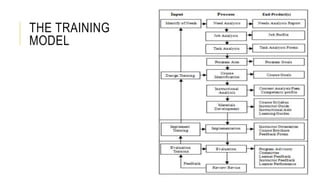
This document outlines a training program for supervisors in garment factories. It discusses the objectives of the Supervisor Skills Training program which is to equip direct and indirect supervisors with knowledge and skills to effectively manage workers. It describes the training methodology which involves 4 phases: needs analysis, model design/review, implementing the training course, and evaluating the training effectiveness. The training covers key areas like discipline, style analysis, and operator training. Checklists are also provided to supervisors to help monitor quality and employees.