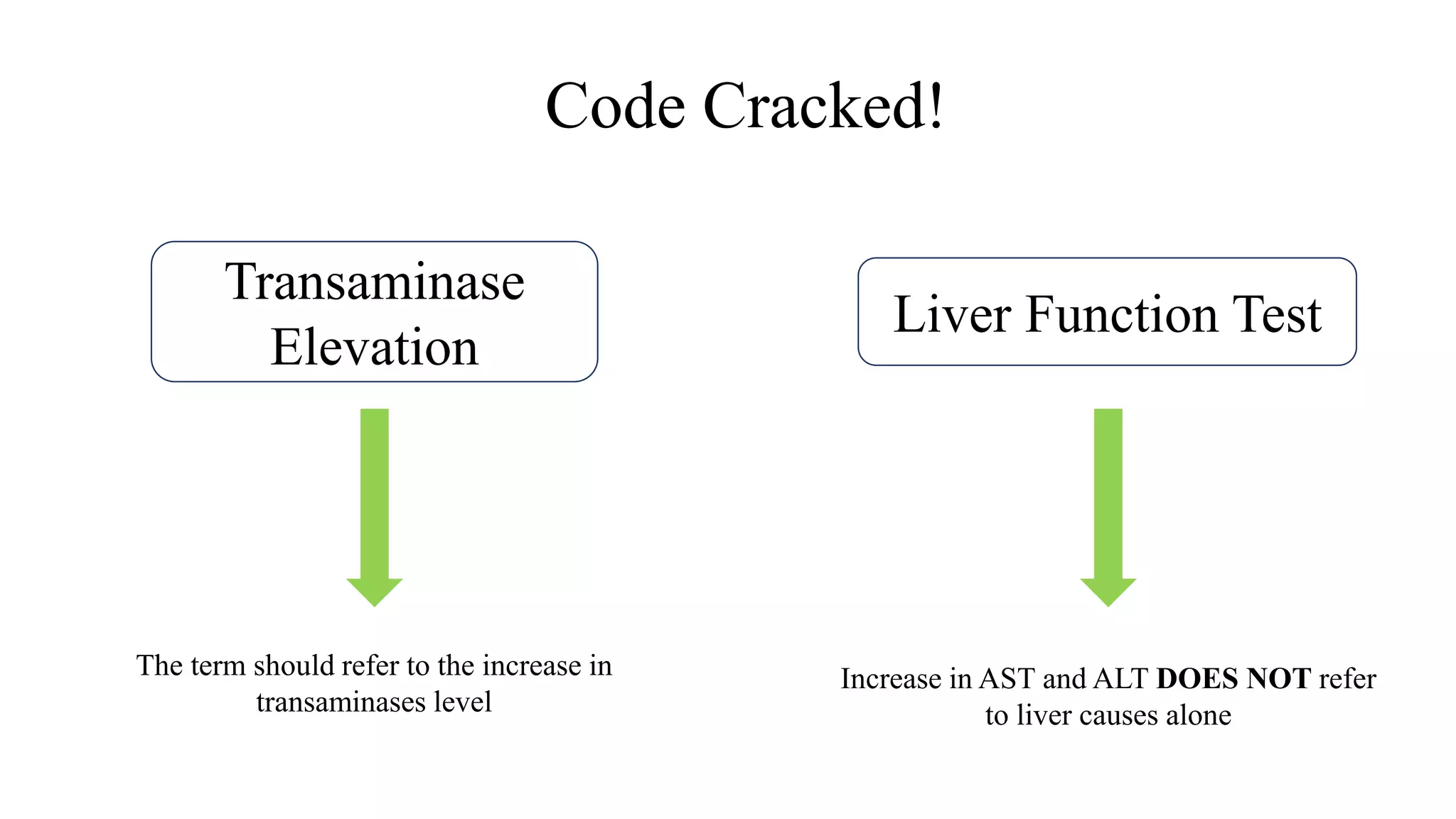
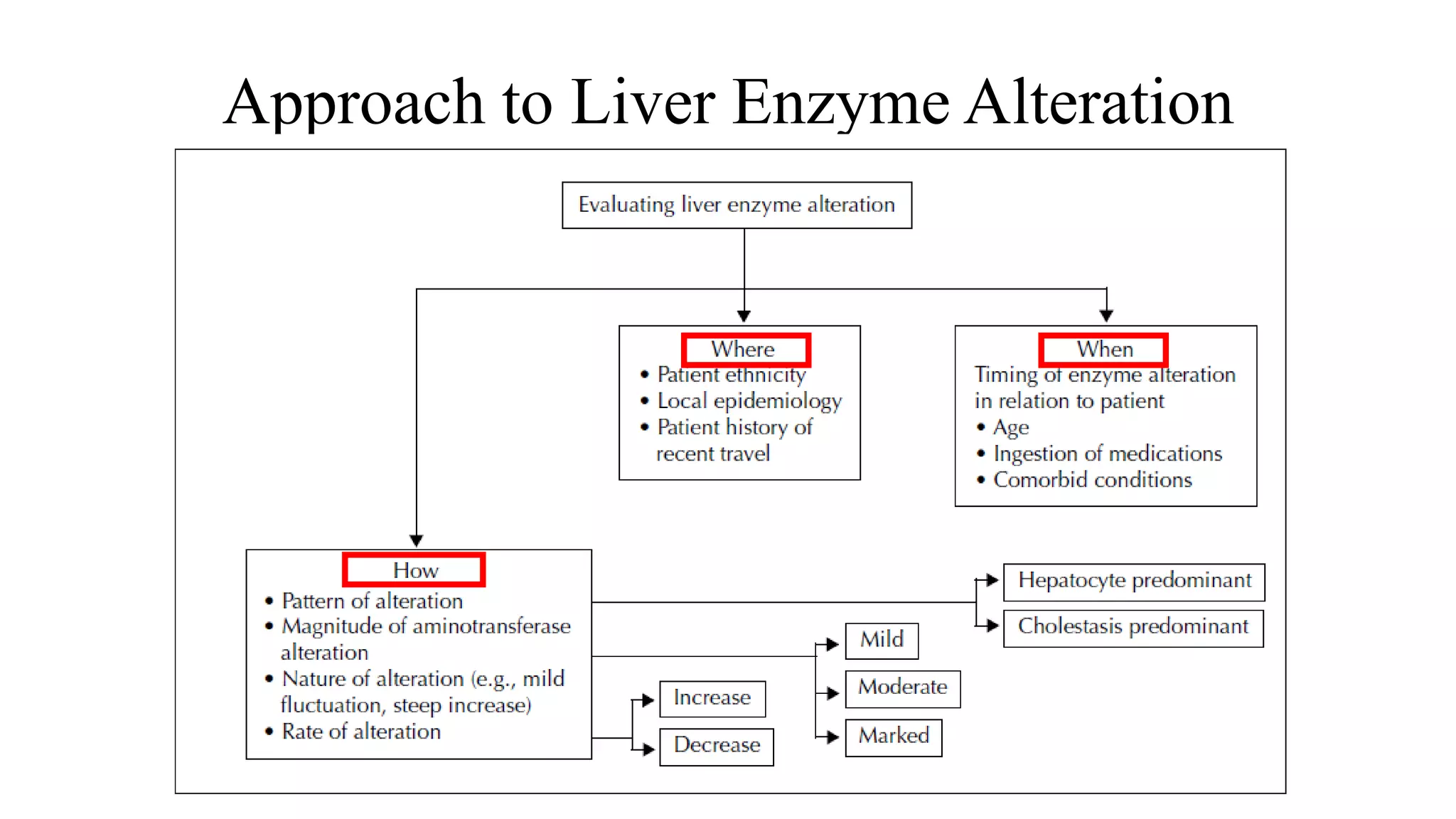
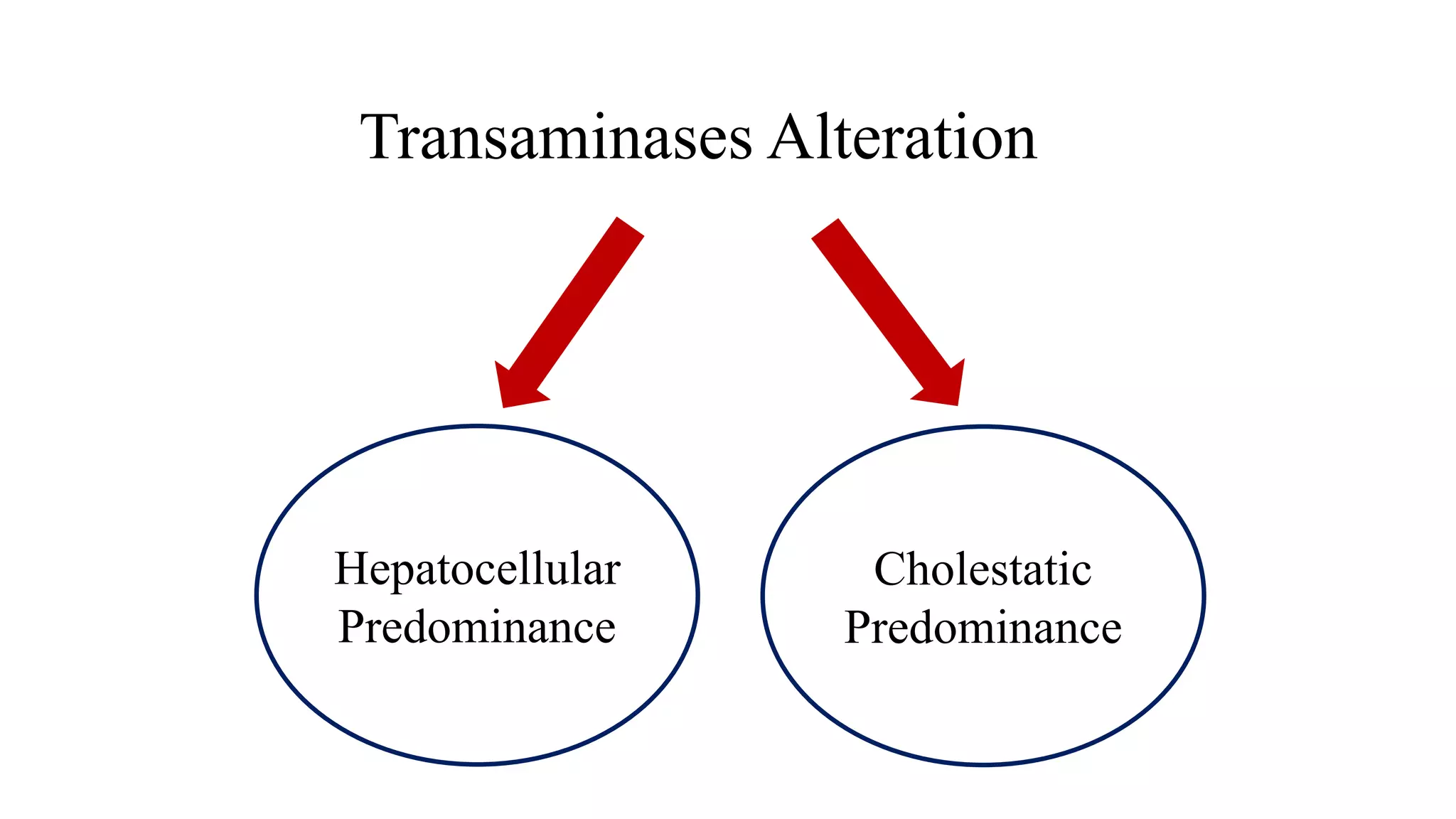
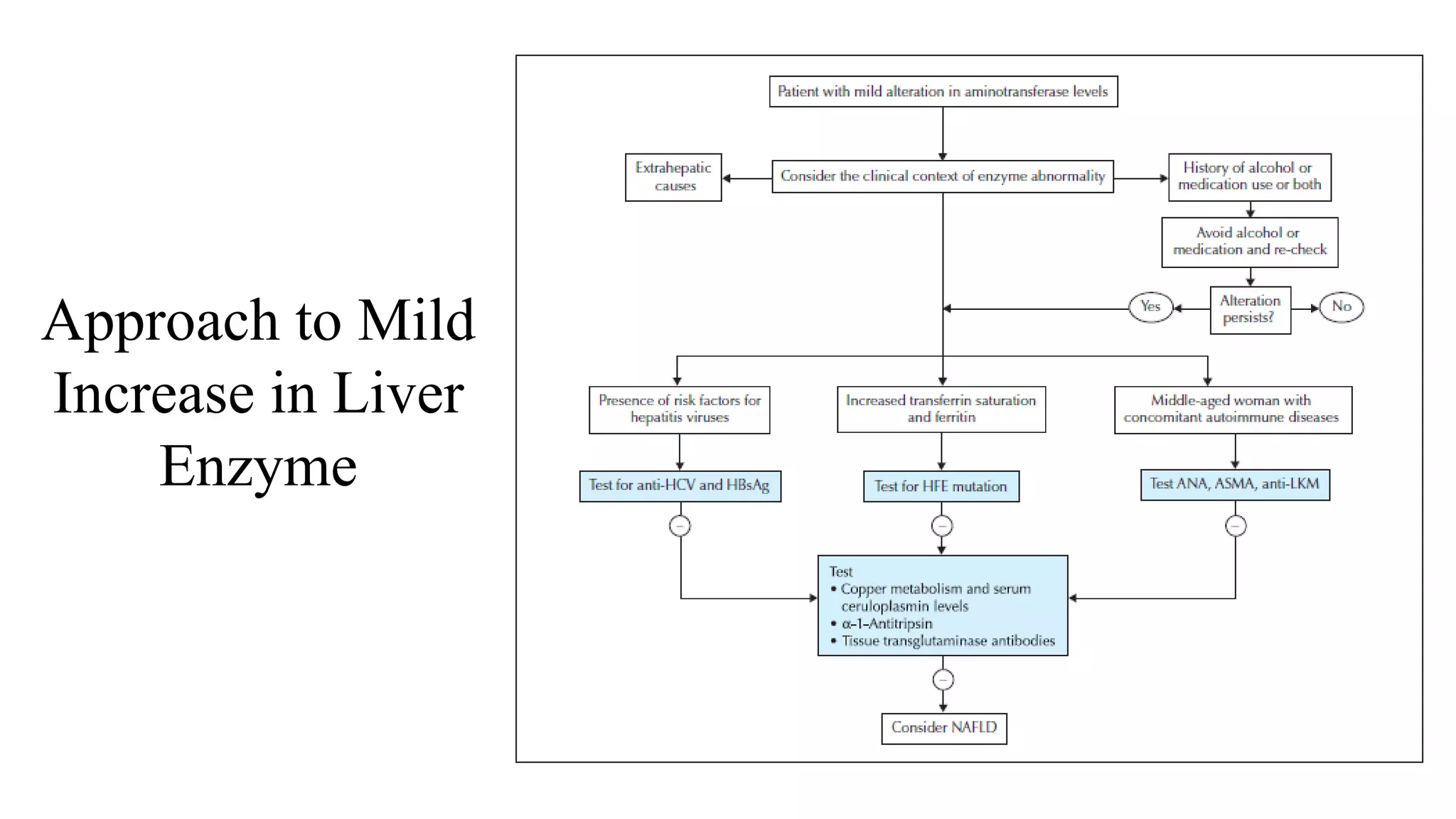
