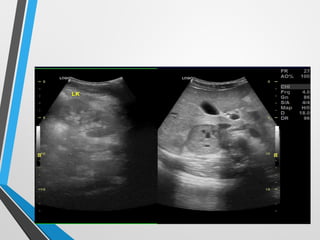
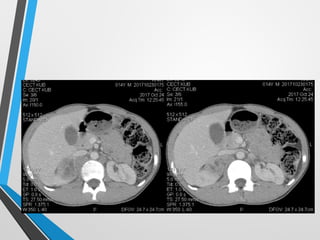
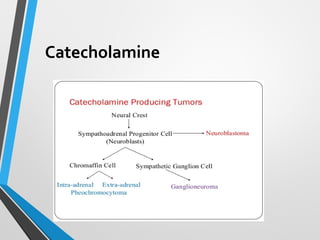
The document presents a case study of a 14-year-old boy diagnosed with pheochromocytoma after experiencing severe hypertension and fainting. Initial ultrasound and subsequent CT scans indicated the presence of solid masses in the adrenal glands and renal hilum, prompting further investigation for urinary catecholamines. Pheochromocytoma is a neuroendocrine tumor of the adrenal gland that can cause significant cardiovascular symptoms due to excessive catecholamine secretion.