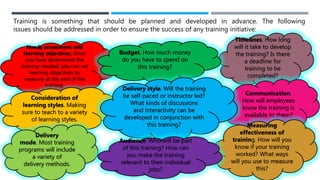
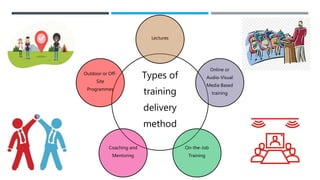
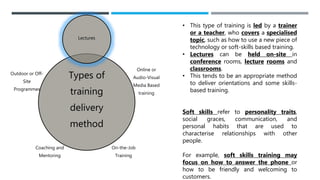
The document outlines the importance of training and development in organizations, emphasizing employee orientation, in-house training, mentoring, and external training as key components. It details various types of training delivery methods and essential factors for successful training initiatives, including needs assessment, learning objectives, and measuring effectiveness. Additionally, it highlights the significance of socialization and structured guidance to reduce employee turnover and enhance job performance.