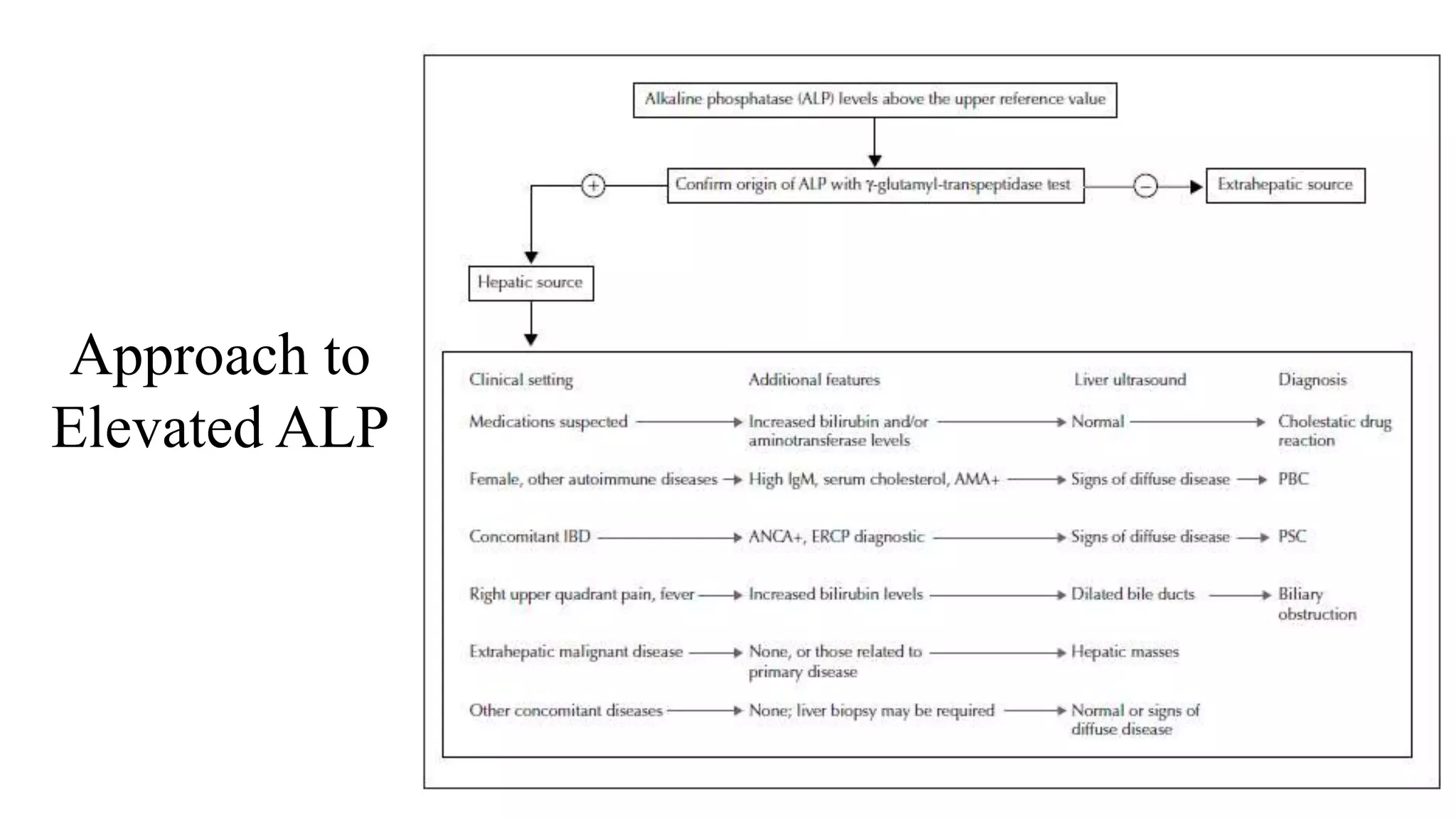
This document provides guidance on interpreting liver enzyme test results. It explains that increases in aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) should be referred to as "transaminase elevation" rather than "transaminitis" as laboratory tests cannot be inflamed. Specific liver enzymes like alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase, and bilirubin are discussed in terms of their clinical significance and causes of elevation. Approaches to mild or moderate/marked increases in liver enzymes are outlined, emphasizing the importance of considering a patient's clinical context over isolated lab results.