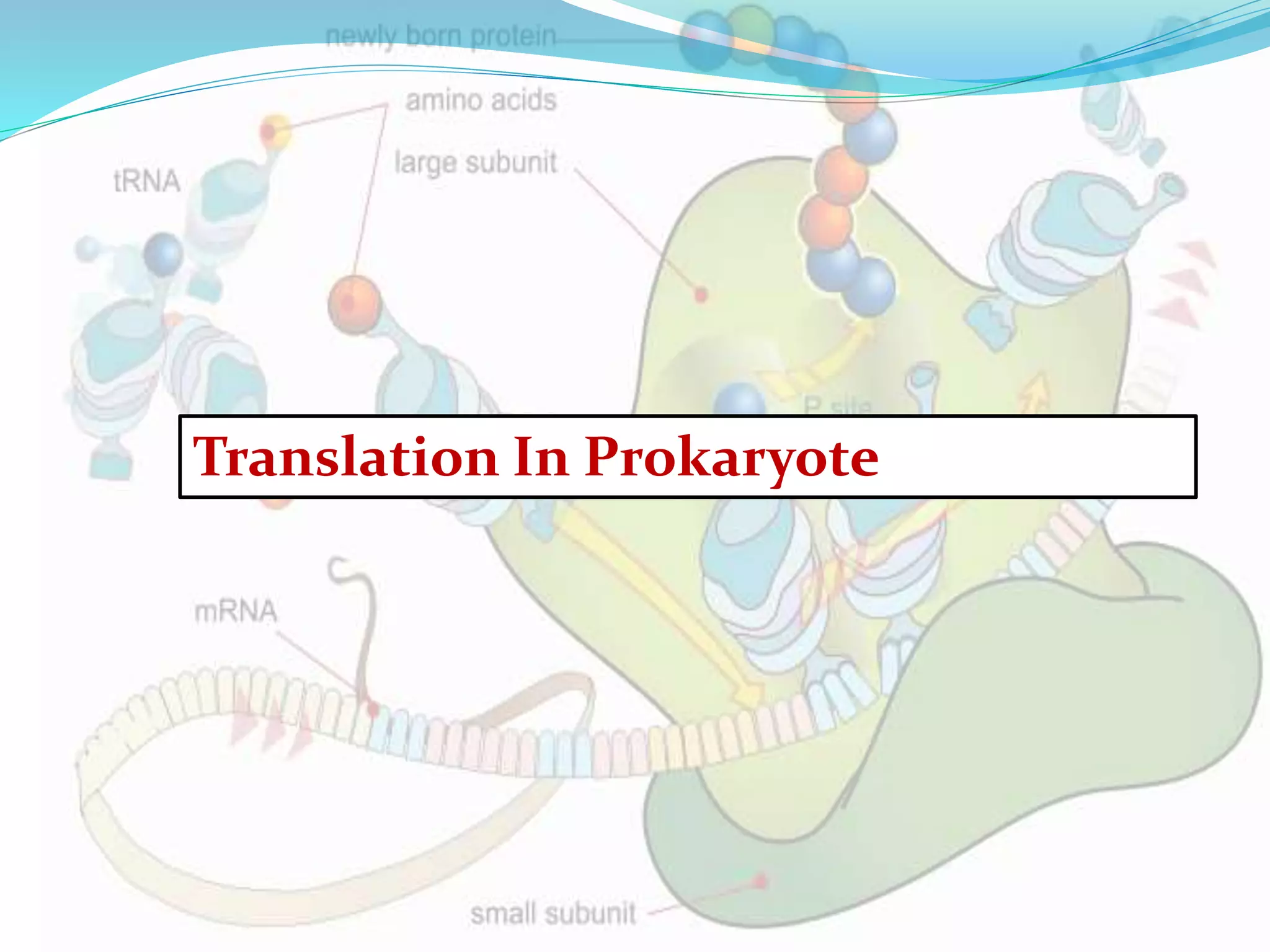
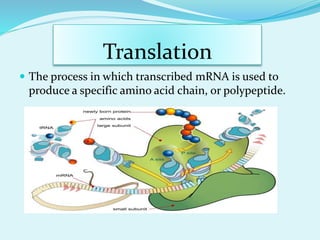
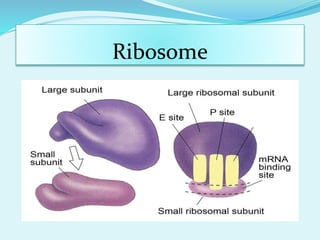
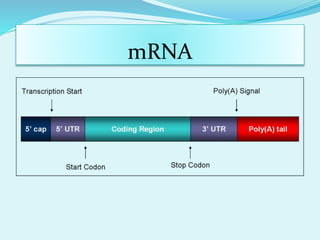
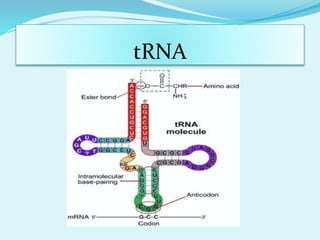
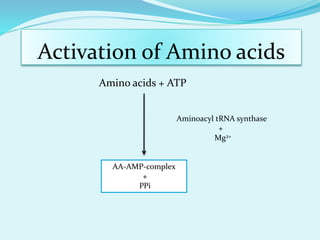
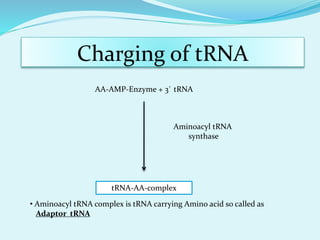
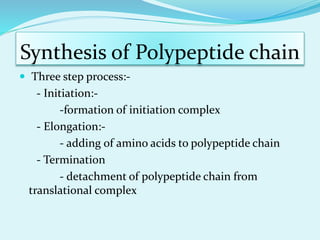
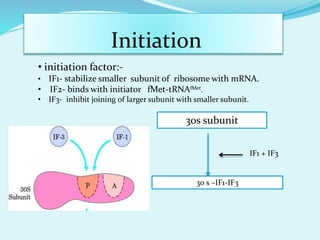
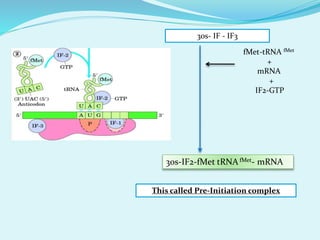
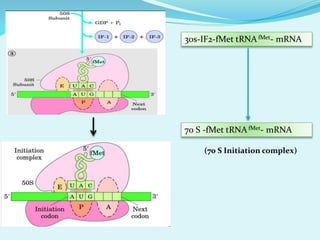
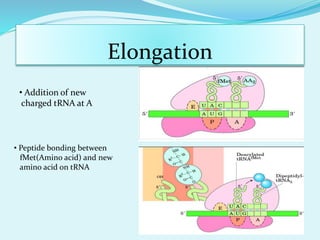
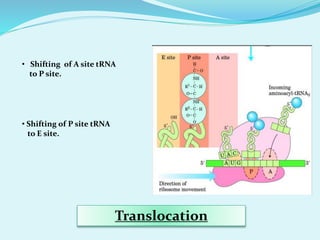
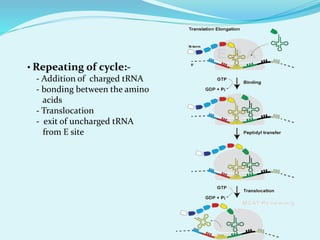
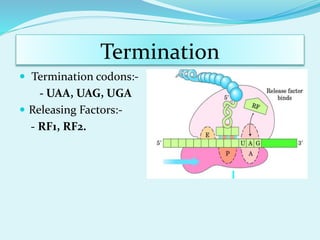
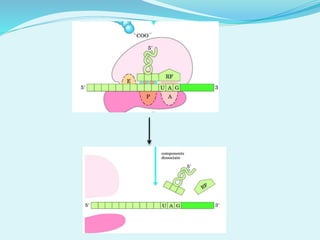
Translation in prokaryotes involves mRNA being used to produce a polypeptide chain. It begins with the initiation of a complex including the small ribosomal subunit, mRNA, and initiator tRNA. Elongation then occurs through the addition of amino acids to the growing chain via charged tRNAs. Termination happens when release factors bind to stop codons on the mRNA and allow dissociation of the completed protein from the ribosome.