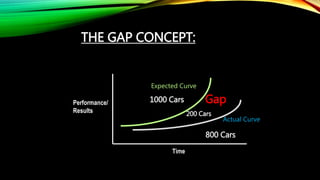
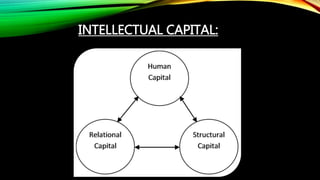
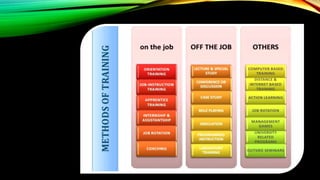
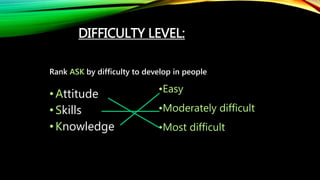
The document discusses the significance of training and development in human resource management, emphasizing its role in enhancing individual and organizational performance. It outlines the definitions, importance, challenges, and principles of effective training methodologies, as well as the steps involved in the training process. The conclusion reinforces the necessity for organizations to invest in training to adapt to changing environments and improve overall competitiveness.