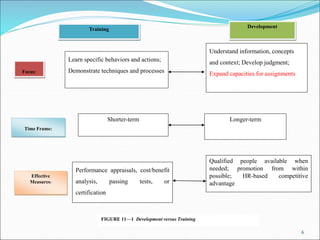
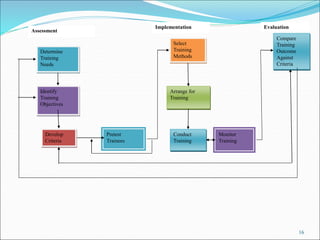
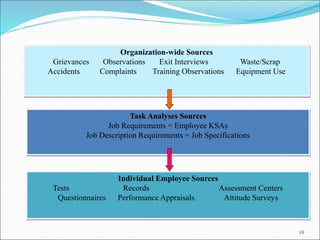
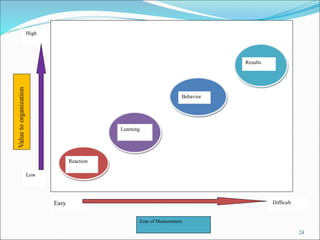
The document discusses the significance of training and development, highlighting that training is often underfunded and cut during tough times despite its importance for improving employee performance and job-specific skills. It differentiates between training, which focuses on immediate job-related skills, and development, which enhances broader capabilities for future roles. Additionally, it outlines key phases in the training process, emphasizes the importance of needs assessment, training objectives, selection of methods, and evaluation of effectiveness in ensuring that training meets its goals.