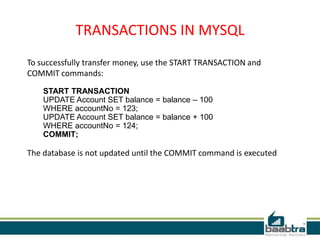
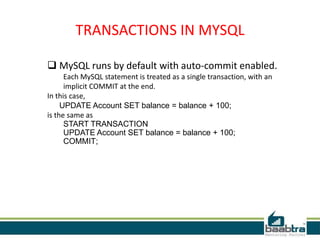
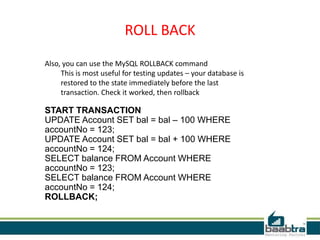
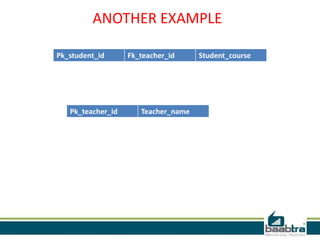
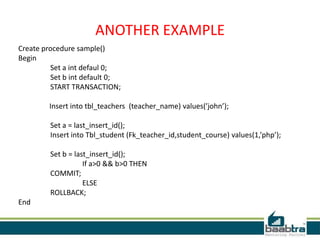
This document discusses database transactions in MySQL. It defines a transaction as a logical unit of work that maintains data integrity. Transactions have ACID properties - atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. MySQL runs with implicit transactions by default, but explicit transactions can be defined using START TRANSACTION, COMMIT, and ROLLBACK commands. Transactions allow multiple statements to be executed atomically and ensure data integrity even if errors occur.